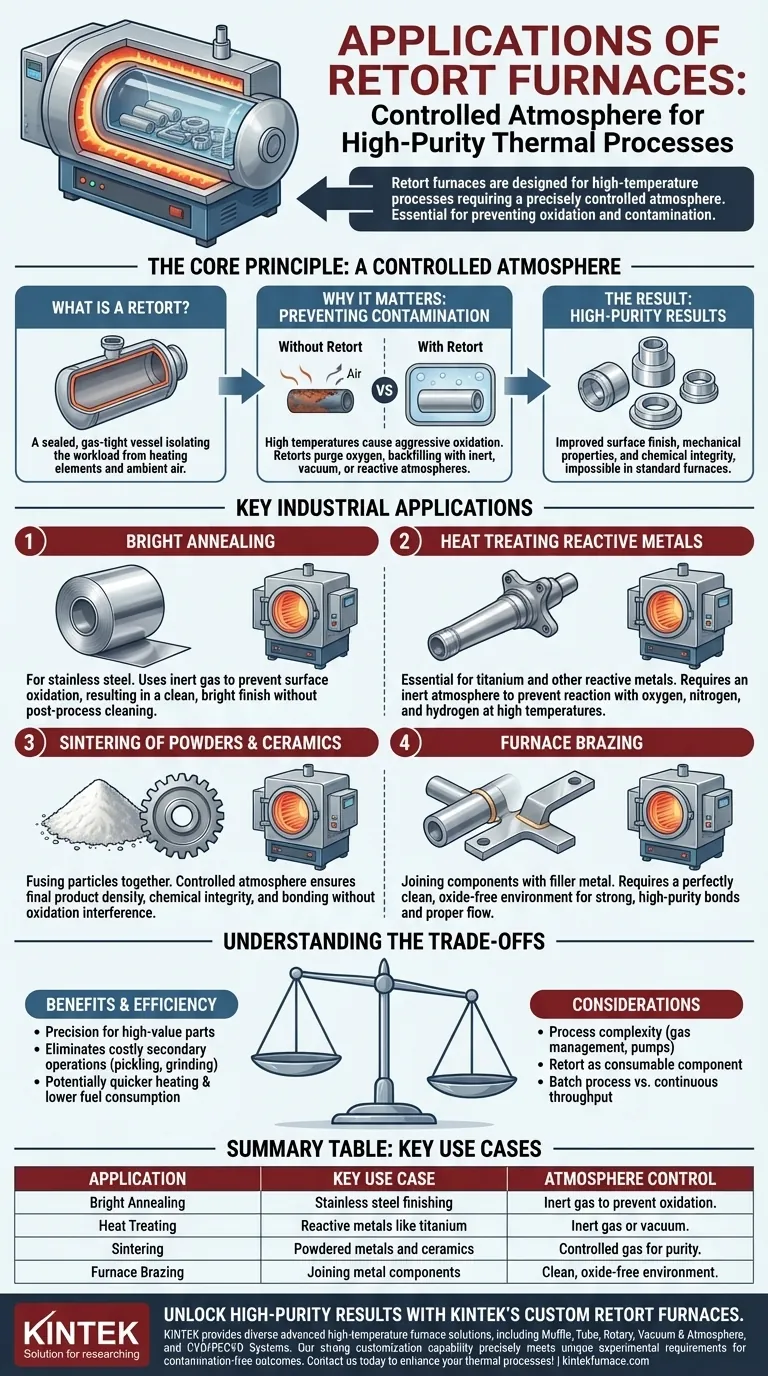
Retort furnaces are specifically designed for high-temperature thermal processes that require a precisely controlled atmosphere. They are essential for applications like the bright annealing of stainless steel, heat treating reactive metals such as titanium, and the sintering of advanced ceramics and powdered metals where preventing oxidation and contamination is critical.
The defining feature of a retort furnace isn't just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its use of a sealed container—the retort—to isolate the material from the ambient air and heating elements. This isolation is the key to achieving high-purity results that are impossible in a standard furnace.

The Core Principle: A Controlled Atmosphere
What is a Retort?
A retort is a sealed, gas-tight vessel, typically made of high-temperature metal alloys or ceramics, that is placed inside a furnace.
The material being processed sits inside the retort. The furnace heats the outside of the retort, and the heat transfers to the material inside.
This design separates the workload from the furnace's heating elements and the surrounding air, giving you complete control over the gaseous environment around your parts.
Why It Matters: Preventing Contamination
At high temperatures, most materials—especially metals—react aggressively with oxygen in the air. This reaction, called oxidation, can ruin a material's surface finish, mechanical properties, and chemical purity.
By using a retort, you can purge the oxygen and backfill the container with a specific atmosphere. This could be an inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent any reaction, a vacuum to remove all gases, or a reactive gas to create a specific chemical change.
Key Industrial Applications in Detail
The ability to control the atmosphere makes retort furnaces indispensable in several high-value manufacturing processes.
Heat Treating Specialty Metals
Processes for metals like stainless steel and titanium demand an oxygen-free environment.
Bright annealing of stainless steel, for example, uses a retort to prevent surface oxidation, resulting in a clean, "bright" finish that doesn't require post-process cleaning or pickling.
Similarly, heat treating titanium parts requires an inert atmosphere because titanium is extremely reactive with oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen at elevated temperatures.
Sintering of Powders and Ceramics
Sintering is the process of fusing particles together using heat, common in powder metallurgy and technical ceramics manufacturing.
A controlled atmosphere is vital to ensure the final product has the desired density and chemical integrity. Any oxygen present could interfere with the bonding process or alter the material's final composition.
Furnace Brazing
Brazing joins two metal components using a filler metal that melts at a lower temperature than the base parts.
For the filler metal to flow properly and create a strong bond, the surfaces must be perfectly clean and free of oxides. A retort furnace provides the ideal clean, controlled environment for high-strength, high-purity brazing operations.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, retort furnaces come with specific operational considerations.
Process Complexity and Cost
Managing the atmosphere adds a layer of complexity. It requires vacuum pumps, gas management systems, and careful monitoring to ensure the integrity of the retort's seal.
The retort itself is also a consumable component. Over many high-temperature cycles, it can degrade and will eventually need to be replaced, adding to the operational cost.
Throughput vs. Precision
Most retort furnace operations are batch processes. This means you load a batch of parts, run the cycle, cool it down, and unload.
This is perfect for high-value components where precision is paramount, but it may offer lower throughput than a continuous furnace (like a belt or tunnel furnace) used for mass production of less sensitive parts.
Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency
Despite the added complexity, retort furnaces can be more cost-effective for specific jobs.
By preventing oxidation, they eliminate the need for costly and time-consuming secondary operations like acid pickling, grinding, or polishing. The references also note they can offer quicker heating times and decreased fuel consumption, further improving efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a retort furnace comes down to one question: how critical is atmospheric control to your final product?
- If your primary focus is a bright, oxide-free finish on reactive metals: A retort furnace is essential for processes like bright annealing stainless steel or heat treating titanium.
- If your primary focus is developing or producing high-purity materials: For sintering advanced ceramics, metal powders, or conducting material synthesis research, a retort furnace is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is creating strong, clean joints between components: A retort furnace provides the ideal oxide-free environment required for high-quality furnace brazing.
Ultimately, a retort furnace is the definitive tool for any high-temperature process where the integrity of the material cannot be compromised by the atmosphere.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Use Case | Atmosphere Control |
|---|---|---|
| Bright Annealing | Stainless steel finishing | Inert gas to prevent oxidation |
| Heat Treating | Reactive metals like titanium | Inert gas or vacuum |
| Sintering | Powdered metals and ceramics | Controlled gas for purity |
| Furnace Brazing | Joining metal components | Clean, oxide-free environment |
Unlock High-Purity Results with KINTEK's Custom Retort Furnaces
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're bright annealing stainless steel, sintering ceramics, or brazing critical components, our retort furnaces deliver precise atmospheric control for contamination-free outcomes. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your thermal processes and boost efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing



















