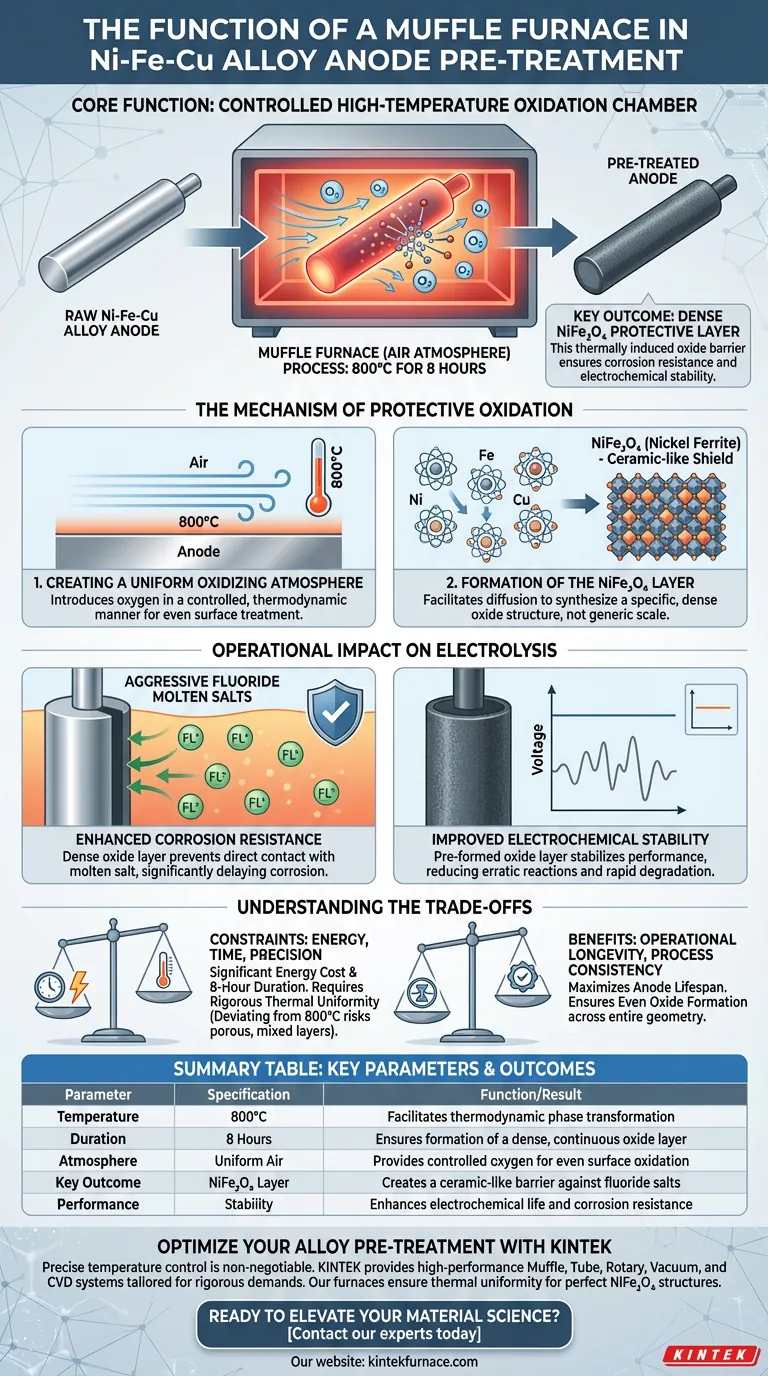
In the pre-treatment of Ni-Fe-Cu alloy anodes, the Muffle Furnace functions as a controlled high-temperature oxidation chamber. It subjects the alloy to a uniform air environment at precisely 800°C for a duration of 8 hours to engineer the material's surface properties before use.
The Muffle Furnace is critical for generating a dense $\text{NiFe}_2\text{O}_4$ protective layer on the anode surface. This thermally induced oxide barrier is the primary mechanism that ensures the anode's corrosion resistance and electrochemical stability when submerged in aggressive fluoride molten salts.
The Mechanism of Protective Oxidation
To understand the necessity of the Muffle Furnace, you must look beyond the simple application of heat. The goal is not merely to warm the material, but to drive a specific chemical phase transformation on the surface of the alloy.
Creating a Uniform Oxidizing Atmosphere
The Muffle Furnace uses an air atmosphere to introduce oxygen to the alloy surface in a highly controlled manner.
By maintaining a steady temperature of 800°C, the furnace ensures that the oxidation process is thermodynamic rather than chaotic. This consistency is vital for treating the entire surface area of the anode evenly.
Formation of the $\text{NiFe}_2\text{O}_4$ Layer
The core purpose of this 8-hour heat treatment is the synthesis of $\text{NiFe}_2\text{O}_4$ (nickel ferrite).
This is not a generic rust or scale; it is a specific, dense oxide structure. The Muffle Furnace facilitates the diffusion of atoms required to build this layer, transforming the raw alloy surface into a ceramic-like shield.
Operational Impact on Electrolysis
The pre-treatment in the Muffle Furnace directly dictates the lifespan and efficiency of the anode during the actual electrolysis process.
Enhanced Corrosion Resistance
Fluoride molten salts are chemically aggressive and can rapidly degrade untreated metals.
The dense oxide layer formed in the furnace acts as a physical and chemical barrier. It prevents the molten salt from directly contacting the vulnerable reactive metal underneath, significantly delaying corrosion.
Improved Electrochemical Stability
Beyond physical protection, the pre-treatment stabilizes the anode's electrochemical performance.
Anodes that undergo this specific thermal oxidation maintain consistent behavior during electrolysis. The pre-formed oxide layer reduces the likelihood of erratic reactions or rapid degradation that would occur if the raw alloy were exposed directly to the electrolyte.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the Muffle Furnace pre-treatment is effective, it introduces specific constraints that must be managed.
Energy and Time Intensity
The requirement for 8 hours at 800°C represents a significant energy cost and processing bottleneck. This is a batch process that cannot be rushed; shortening the time or lowering the temperature risks forming a porous or incomplete oxide layer that will fail in the molten salt.
Criticality of Temperature Precision
The formation of the specific $\text{NiFe}_2\text{O}_4$ phase is temperature-dependent. Deviating significantly from the 800°C target may result in mixed oxide phases that do not offer the same density or protective qualities. The furnace must be capable of rigorous thermal uniformity to prevent "hot spots" or "cold spots" on the anode surface.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The use of a Muffle Furnace in this context is about trading processing time for operational longevity.
- If your primary focus is Maximizing Anode Lifespan: Adhere strictly to the 800°C for 8 hours protocol to ensure the oxide layer is fully dense and continuous.
- If your primary focus is Process Consistency: Ensure your furnace is calibrated for high thermal uniformity to guarantee the $\text{NiFe}_2\text{O}_4$ phase forms evenly across the entire geometry of the anode.
The Muffle Furnace transforms the anode from a raw metal alloy into a composite component capable of surviving the extreme environment of fluoride electrolysis.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Specification | Function/Result |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 800°C | Facilitates thermodynamic phase transformation |
| Duration | 8 Hours | Ensures formation of a dense, continuous oxide layer |
| Atmosphere | Uniform Air | Provides controlled oxygen for even surface oxidation |
| Key Outcome | NiFe2O4 Layer | Creates a ceramic-like barrier against fluoride salts |
| Performance | Stability | Enhances electrochemical life and corrosion resistance |
Optimize Your Alloy Pre-Treatment with KINTEK
Precise temperature control is non-negotiable when engineering dense oxide layers for electrolysis. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored for rigorous lab and industrial demands.
Our customizable high-temperature furnaces ensure the thermal uniformity required to synthesize perfect $\text{NiFe}_2\text{O}_4$ protective structures, maximizing your anode lifespan and process efficiency.
Ready to elevate your material science? Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your unique needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Kamaljeet Singh, Guðrún Sævarsdóttir. Overpotential on Oxygen-Evolving Platinum and Ni-Fe-Cu Anode for Low-Temperature Molten Fluoride Electrolytes. DOI: 10.1007/s11837-024-06425-5
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is heating rate control critical for AA7050 alloy treatment? Master Microstructural Evolution in Lab Furnaces
- How does a high-temperature electric furnace contribute to the melting process of radiation shielding glass?
- How are programmable muffle furnaces utilized in solar material testing? Ensuring Durability in High-Temp CST Systems
- Why is a laboratory muffle furnace used to bake experimental apparatus? Ensure Purity in Shale Oil & Gas Simulations
- What are the final considerations when choosing a muffle furnace? Ensure Long-Term Value and Safety
- What are the primary process objectives when using a laboratory high-temperature Muffle Furnace for precursor treatment?
- What temperature information is displayed simultaneously on the controls? Monitor Real-Time and Target Temperatures for Precision
- What are the common applications of a muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment for Your Lab



















