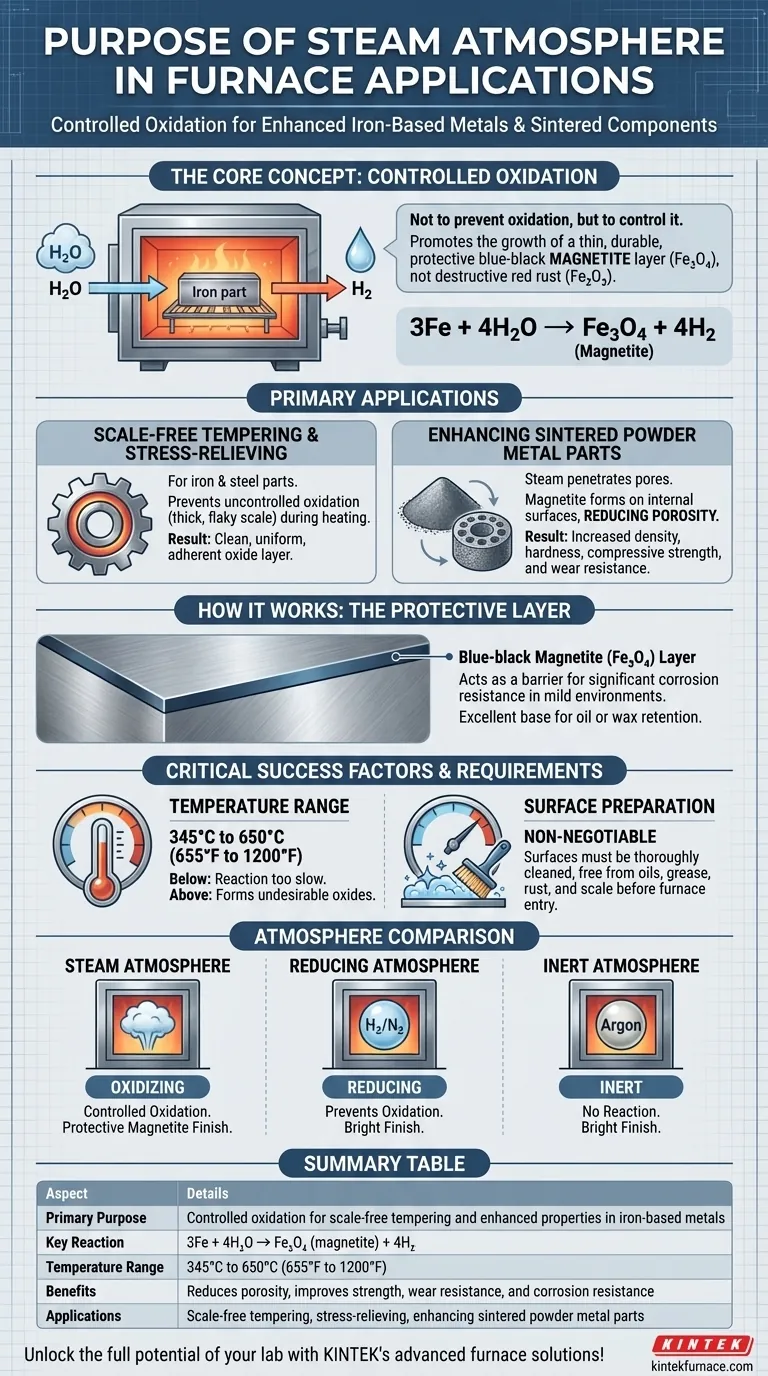
In furnace applications, a steam atmosphere is primarily used to perform scale-free tempering and stress-relieving on iron-based metals. It also serves to enhance the physical properties of sintered iron components by creating a specific, controlled oxide layer that improves strength, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance.
The core purpose of a steam atmosphere is not to prevent oxidation entirely, but to control it. It facilitates the growth of a thin, durable, and protective blue-black magnetite layer (
Fe₃O₄) instead of the destructive, flaky red rust or scale (Fe₂O₃) that forms in an air atmosphere.

The Primary Applications of Steam Treatment
Steam treatment is a highly effective and economical process when applied correctly. Its benefits are most pronounced in two specific areas.
Scale-Free Tempering and Stress-Relieving
When tempering or stress-relieving iron and steel parts, heating them in air causes uncontrolled oxidation, forming a thick, flaky scale that must be cleaned off later.
Using a steam atmosphere within a specific temperature range—typically 345° to 650°C (655° to 1200°F)—prevents this. The steam reacts with the iron surface to form a uniform and adherent oxide layer, resulting in a clean, "scale-free" finish.
Enhancing Sintered Powder Metal Parts
Sintered parts, made from pressed metal powder, are inherently porous. Steam treatment is exceptionally effective here because the steam can penetrate these pores.
The resulting magnetite layer forms on the internal surfaces within the part, effectively reducing porosity. This process increases the part's density, hardness, compressive strength, and overall wear resistance.
How the Steam Atmosphere Works
Understanding the simple chemistry behind steam treatment reveals why it is so effective. It's a process of harnessing a specific chemical reaction while preventing another.
The Controlled Oxidation Reaction
The goal is to promote the reaction of iron with water vapor to create magnetite:
3Fe + 4H₂O → Fe₃O₄ (magnetite) + 4H₂
This reaction produces a stable, hard, and tightly bonded oxide. It deliberately avoids the uncontrolled reaction with oxygen in the air, which produces flaky, porous iron(III) oxide, or common rust.
The Result: A Blue-Black Protective Layer
The Fe₃O₄ magnetite layer is visually distinct, appearing as a blue, blue-black, or gunmetal grey finish.
This layer is not just aesthetic; it acts as a barrier that provides significant corrosion resistance in mild environments and serves as an excellent base for oil or wax retention, further improving its protective properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Requirements
While powerful, steam treatment is not a universal solution. Its success depends entirely on adhering to specific operational parameters.
Critical Temperature Range
The process is only effective within its designated temperature window (345° to 650°C).
Below this range, the reaction is too slow to be practical. Above it, you risk forming different, less desirable types of iron oxides, defeating the purpose of the controlled process.
Surface Preparation is Non-Negotiable
The quality of the final oxide layer is directly dependent on the condition of the initial part. Surfaces must be thoroughly cleaned and free from oils, grease, and pre-existing rust or scale before entering the furnace.
Any contaminants will interfere with the steam-iron reaction, leading to a non-uniform, patchy, and ineffective oxide layer.
Comparison to Other Atmospheres
Steam is an oxidizing atmosphere. It should not be confused with atmospheres designed to prevent oxidation entirely.
For processes like bright annealing or brazing, where no surface oxidation is permissible, a reducing atmosphere (like rich exothermic or hydrogen-nitrogen blends) or an inert atmosphere (like argon) is required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace atmosphere is crucial for achieving the desired material properties and finish.
- If your primary focus is corrosion and wear resistance on iron parts: Steam treatment is a cost-effective method for creating a durable, protective magnetite finish.
- If your primary focus is tempering or stress-relieving without heavy, flaky scale: A steam atmosphere provides a controlled environment to produce a clean, uniform, and aesthetically pleasing oxide layer.
- If your primary focus is a "bright" finish with zero oxidation: You must use a reducing or inert atmosphere, as steam is inherently an oxidizing agent.
By understanding its function as a controlled oxidizing agent, you can effectively leverage a steam atmosphere to enhance your parts rather than damage them.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Controlled oxidation for scale-free tempering and enhanced properties in iron-based metals |
| Key Reaction | 3Fe + 4H₂O → Fe₃O₄ (magnetite) + 4H₂ |
| Temperature Range | 345°C to 650°C (655°F to 1200°F) |
| Benefits | Reduces porosity, improves strength, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance |
| Applications | Scale-free tempering, stress-relieving, enhancing sintered powder metal parts |
Unlock the full potential of your lab with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, such as steam atmosphere applications for enhanced metal properties. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can boost your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance



















