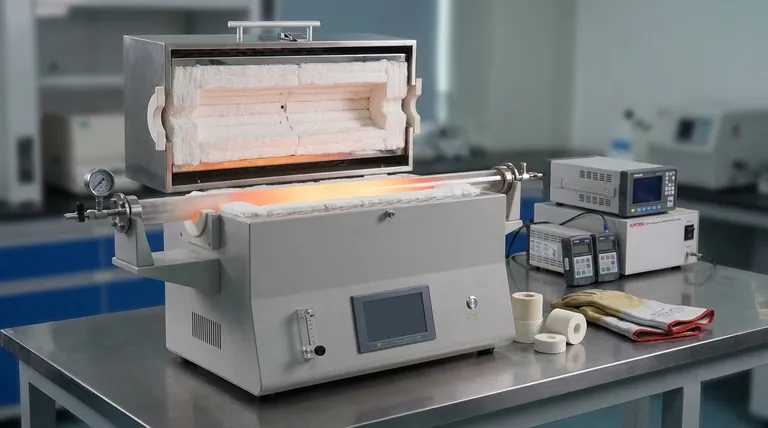
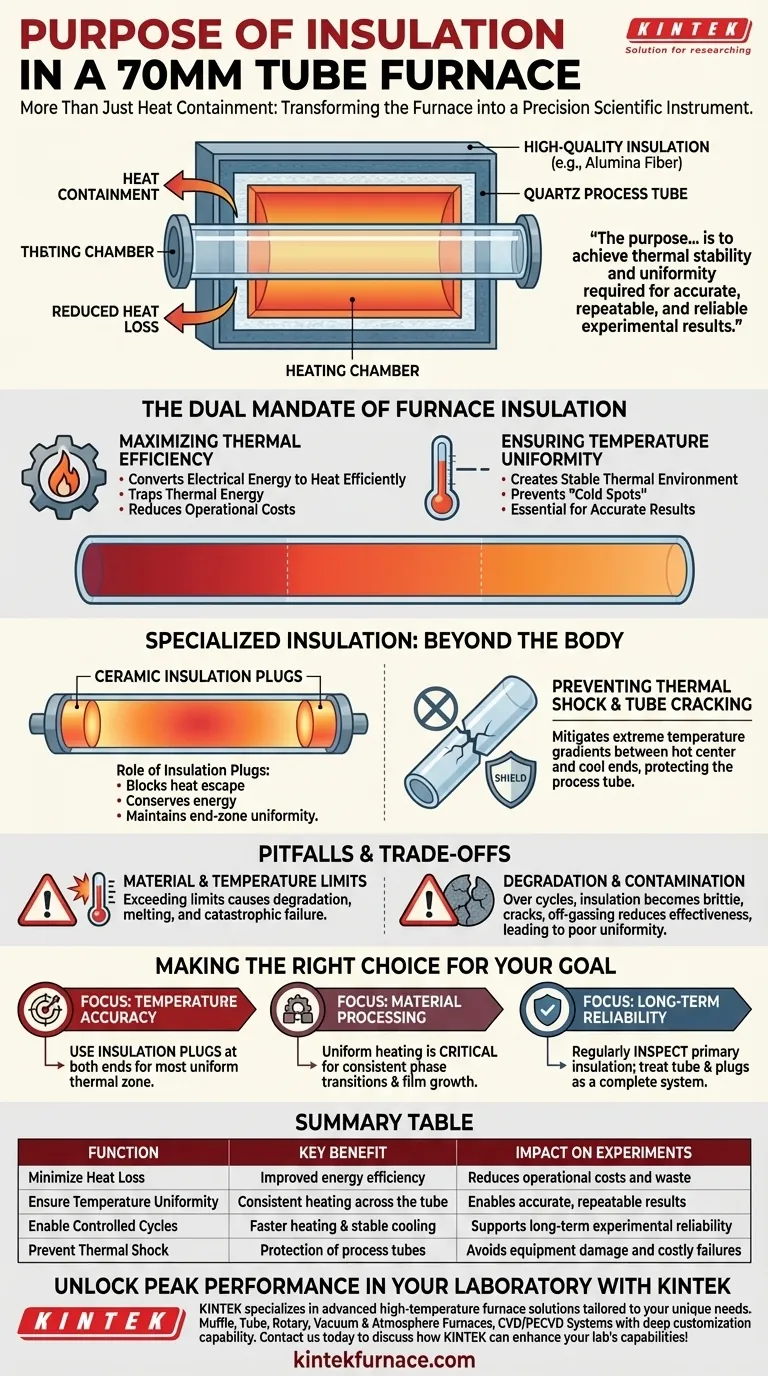
At its core, the insulation in a 70mm tube furnace serves two primary and inseparable functions. It is engineered to minimize heat loss to the surrounding environment and, just as critically, to ensure a highly consistent and uniform temperature along the length of the process tube.
The purpose of insulation is not merely to make the furnace efficient, but to transform it into a precision scientific instrument. Effective insulation is the key to achieving the thermal stability and uniformity required for accurate, repeatable, and reliable experimental results.

The Dual Mandate of Furnace Insulation
Insulation's role extends beyond simply keeping the heat in. It directly dictates the performance, accuracy, and even the safety of the furnace's operation.
Maximizing Thermal Efficiency
A tube furnace works by converting electrical energy into heat. Without proper insulation, a significant portion of that heat would radiate away from the heating chamber, wasting energy and increasing operational costs.
High-quality insulation materials, such as alumina fiber or polycrystalline wool, act as a powerful barrier. They trap thermal energy within the chamber, concentrating it on the process tube where it is needed.
Ensuring Temperature Uniformity
For scientific applications like catalyst preparation or semiconductor annealing, temperature accuracy is paramount. The entire sample inside the tube must be at the precise target temperature.
Insulation ensures this by creating a stable thermal environment. By preventing "cold spots" caused by heat escaping, it guarantees a uniform temperature profile across the heated zone, which is essential for valid experimental outcomes. In many designs, the heating elements are embedded directly into the insulation matrix to further enhance this effect.
Enabling Controlled Heating Cycles
Effective insulation allows the furnace to reach its setpoint temperature more quickly because less energy is wasted. It also helps maintain stability during long experiments and contributes to a more controlled and predictable cooling rate.
Beyond the Furnace Body: Specialized Insulation
Insulation is not just a feature of the furnace walls. Specialized components are used to manage heat at the most vulnerable points of the system.
The Role of Insulation Plugs
Even with a perfectly insulated chamber, significant heat can escape through the open ends of the process tube. Ceramic insulation plugs are inserted into the ends of the tube to block this path.
These plugs are crucial for maintaining temperature uniformity at the very ends of the heated zone and for conserving energy, especially during high-temperature operation.
Preventing Thermal Shock and Tube Cracking
Perhaps the most critical function of insulation plugs is mitigating thermal gradients. An extreme temperature difference between the hot center of the tube and its cooler, exposed ends creates immense physical stress.
This stress can cause expensive quartz or ceramic tubes to crack or shatter. By reducing heat loss at the ends, insulation plugs minimize these gradients, protecting the integrity of the process tube.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Trade-offs
While essential, insulation is not without its own set of limitations and considerations that you must be aware of.
Material and Temperature Limits
Insulation materials are rated for a maximum operating temperature. Using a furnace beyond the limit of its insulation can cause the material to degrade, shrink, or even melt, leading to catastrophic failure of the furnace.
Degradation and Contamination
Over hundreds of heating cycles, insulation can become brittle and develop cracks. It can also become contaminated by process off-gassing, reducing its effectiveness.
This degradation leads to poor energy efficiency and, more importantly, a loss of temperature uniformity, which can compromise your results. Regular visual inspection is a key part of furnace maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding how insulation works allows you to optimize your process and protect your equipment.
- If your primary focus is temperature accuracy: Always use insulation plugs at both ends of your process tube to ensure the most uniform thermal zone possible.
- If your primary focus is material processing: The uniform heating provided by good insulation is critical for preventing sample damage and ensuring consistent phase transitions or film growth.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability: Regularly inspect the furnace's primary insulation for signs of cracking or degradation and treat the process tube and plugs as a complete system to prevent thermal shock.
By viewing insulation as a core performance component, you can ensure your tube furnace operates not just as a heater, but as the precision instrument it was designed to be.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Impact on Experiments |
|---|---|---|
| Minimize Heat Loss | Improved energy efficiency | Reduces operational costs and waste |
| Ensure Temperature Uniformity | Consistent heating across the tube | Enables accurate, repeatable results |
| Enable Controlled Cycles | Faster heating and stable cooling | Supports long-term experimental reliability |
| Prevent Thermal Shock | Protection of process tubes | Avoids equipment damage and costly failures |
Unlock Peak Performance in Your Laboratory with KINTEK
Are you striving for precise temperature control and uniform heating in your experiments? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. With our strong deep customization capability, we can design furnaces that precisely meet your experimental requirements, ensuring reliability and efficiency.
Don't let insulation issues compromise your results—contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can enhance your lab's capabilities and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















