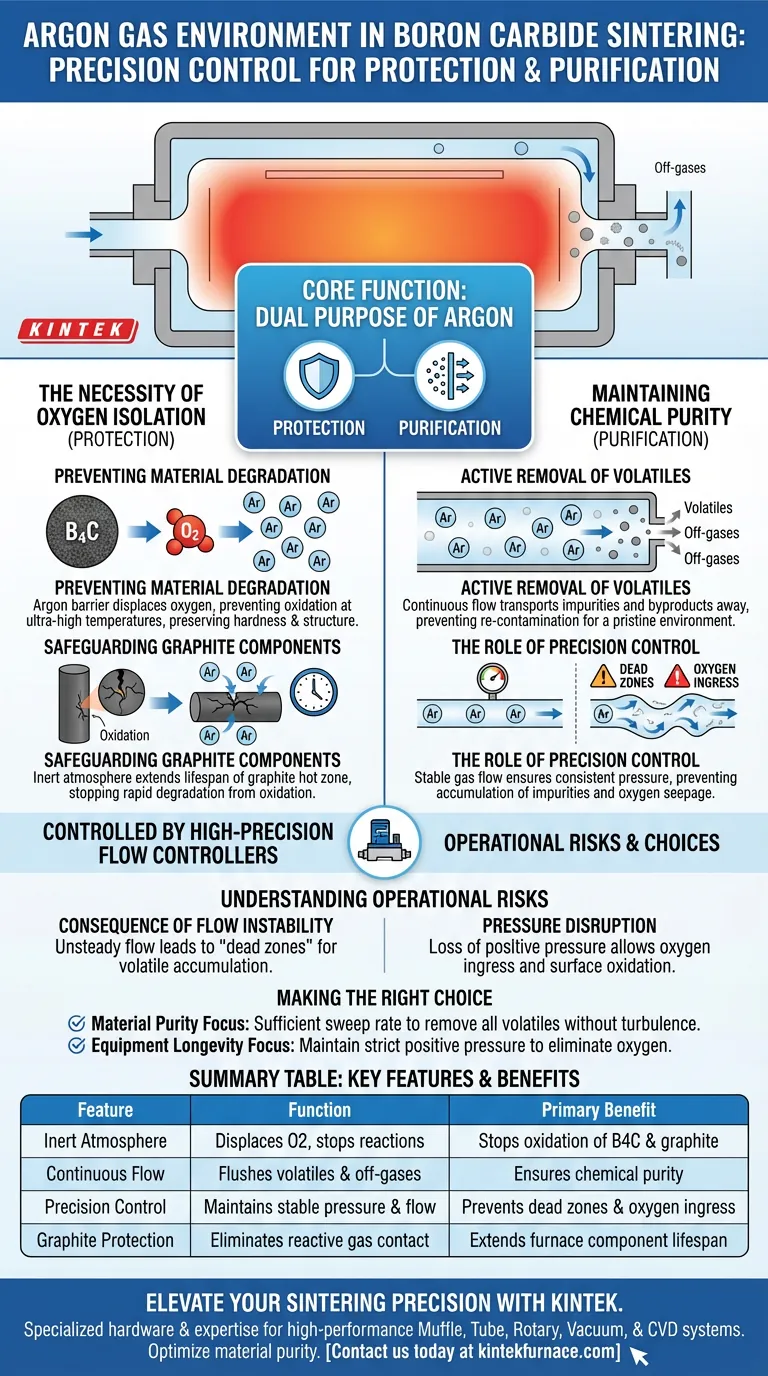
The primary function of an Argon gas environment in Boron Carbide sintering is to establish a strictly controlled, inert atmosphere that prevents material degradation. Controlled by high-precision flow controllers, this continuous gas flow effectively isolates oxygen to stop oxidation and actively removes volatile impurities, ensuring both the final product and the furnace components maintain their chemical integrity.
Core Takeaway: The Argon environment serves a dual purpose: protection and purification. It safeguards the Boron Carbide and graphite components from oxidative damage while simultaneously flushing out contaminants to maintain a pristine sintering environment.

The Necessity of Oxygen Isolation
Preventing Material Degradation
Boron Carbide requires ultra-high temperatures to sinter effectively. At these elevated thermal levels, the material becomes highly reactive to oxygen.
The Argon gas acts as a protective barrier. By displacing oxygen within the furnace, it prevents the Boron Carbide from oxidizing, which would otherwise compromise the material's hardness and structural properties.
Safeguarding Graphite Components
The sintering furnace relies on graphite components to withstand the intense heat. However, graphite is extremely susceptible to oxidation, which can lead to rapid degradation of the equipment.
The inert Argon atmosphere extends the lifespan of these internal components. It ensures that the graphite remains stable and does not erode during the heating cycle.
Maintaining Chemical Purity
Active Removal of Volatiles
Sintering is not a static process; it generates volatile impurities and off-gases. If these byproducts remain stationary, they can re-contaminate the Boron Carbide.
The continuous flow of Argon acts as a transport mechanism. It physically carries these volatile impurities away from the sintering zone, ensuring the internal environment remains chemically pure.
The Role of Precision Control
The use of high-precision flow controllers is not merely for convenience; it is a critical quality control measure.
Stable gas flow ensures a consistent protective pressure. This precision prevents fluctuations that could allow oxygen ingress or result in the incomplete removal of impurities.
Understanding the Operational Risks
The Consequence of Flow Instability
While the Argon environment provides essential protection, its effectiveness is entirely dependent on the stability of the flow.
If the high-precision controllers fail to maintain a steady stream, "dead zones" may occur where volatiles accumulate. Conversely, a disruption in positive pressure can allow oxygen to seep back into the chamber, leading to immediate surface oxidation of the Boron Carbide.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
To maximize the quality of your Boron Carbide sintering, consider your primary operational objectives:
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Ensure your flow rate is calculated to sufficiently sweep away all generated volatiles without causing turbulence.
- If your primary focus is Equipment Longevity: Prioritize maintaining positive pressure to strictly eliminate oxygen and protect your graphite hot zone components.
Precision in your gas control strategy is the difference between a contaminated sample and a high-performance ceramic.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Sintering Process | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Atmosphere | Displaces oxygen and prevents chemical reactions | Stops oxidation of B4C and graphite |
| Continuous Flow | Flushes out volatile off-gases and impurities | Ensures chemical purity of the ceramic |
| Precision Control | Maintains stable pressure and flow rates | Prevents 'dead zones' and oxygen ingress |
| Graphite Protection | Eliminates reactive gas contact with hot zone | Extends furnace component lifespan |
Elevate Your Sintering Precision with KINTEK
Don't let oxidation compromise your advanced ceramics. KINTEK provides the specialized hardware and technical expertise needed to master the Boron Carbide sintering process. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all customizable to integrate high-precision gas flow controllers for your unique lab needs.
Ready to optimize your material purity? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace solution and protect your high-temp investments.
Visual Guide
References
- Hala Mohamed, Rehab Mahmoud. Waste Biomass Utilization for the Production of Adsorbent and Value-Added Products for Investigation of the Resultant Adsorption and Methanol Electro-Oxidation. DOI: 10.3390/catal14090574
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is an argon atmosphere required for CeO2 nanostructures? Unlock High-Performance Carbonization
- What is the function of an automatic cycling high-temperature box furnace in TCF testing? Expert Simulation Guide
- What are the advantages of using a controlled atmosphere furnace? Achieve Precise Material Processing and Quality
- What are the common applications of program-controlled atmosphere furnaces? Essential for High-Temp Material Processing
- What is the function of a tube atmosphere furnace? Precision Mn1/CeO2 Catalyst Reduction & Fabrication
- What protective function does furnace atmosphere provide? Essential for Preventing Oxidation and Decarburization
- What are some specific applications of retort furnaces? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment
- How does an atmosphere furnace contribute to research and development? Unlock Advanced Material Innovation



















