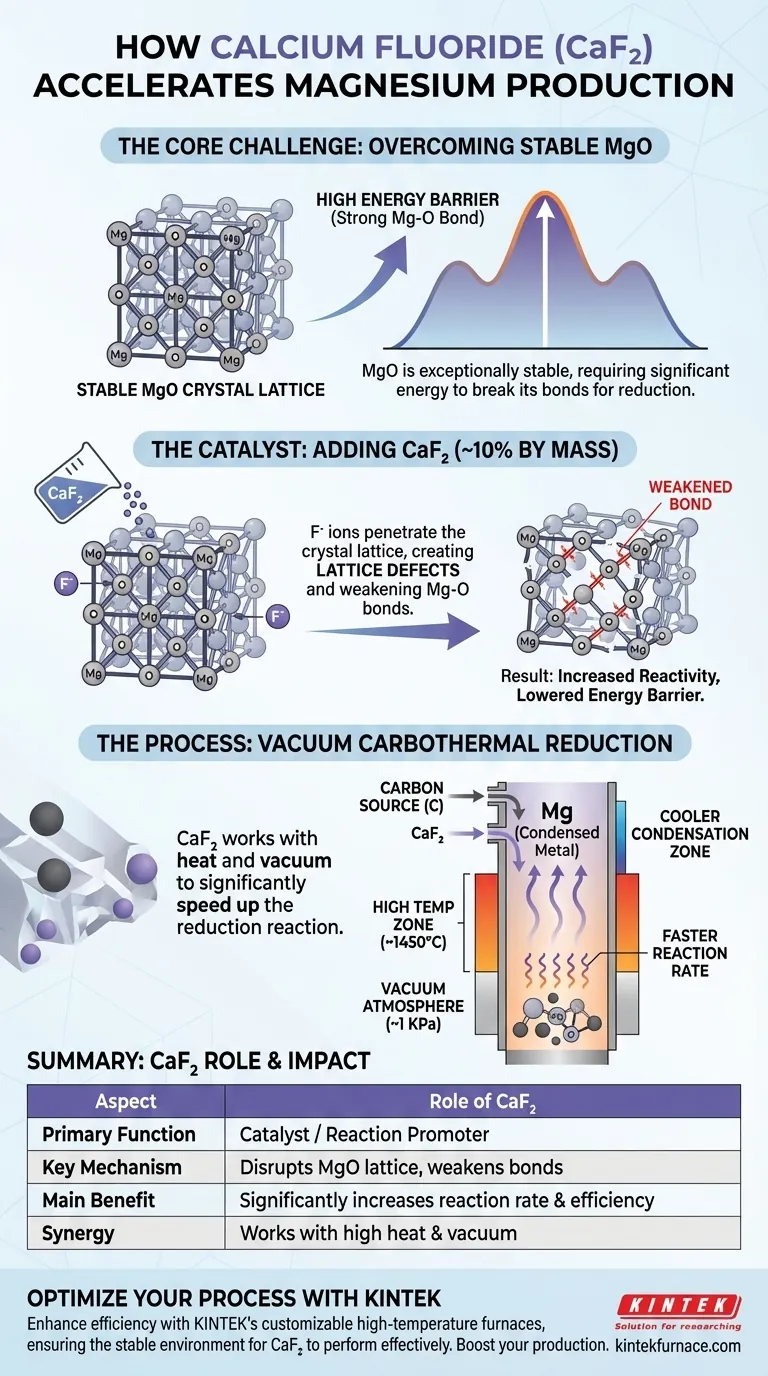
In magnesium production, the addition of calcium fluoride (CaF2) serves a single, critical purpose: to act as a catalyst or reaction promoter. It significantly accelerates the rate of the vacuum carbothermal reduction reaction. It achieves this by chemically disrupting the highly stable crystal structure of magnesium oxide (MgO), making it easier for the reduction to occur.
The core challenge in this process is the immense stability of the magnesium oxide (MgO) molecule. Calcium fluoride is added specifically to weaken the chemical bonds within the MgO crystal lattice, lowering the energy required for the reaction and dramatically improving the overall speed and efficiency of magnesium production.
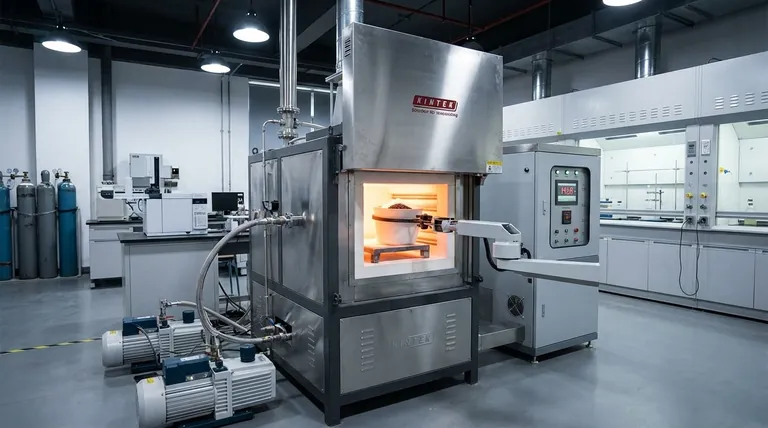

The Core Challenge: Overcoming MgO's Stability
A Highly Stable Compound
Magnesium oxide is an exceptionally stable ceramic material with a strong, tightly packed crystal lattice. The bond between magnesium and oxygen (Mg-O) is powerful and requires a significant amount of energy to break.
The Energy Barrier
This inherent stability creates a high energy barrier for the carbothermal reduction process. While the necessary high temperatures and vacuum conditions help, the reaction would remain impractically slow without a way to lower this barrier.
How Calcium Fluoride Accelerates the Reaction
The Mechanism: Lattice Disruption
When added to the raw materials, typically around 10% by mass, the calcium fluoride introduces fluoride ions (F-). These ions penetrate the magnesium oxide's crystal lattice.
This infiltration creates lattice defects—imperfections and points of weakness—within the otherwise uniform and stable MgO structure.
The Impact: Increased Reactivity
These defects destabilize the crystal and effectively weaken the surrounding Mg-O bonds. With its structure compromised, the magnesium oxide becomes significantly more chemically reactive.
The Result: Faster Reduction Rates
Because the Mg-O bonds are easier to break, the reduction reaction with carbon proceeds much more quickly and at a lower effective temperature. This leads to a higher final reduction rate and a more efficient conversion of MgO into magnesium vapor.
The Role of the Process Environment
The Need for Heat and Vacuum
This chemical acceleration works in tandem with the physical environment. A vertical tube furnace provides the high temperatures (e.g., 1723 K or 1450°C) needed to supply the reaction's energy.
Simultaneously, a high-vacuum atmosphere (e.g., 1 KPa) is maintained. The vacuum lowers the boiling point of magnesium, allowing it to turn into a vapor at a lower temperature and be easily removed, which helps pull the reaction forward and saves considerable energy.
Facilitating Collection
The magnesium vapor then rises and condenses in a cooler zone of the furnace. The vertical furnace design helps create a temperature gradient that facilitates this directional migration for efficient collection.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Purity Considerations
Introducing any additive, including CaF2, creates the potential for contamination in the final product. Process control must be precise to minimize the carry-over of fluoride compounds into the condensed magnesium.
Cost vs. Benefit
The cost of the CaF2 additive and its handling must be factored into the overall process economics. However, the dramatic increase in reaction speed and subsequent energy savings far outweigh this cost, making its use standard industrial practice.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Here are the key takeaways based on your primary objective:
- If your primary focus is maximizing reaction speed: The addition of CaF2 is the most effective lever, as it directly targets the rate-limiting step of breaking the stubborn Mg-O bond.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: CaF2 works synergistically with the vacuum environment, enabling faster reactions at lower effective temperatures, which reduces the overall energy consumption per unit of magnesium produced.
- If your primary focus is product purity: While CaF2 is essential for kinetics, you must validate that subsequent refining and condensation steps are adequate to remove any potential fluoride-based impurities.
Ultimately, using calcium fluoride is a strategic chemical intervention that transforms the carbothermal reduction of magnesium from a sluggish, high-energy process into an efficient industrial reality.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role of Calcium Fluoride (CaF2) |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Acts as a catalyst/reaction promoter |
| Key Mechanism | Disrupts the MgO crystal lattice, weakening Mg-O bonds |
| Main Benefit | Significantly increases reaction rate and efficiency |
| Typical Usage | ~10% by mass of raw materials |
| Synergy | Works with high temperature and vacuum to lower energy costs |
Optimize Your High-Temperature Metallurgical Processes with KINTEK
Are you looking to enhance the efficiency and yield of your metal production, like magnesium via carbothermal reduction? The right furnace technology is critical for maintaining the precise high-temperature and vacuum conditions required.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, and other lab high-temperature furnaces, all customizable for unique needs. Our robust and reliable equipment ensures the stable environment necessary for catalytic additives like CaF2 to perform effectively, helping you achieve faster reaction times and lower energy consumption.
Ready to boost your production efficiency? Contact our experts today to discuss a furnace solution tailored to your specific process challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















