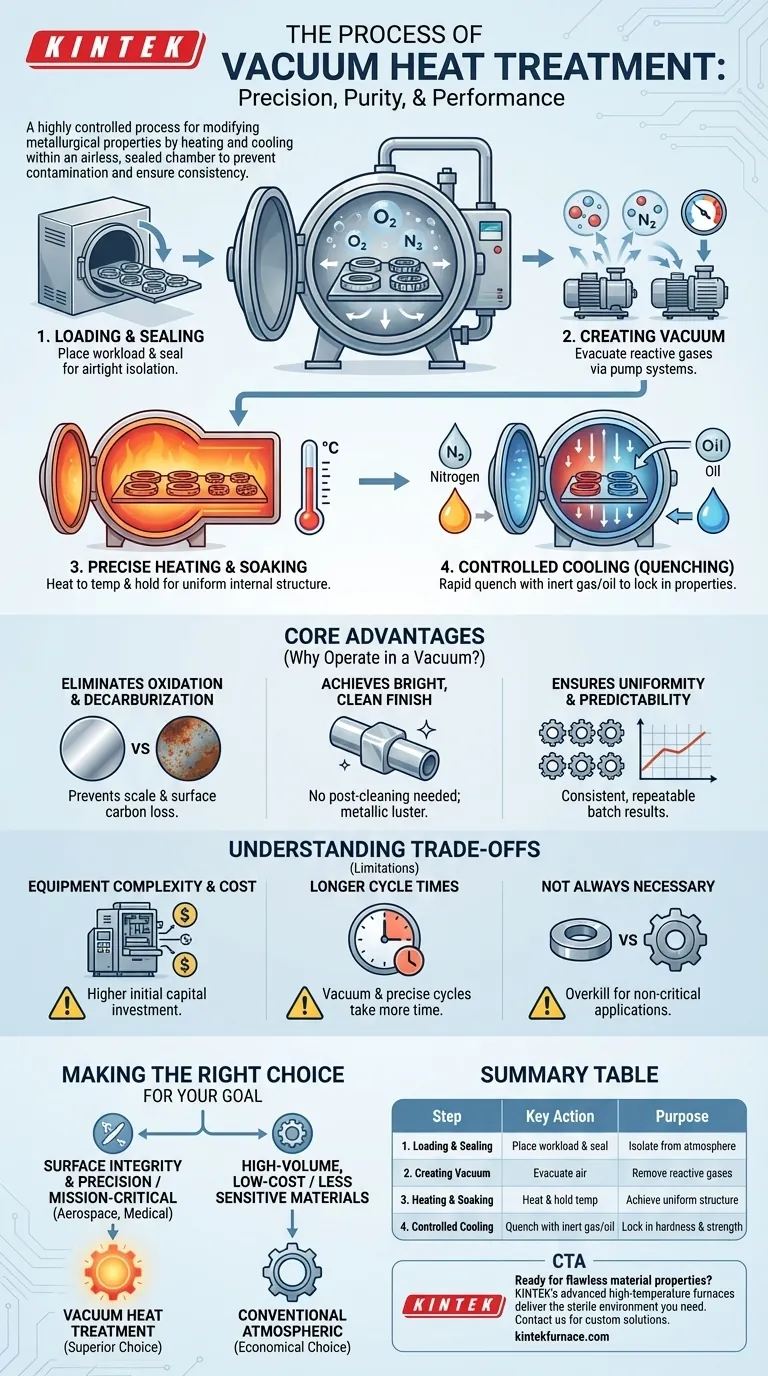
At its core, vacuum heat treatment is a highly controlled process for modifying the metallurgical properties of a material by heating and cooling it within an airless, sealed chamber. This method involves placing the parts into a furnace, evacuating the air to create a vacuum, heating the material to a precise temperature, and then cooling it in a controlled manner. By removing reactive gases like oxygen, the process prevents surface contamination and ensures the material achieves its desired characteristics with exceptional consistency.
The fundamental challenge in heat treatment is that high temperatures cause materials, especially metals, to react with gases in the air, leading to oxidation and inconsistencies. Vacuum heat treatment solves this by creating a sterile, low-pressure environment, providing unparalleled control over the final surface finish and internal structure of the material.

Deconstructing the Vacuum Heat Treatment Cycle
The vacuum heat treatment process is a meticulously sequenced operation. Each step is critical for achieving the final desired outcome, from surface hardness to internal strength.
Step 1: Loading and Sealing
The process begins by placing the materials, or "workload," into the furnace chamber. Once loaded, the chamber is sealed to create an airtight environment, isolating the workload from the outside atmosphere.
Step 2: Creating the Vacuum
A sophisticated vacuum system, often comprising multiple pumps (e.g., backing, booster, and diffusion pumps), activates to remove the air from the chamber. This evacuation eliminates oxygen, nitrogen, and other reactive gases, preventing oxidation and decarburization during the heating stage.
Step 3: Precise Heating and Soaking
With the vacuum established, the furnace's heating elements raise the material's temperature to a specific point. The vacuum ensures uniform heating, as there are no air currents to create hot or cold spots. The material is then "soaked" or held at this temperature to ensure the entire part achieves a consistent internal structure.
Step 4: Controlled Cooling (Quenching)
This is the most critical phase for locking in the desired properties. The material is cooled rapidly in a highly controlled manner. Common methods include vacuum gas quenching, where an inert gas like nitrogen or argon is introduced to cool the part, or vacuum oil quenching for different cooling characteristics. The speed and medium of the quench determine the final hardness and strength.
Why Operate in a Vacuum? The Core Advantages
Choosing to perform heat treatment in a vacuum is a deliberate decision driven by the need for quality and precision. The benefits are directly tied to the absence of a reactive atmosphere.
Eliminating Oxidation and Decarburization
This is the primary advantage. By removing oxygen, the process prevents the formation of scale, leaving a clean, unblemished surface. It also prevents decarburization—the loss of carbon from the surface of steel—which preserves the material's intended hardness and wear resistance.
Achieving a Bright, Clean Finish
Parts emerge from a vacuum furnace with a bright, metallic luster. This often eliminates the need for secondary cleaning operations like sandblasting or chemical pickling, saving time and reducing costs in the overall manufacturing chain.
Ensuring Uniformity and Predictability
The vacuum environment allows for extremely precise temperature control and uniform heat transfer. This leads to highly consistent and repeatable results from batch to batch, which is critical for high-performance components where variability is unacceptable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum heat treatment is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
Vacuum furnaces and their associated pumping systems are significantly more complex and carry a higher capital cost than conventional atmospheric furnaces. This initial investment can be a barrier for some operations.
Longer Cycle Times
The process of achieving a deep vacuum and executing precisely controlled heating and cooling cycles can take longer than traditional heat treatment methods. This can impact overall throughput for high-volume production.
Not Always Necessary
For many low-alloy materials or applications where surface finish and absolute precision are not the primary drivers, simpler and more cost-effective atmospheric treatments are often sufficient. The added expense of vacuum treatment is only justified when the benefits are required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a heat treatment method depends entirely on the requirements of the final component.
- If your primary focus is surface integrity and precision: Vacuum heat treatment is the superior choice, as it eliminates oxidation and allows for unparalleled process control.
- If your primary focus is treating mission-critical components for aerospace or medical use: The reliability and pristine finish of vacuum heat treatment are non-negotiable and often a specification requirement.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost processing of less sensitive materials: Conventional atmospheric heat treatment may be a more economical and faster solution.
Ultimately, investing in vacuum heat treatment is a strategic decision to prioritize material quality, consistency, and a flawless final product.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Loading & Sealing | Place workload in chamber and seal | Isolate from atmosphere |
| 2. Creating Vacuum | Evacuate air using pump systems | Remove reactive gases (O2, N2) |
| 3. Heating & Soaking | Heat to precise temperature and hold | Achieve uniform internal structure |
| 4. Controlled Cooling | Quench with inert gas or oil | Lock in hardness and strength |
Ready to achieve flawless material properties with precision vacuum heat treatment?
KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including our Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, are engineered to deliver the sterile, controlled environment your mission-critical components demand. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide the deep customization capability needed to meet your unique experimental and production requirements.
Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's efficiency and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety



















