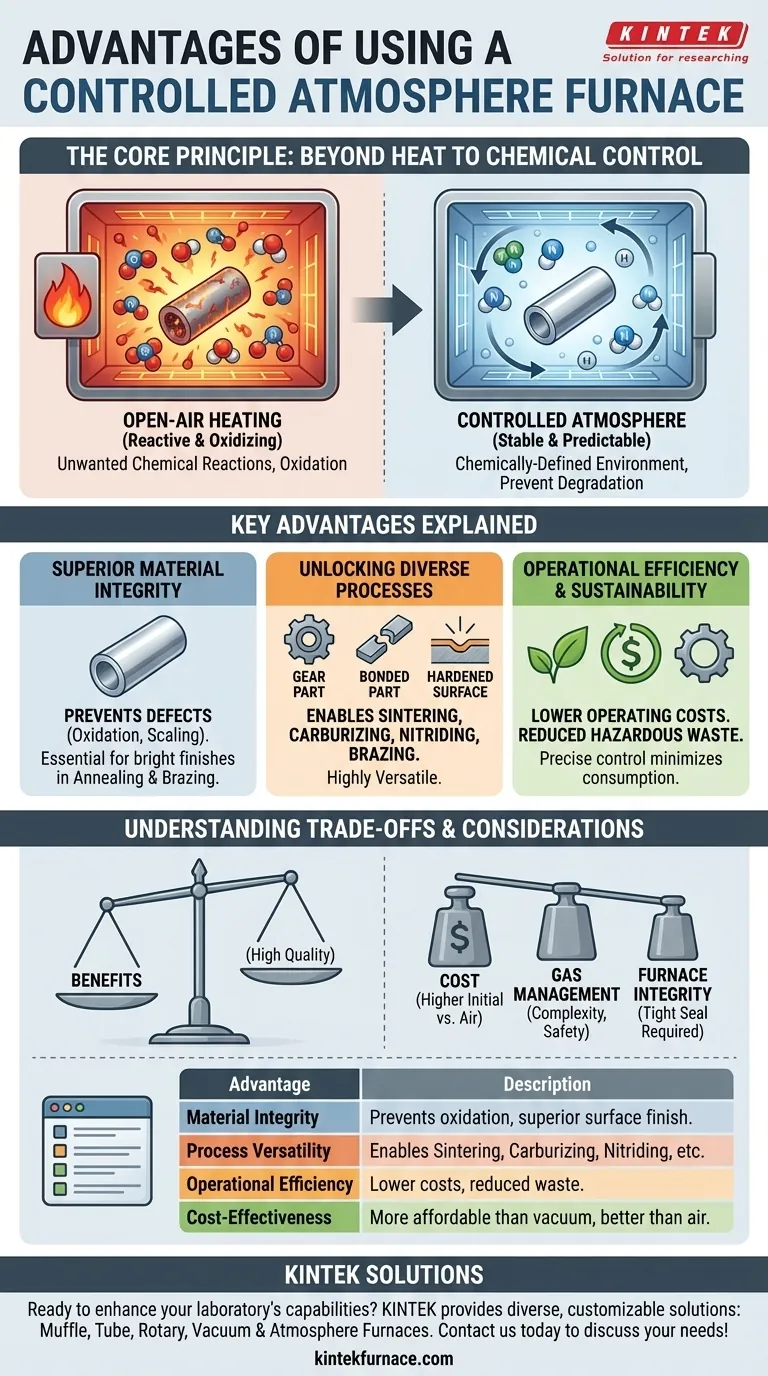
At their core, controlled atmosphere furnaces provide a distinct set of advantages by fundamentally changing the environment in which a material is heated. Their primary benefits are the prevention of unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation, precise control over the heat treatment process, improved operational efficiency, and the versatility to handle a wide range of materials and applications, from industrial production to laboratory research.
The crucial advantage of a controlled atmosphere furnace is not just the application of heat, but the ability to create a chemically-defined environment. This control over the furnace atmosphere is what prevents material degradation and enables specific, desirable transformations that are impossible in open-air heating.
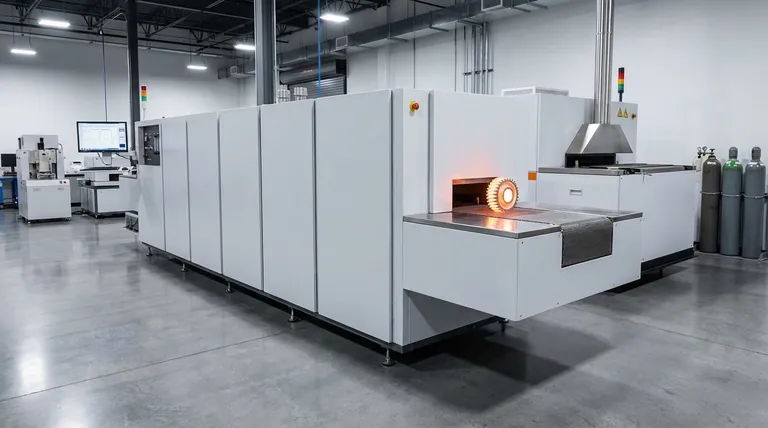

The Core Principle: Beyond Heat to Chemical Control
The defining feature of a controlled atmosphere furnace is its ability to replace the ambient air (which is reactive, primarily containing nitrogen and oxygen) with a specific gas or gas mixture. This creates a stable, predictable environment at high temperatures.
What is a "Controlled Atmosphere"?
A controlled atmosphere is a carefully managed gas mixture designed for a specific process. The gases can be inert, like argon or nitrogen, to prevent any chemical reactions. They can also be reactive, like hydrogen or carbon-monoxide mixtures, to intentionally cause a surface reaction like carburizing.
Why It Matters
At elevated temperatures, most materials are highly susceptible to reacting with oxygen in the air, leading to oxidation, scaling, and decarburization. By removing the oxygen, the furnace protects the material's surface integrity, mechanical properties, and final appearance.
Key Advantages Explained
The ability to control the furnace's chemical environment translates directly into several critical operational advantages.
Achieving Superior Material Integrity
A controlled atmosphere is essential for preventing defects. By eliminating oxygen, you prevent the formation of scale on metal parts, which preserves surface finish and dimensional accuracy. This is critical for processes like brazing, where clean surfaces are required for the filler metal to bond properly, and annealing, where a bright, clean finish is desired.
Unlocking Diverse Material Processes
This technology is highly versatile, enabling processes that are simply not feasible in an air furnace.
- Sintering: Powdered metals or ceramics are heated to bond particles together, and a controlled atmosphere prevents oxidation of the fine powders.
- Carburizing: A carbon-rich atmosphere is used to diffuse carbon into the surface of steel parts to increase surface hardness.
- Nitriding: A nitrogen-rich atmosphere is used to create a very hard case on the surface of steel components.
- Brazing & Annealing: An inert or reducing atmosphere ensures clean, oxide-free surfaces for strong joints and bright finishes.
Driving Operational Efficiency and Sustainability
Modern controlled atmosphere furnaces are designed for efficiency. Advanced insulation reduces heat loss, and precise process control minimizes gas consumption and cycle times, lowering operating costs. By avoiding harsh chemical baths for post-process cleaning (to remove scale, for instance), they also reduce the use of toxic chemicals and the generation of hazardous waste.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, these furnaces introduce unique operational requirements that must be managed.
Cost Comparison vs. Other Furnaces
A controlled atmosphere furnace is more complex and has a higher initial cost than a simple air furnace. However, it is often significantly less expensive than a vacuum furnace, which serves many similar high-purity applications but at a higher capital and operational cost.
The Complexity of Gas Management
The primary operational challenge is the management of process gases. You must have a reliable supply of the correct gases, precise flow control systems, and robust safety protocols. Handling flammable or toxic gases like hydrogen or ammonia requires specialized safety systems, ventilation, and operator training to prevent accidents.
The Importance of Furnace Integrity
The effectiveness of the furnace depends entirely on its mechanical design. A tight seal is paramount to prevent external air from infiltrating and contaminating the atmosphere. Likewise, the internal design must ensure uniform atmosphere flow so that all parts of the workload are exposed to the same gas conditions, ensuring consistent results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace depends on balancing your material requirements with operational complexity and cost.
- If your primary focus is maximum material purity and a pristine surface finish: A controlled atmosphere furnace is essential to prevent oxidation and other unwanted surface reactions.
- If your primary focus is process versatility for R&D or varied production: This furnace's ability to run many different processes like sintering, brazing, and carburizing makes it a flexible asset.
- If your primary focus is balancing cost-effective production with high-quality results: A controlled atmosphere furnace provides a significant quality upgrade over air furnaces without the higher cost of a full vacuum system.
Ultimately, investing in a controlled atmosphere furnace is a decision to prioritize precise control over your material's final properties.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Material Integrity | Prevents oxidation, scaling, and decarburization for superior surface finish and properties. |
| Process Versatility | Enables sintering, carburizing, nitriding, brazing, and annealing in controlled environments. |
| Operational Efficiency | Reduces heat loss, gas consumption, and hazardous waste, lowering operating costs. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | More affordable than vacuum furnaces while offering high-quality results over air furnaces. |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with advanced high-temperature solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with controlled atmosphere furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering improved material integrity, process versatility, and operational efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific needs and drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the relationship between temperature and the furnace atmosphere in material processing? Master the Critical Heat-Environment Balance
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What industries commonly use inert atmosphere heat treating? Key Applications in Military, Automotive, and More
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What are the two main types of atmosphere furnaces and their characteristics? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab



















