In essence, a tube furnace is a specialized piece of equipment designed to heat materials with exceptional precision within a contained, cylindrical chamber. Its primary purpose is to create a highly uniform and stable thermal environment, often while controlling the atmospheric conditions surrounding the sample, making it indispensable for advanced material synthesis, heat treatment, and scientific research.
The true value of a tube furnace is not simply its ability to generate high temperatures, but its capacity to create a tightly controlled and isolated processing environment. This allows for experiments and production processes that would be impossible in a standard oven.

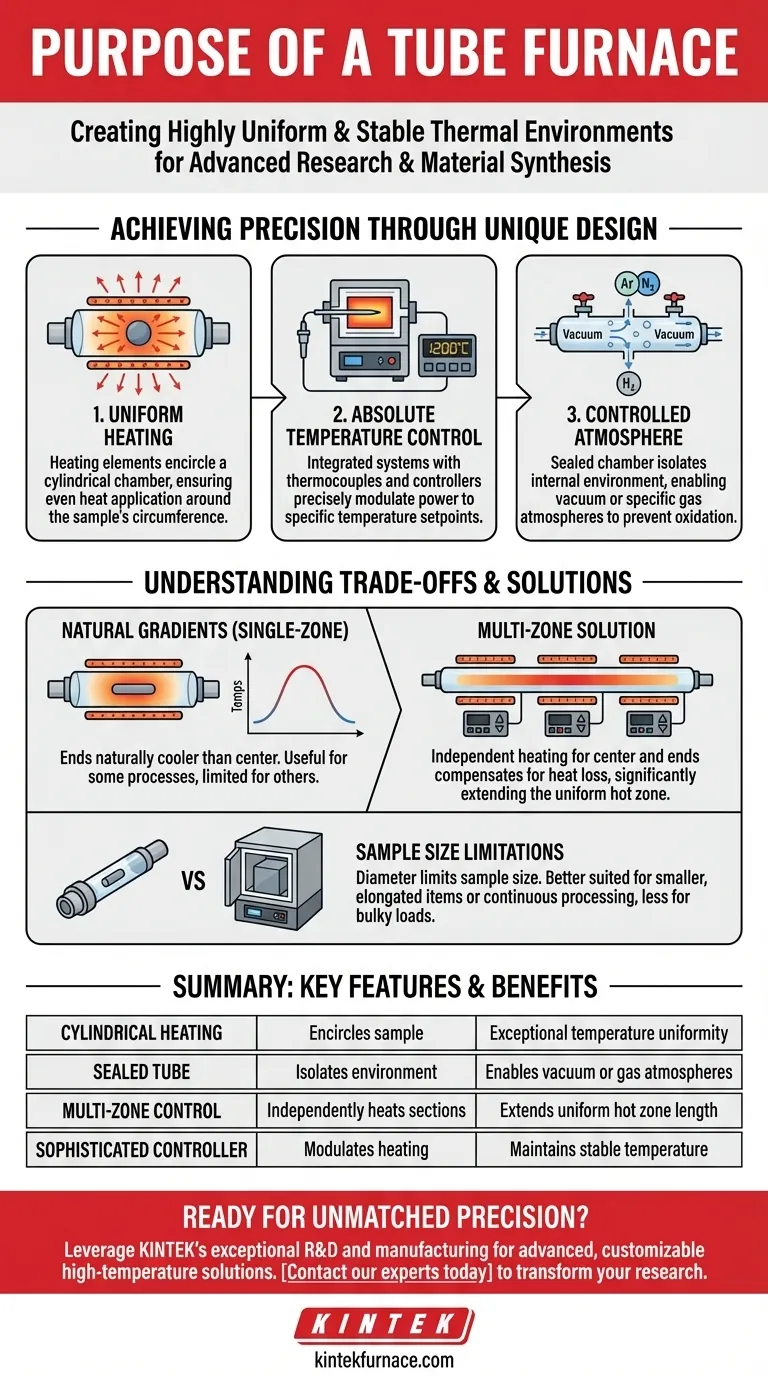
How a Tube Furnace Achieves Precision
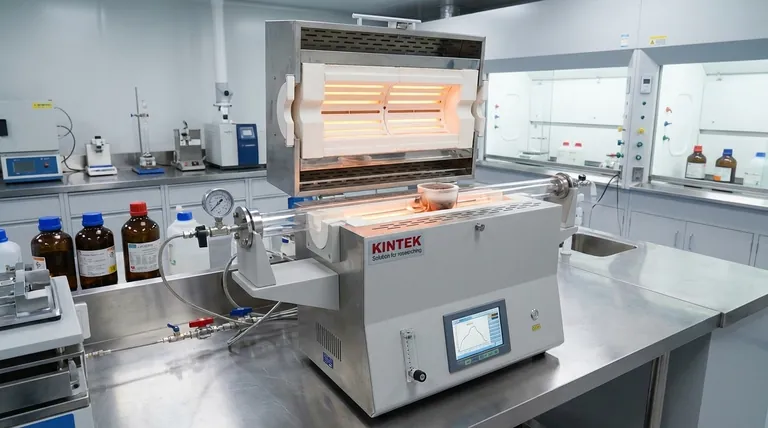
A tube furnace's purpose is defined by its unique design, which enables a level of control that other heating methods cannot easily match. This control is achieved through three key principles.
The Core Design: Uniform Heating
A tube furnace consists of heating elements that encircle a ceramic or quartz tube. This cylindrical arrangement ensures that heat is applied evenly around the circumference of the sample placed inside.
The central portion of the tube, known as the "hot zone," receives the most consistent thermal radiation, resulting in a highly uniform temperature profile along its length.
Absolute Temperature Control
These furnaces are integrated with sophisticated temperature control systems. A thermocouple measures the temperature inside the furnace, feeding data back to a controller.
This controller then precisely modulates the power sent to the heating elements, allowing the furnace to maintain a specific temperature setpoint with very little deviation.
Controlled Atmosphere Processing
The sealed nature of the tube is a critical feature. It allows the internal environment to be completely isolated from the outside air.
This isolation makes it possible to either create a vacuum or introduce specific process gases (such as nitrogen, argon, or hydrogen). This capability is essential for preventing oxidation and enabling processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the design of a tube furnace presents inherent characteristics and limitations that you must understand to use it effectively.
Natural Temperature Gradients
In a standard single-zone furnace, the temperature is not perfectly uniform along the entire length of the tube. The ends of the tube are naturally cooler than the center.
For some processes, this gradient can be a useful feature. For others that require a longer, uniform hot zone, it is a significant limitation.
The Solution: Multi-Zone Furnaces
To overcome this, advanced multi-zone furnaces were developed. A 3-zone furnace, for example, has separate heating elements and controllers for the center and each of the two ends.
This allows the end zones to be heated to a higher temperature, compensating for natural heat loss and extending the length of the uniform hot zone significantly.
Sample Size and Throughput
The diameter of the furnace tube inherently limits the size of the sample that can be processed. While some models are designed for continuous production by passing material through the tube, they are generally less suited for processing large, bulky items compared to a box furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right heating method depends entirely on your process requirements. The tube furnace excels where control is paramount.
- If your primary focus is process purity and atmosphere control: The sealed tube environment is the definitive advantage, protecting your sample from unwanted reactions.
- If your primary focus is temperature uniformity over a specific length: A multi-zone tube furnace is the superior choice for consistent heat treatment.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and cost-effectiveness for small samples: A standard single-zone tube furnace provides excellent performance for many lab-scale applications.
Ultimately, the purpose of a tube furnace is to provide an unmatched level of control, turning simple heating into a precise and repeatable scientific process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical Heating | Encircles the sample with heat | Achieves exceptional temperature uniformity |
| Sealed Tube | Isolates the internal environment | Enables vacuum or specific gas atmospheres |
| Multi-Zone Control | Independently heats different tube sections | Extends the length of the uniform hot zone |
| Sophisticated Controller | Precisely modulates heating elements | Maintains stable temperature setpoints |
Ready to achieve unmatched precision in your lab?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our tube furnaces are engineered for superior performance, complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for material synthesis, heat treatment, and controlled atmosphere processing.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK tube furnace can transform your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















