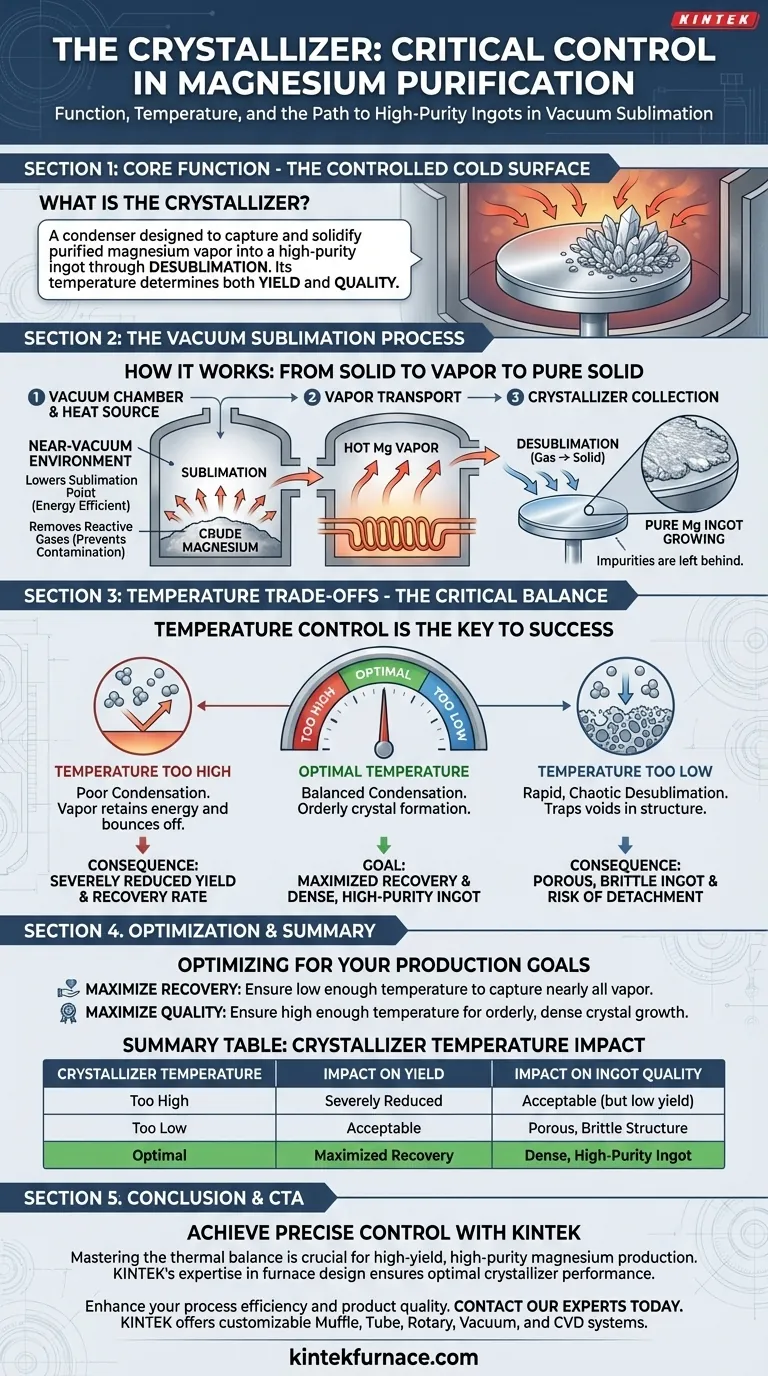
At its core, the crystallizer in a vacuum sublimation furnace functions as a controlled cold surface designed to capture and solidify purified magnesium vapor. This component, also called a condenser, is where the gaseous magnesium transforms back into a high-purity solid ingot. Its temperature is the single most critical control parameter because it directly governs both the quantity (yield) and quality (density) of the final product.
The central challenge is maintaining a precise thermal balance. The crystallizer must be cold enough to force the hot magnesium vapor to condense efficiently, but not so cold that it creates a structurally weak or porous ingot.

How Vacuum Sublimation Achieves Purity
To understand the crystallizer's role, you must first understand the environment in which it operates. The process relies on turning solid crude magnesium directly into a gas and then back into an even purer solid, bypassing the liquid phase.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
A high-performance vacuum pump is fundamental to the entire process. It creates a near-vacuum environment inside the furnace, which achieves two essential goals.
First, it dramatically lowers the sublimation point of magnesium. This allows the metal to turn into a vapor at a much lower, more energy-efficient temperature.
Second, the vacuum removes reactive atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen. This prevents the hot, highly reactive magnesium vapor from forming oxides or nitrides, which would contaminate the final product.
The Principle of Desublimation
Inside this vacuum, crude magnesium is heated until it sublimates, turning from a solid into a hot gas. This vapor then travels away from the heat source towards the much cooler crystallizer.
When the hot magnesium vapor makes contact with the cold surface of the crystallizer, it undergoes desublimation—an immediate phase transition from gas directly back to a solid. The impurities, having different sublimation points, are left behind.
The Crystallizer's Function in Collection
The crystallizer is the designated collection point for this purified magnesium. It is engineered to create a precise temperature differential within the furnace chamber.
Creating a Controlled Cold Zone
Typically designed as a disc, the crystallizer is actively cooled, often by circulating water internally. This makes it the coldest component within the high-temperature furnace.
This temperature difference acts as a magnet for the hot magnesium vapor, ensuring the purified metal consolidates in a predictable and controlled location.
Capturing and Growing the Ingot
As the magnesium vapor molecules collide with the cold surface, they rapidly lose their thermal energy. This forces them to condense and form solid crystals.
Over the course of the process, these crystals build upon one another, adhering to the disc and growing into a single, high-purity magnesium ingot.
Understanding the Temperature Trade-offs
The success of the entire purification cycle hinges on getting the crystallizer's temperature exactly right. Deviating even slightly in either direction introduces significant problems that compromise the final result.
The Risk of a Temperature Too High
If the crystallizer surface is too warm, it lacks the necessary thermal differential to efficiently condense the magnesium vapor.
The vapor molecules will strike the surface but retain too much energy to solidify, bouncing off instead. This leads to poor condensation efficiency and results in a severely reduced recovery rate, or yield.
The Danger of a Temperature Too Low
Conversely, if the crystallizer is too cold, the desublimation process happens too rapidly and chaotically. This shock-cooling effect traps voids within the crystal structure as it forms.
This results in a porous and brittle ingot, which compromises its metallurgical quality. Furthermore, this poor structure can lead to the ingot detaching from the crystallizer and falling back into the crucible, ruining the entire batch.
Optimizing Crystallizer Temperature for Your Goal
Controlling the crystallizer temperature is a balancing act between competing objectives. Your specific production priority will determine your ideal temperature setpoint within the optimal range.
- If your primary focus is maximizing recovery rate: You must ensure the temperature is low enough to capture nearly all the vapor, avoiding the inefficiency of a surface that is too warm.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum ingot density and quality: You must ensure the temperature is high enough to allow crystals to form in an orderly, dense structure, avoiding the porosity caused by a surface that is too cold.
Ultimately, mastering the temperature of the crystallizer is the key to controlling the outcome of the entire vacuum sublimation process.
Summary Table:
| Crystallizer Temperature | Impact on Yield | Impact on Ingot Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Too High | Severely Reduced (Poor Condensation) | Acceptable, but yield is low |
| Too Low | Acceptable | Porous, Brittle Structure |
| Optimal | Maximized Recovery | Dense, High-Purity Ingot |
Achieve Precise Control in Your Purification Process
Mastering the thermal balance of your vacuum sublimation furnace is the key to high-yield, high-purity magnesium production. KINTEK's expertise in high-temperature furnace design ensures you have the precise control needed for optimal crystallizer performance.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable for your unique purification needs.
Ready to enhance your process efficiency and product quality? Contact our experts today to discuss how our lab furnaces can be tailored for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing



















