While the terms are often used interchangeably, the specialized, high-temperature oven used to transform clay into durable ceramic is properly called a kiln. A kiln is not simply a furnace; it is a precision instrument designed to control extreme heat over many hours to induce specific chemical and physical changes in the material.
The name of the device is less important than its function. A kiln's purpose is to apply a precise thermal cycle, transforming raw, fragile clay into a dense, vitrified, and permanent ceramic object through processes like firing and sintering.
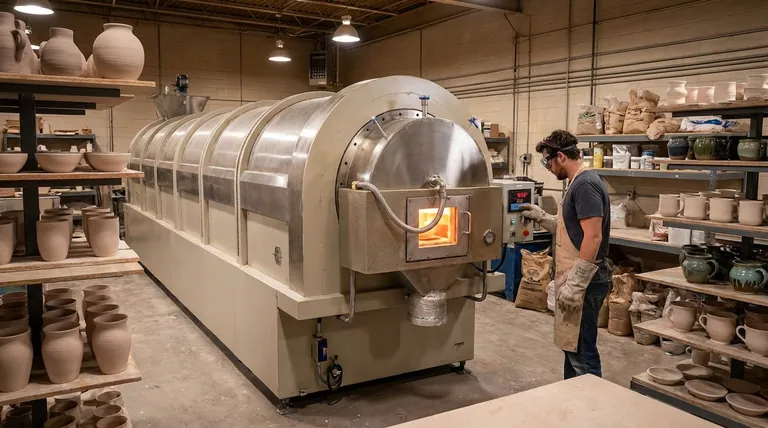

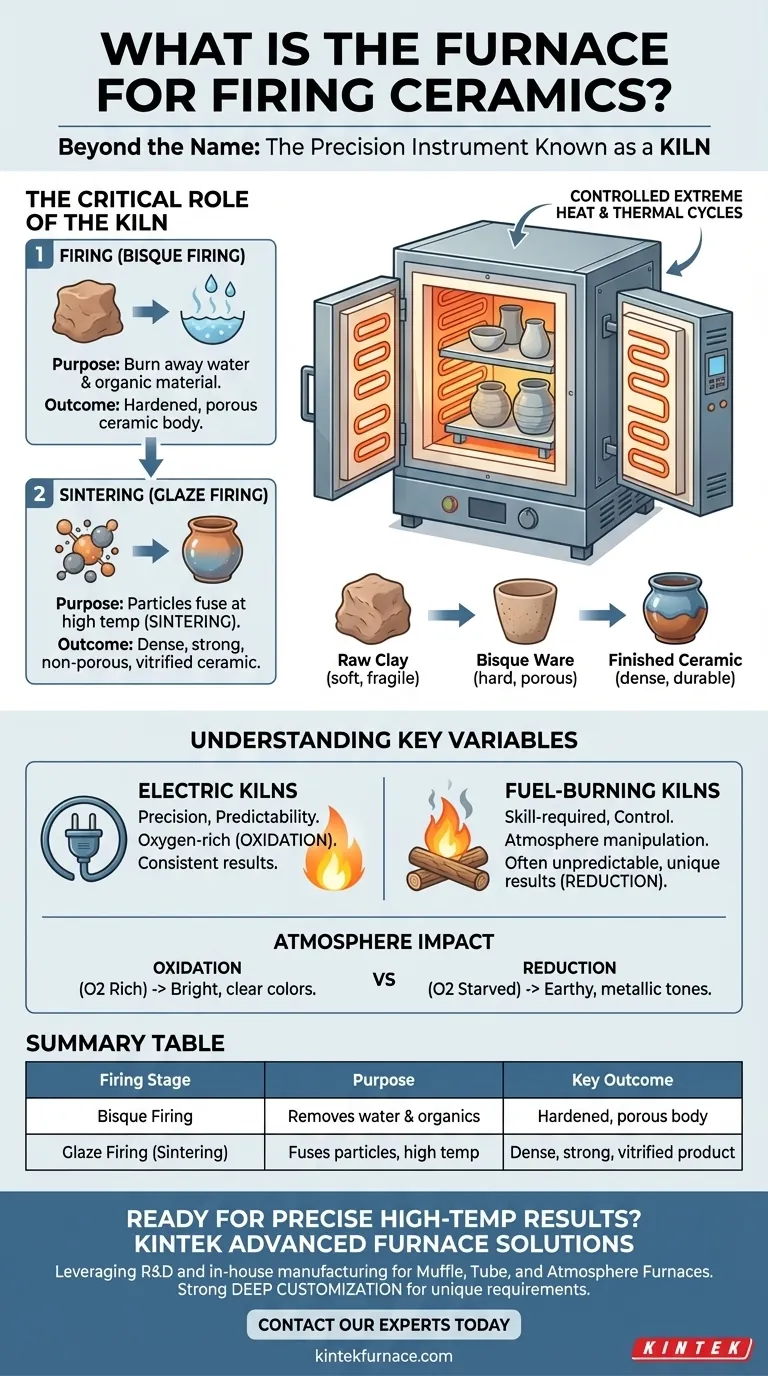
Beyond the Name: The Critical Role of the Kiln
Understanding what a kiln does is far more valuable than simply knowing its name. The transformation from soft clay to hard ceramic is a carefully controlled process that happens in distinct stages, all managed within the kiln.
The Initial Transformation: Firing
The first major stage is often called a bisque firing. In this phase, the kiln heats the ceramic material to a moderately high temperature.
This initial heating serves to burn away any remaining water and organic materials within the clay. The result is a hardened but still porous object, strong enough to be handled and glazed but not yet fully durable or waterproof.
Achieving Final Form: Sintering
To achieve its final strength and durability, the ceramic undergoes a second, higher-temperature firing, often called a glaze firing. During this phase, the critical process of sintering occurs.
The kiln brings the material to a temperature where the ceramic particles begin to fuse together. This process eliminates the pores between particles, dramatically increasing the material's density and strength. This is what makes a ceramic piece non-porous, durable, and suitable for functional use.
The Importance of Precise Control
A modern kiln is a sophisticated tool. Different types of clay and glazes mature at very specific temperatures, and the rate of heating and cooling must be managed precisely.
Heating too quickly can cause trapped water to turn to steam and shatter the piece. Cooling too fast can create thermal shock, resulting in cracks. The kiln's ability to execute a programmed temperature schedule is essential for success.
Understanding the Key Variables
Not all firing processes are the same. The type of kiln and the atmosphere inside it have a profound impact on the final aesthetic and structural properties of the ceramic.
Electric vs. Fuel-Burning Kilns
Electric kilns are prized for their precision and predictability. They create a clean, oxygen-rich environment (oxidation) that produces consistent results, which is ideal for many production potters and hobbyists.
Fuel-burning kilns (using gas, wood, or oil) require more skill to operate but offer greater control over the kiln's atmosphere. By adjusting the fuel and air mixture, an artist can create unique and often unpredictable results that are impossible to achieve in an electric kiln.
The Impact of Firing Atmosphere
The atmosphere refers to the chemical environment inside the kiln. An oxidation atmosphere is rich in oxygen and typically results in bright, clear glaze colors.
A reduction atmosphere is oxygen-starved. This forces the fire to pull oxygen molecules directly from the clay and glazes, causing dramatic and often beautiful chemical changes in the colorants. This is how many classic earthy and metallic tones are achieved in pottery.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
The right firing strategy depends entirely on the intended outcome for the ceramic piece.
- If your primary focus is strength and function: Your main concern is reaching the correct sintering temperature to ensure the clay body becomes fully vitrified, dense, and non-porous.
- If your primary focus is a specific aesthetic: The choice of kiln type and the deliberate manipulation of the firing atmosphere become as crucial as the peak temperature itself.
Ultimately, the kiln is the essential tool that applies controlled thermal energy to bring the vision of the ceramicist or engineer to life.
Summary Table:
| Firing Stage | Purpose | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Bisque Firing | Removes water & organic material | Hardened, porous ceramic body ready for glazing |
| Glaze Firing (Sintering) | Fuses particles at high temperature | Dense, strong, non-porous, and vitrified final product |
Ready to achieve precise, high-temperature results for your ceramic projects?
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions for diverse laboratories. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, and Atmosphere Furnaces, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique sintering and firing requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you optimize your thermal processing.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
People Also Ask
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions



















