At its core, vacuum tempering is a highly controlled heat treatment process for reheating previously hardened steel or alloy components. It is performed inside a sealed furnace from which the air has been removed, allowing the material's properties to be modified without causing unwanted surface reactions like oxidation.
The critical advantage of vacuum tempering is not just the heat treatment itself, but the pristine atmospheric control. By removing oxygen, the process enhances the mechanical properties of a part while simultaneously producing a clean, bright surface finish, often eliminating the need for secondary cleaning operations.
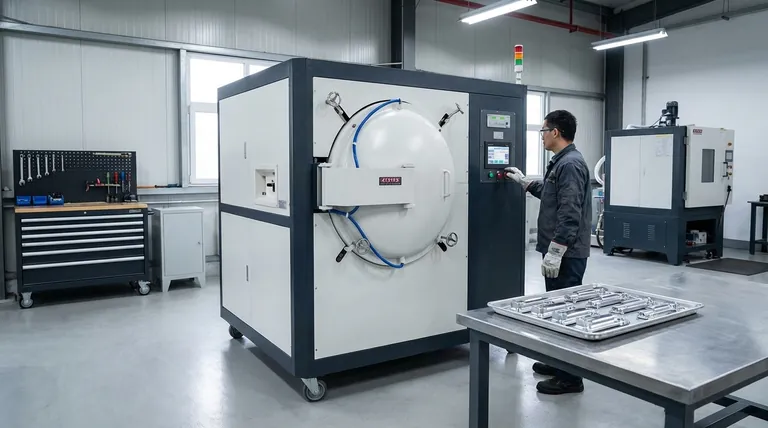

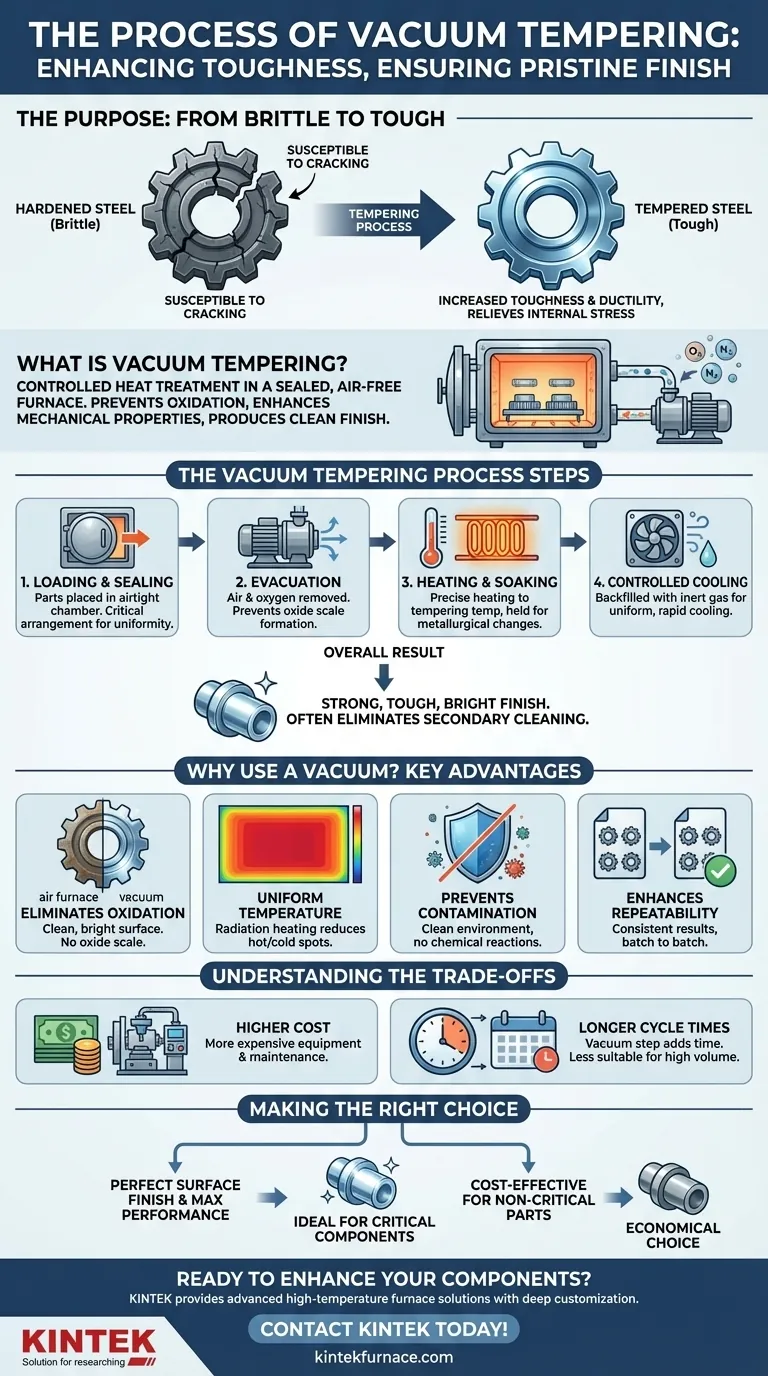
The Purpose of Tempering: From Brittle to Tough
Tempering is a necessary second step after a metal part has been hardened. Understanding its purpose is key to understanding the value of performing it in a vacuum.
The Problem with Hardened Steel
When steel is heated and then rapidly cooled (quenched) to achieve high hardness, it becomes extremely brittle. While very resistant to wear, it is susceptible to cracking or shattering under sharp impact or stress.
This brittleness makes the hardened part unsuitable for most practical applications, from cutting tools to structural components.
How Tempering Provides the Solution
Tempering involves reheating the hardened part to a precise temperature, well below its hardening temperature, and holding it there for a specific time.
This process trades a small amount of hardness for a significant increase in toughness and ductility. It relieves the internal stresses created during quenching, resulting in a component that is both strong and resilient.
How the Vacuum Tempering Process Works
The process is a sequence of highly controlled steps, each contributing to the final quality of the part.
Step 1: Loading and Sealing
Parts are loaded into the vacuum furnace, which is then sealed to create an airtight chamber. The arrangement of the parts is critical to ensure uniform exposure to both heat and the vacuum.
Step 2: Evacuation (Creating the Vacuum)
A vacuum pump system removes the air and other gases from the chamber. The primary goal is to remove oxygen, which is the agent responsible for forming oxide scale (discoloration) on the metal's surface at high temperatures.
Step 3: Controlled Heating and Soaking
Once the desired vacuum level is reached, heating elements raise the temperature of the parts. The control systems in a vacuum furnace are extremely precise, ensuring the entire part heats uniformly.
The parts are then held at the target tempering temperature—a phase known as "soaking"—to allow the metallurgical changes to occur throughout the material.
Step 4: Controlled Cooling
After soaking, the parts must be cooled. In a vacuum furnace, this is often accelerated by backfilling the chamber with a high-purity inert gas, such as argon or nitrogen, which is then circulated by a fan to cool the parts uniformly.
Why Use a Vacuum? The Key Advantages
The use of a vacuum environment is what separates this process from conventional atmospheric furnace tempering.
Eliminates Oxidation and Discoloration
This is the most visible benefit. Without oxygen, no oxide scale can form. Parts emerge from the furnace with a clean, bright, and often shiny surface, exactly as they went in.
This can eliminate the need for costly and time-consuming secondary operations like sandblasting, pickling, or grinding to remove scale.
Ensures Uniform Temperature
In a vacuum, heat is transferred primarily through radiation. This leads to very uniform and consistent heating, reducing the risk of hot or cold spots that could create inconsistent properties within a part.
Prevents Surface Contamination
The vacuum environment is exceptionally clean. It prevents any unwanted chemical reactions on the surface of the part, ensuring its integrity and performance are not compromised by contaminants present in an open-air furnace.
Enhances Process Repeatability
Because the atmosphere is so tightly controlled, vacuum tempering offers exceptionally high repeatability. Every batch can be processed under identical conditions, ensuring consistent results from part to part and batch to batch.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum tempering is not the default choice for every application. Objectivity requires acknowledging its limitations.
Higher Equipment and Operational Costs
Vacuum furnaces and their associated pump systems are significantly more complex and expensive to purchase and maintain than standard atmospheric furnaces.
Longer Cycle Times
The step of pulling a vacuum adds time to the overall process cycle. For high-volume, low-margin parts where surface finish is irrelevant, this extra time can be a disadvantage.
Not Always Necessary
For parts where a layer of oxide scale is acceptable or will be machined off later, the expense and time of vacuum processing may not be justified. A conventional tempering process is often sufficient for these applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right tempering process depends entirely on the requirements of your final component.
- If your primary focus is a perfect surface finish: Vacuum tempering is the ideal choice, as it eliminates the need for post-processing and delivers a visually pristine part.
- If your primary focus is maximum mechanical performance and consistency: The precise temperature uniformity and clean environment of a vacuum furnace provide the ultimate process control.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for non-critical parts: A conventional atmospheric tempering process is likely more economical and efficient if a bit of surface oxidation is acceptable.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum tempering is an investment in quality, consistency, and the final finish of your component.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Loading & Sealing | Parts are placed in an airtight chamber. | Prepares for atmospheric control. |
| 2. Evacuation | Air and oxygen are removed by vacuum pumps. | Prevents oxidation and surface scale. |
| 3. Heating & Soaking | Precise heating to tempering temperature and hold. | Relieves internal stresses, increases toughness. |
| 4. Cooling | Chamber is backfilled with inert gas for uniform cooling. | Maintains part integrity and consistent properties. |
| Overall Result | Parts are strong, tough, and have a bright finish. | Often eliminates need for secondary cleaning. |
Ready to Enhance Your Metal Components with Precision Vacuum Tempering?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories and production facilities with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique heat treatment requirements.
Invest in superior quality and consistency for your most critical components. Let our experts help you achieve bright, oxide-free finishes and enhanced mechanical properties.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss your application and discover the perfect furnace solution for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing



















