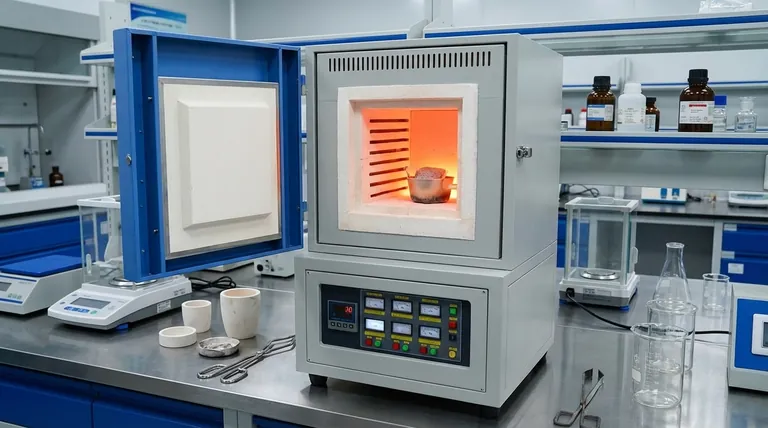
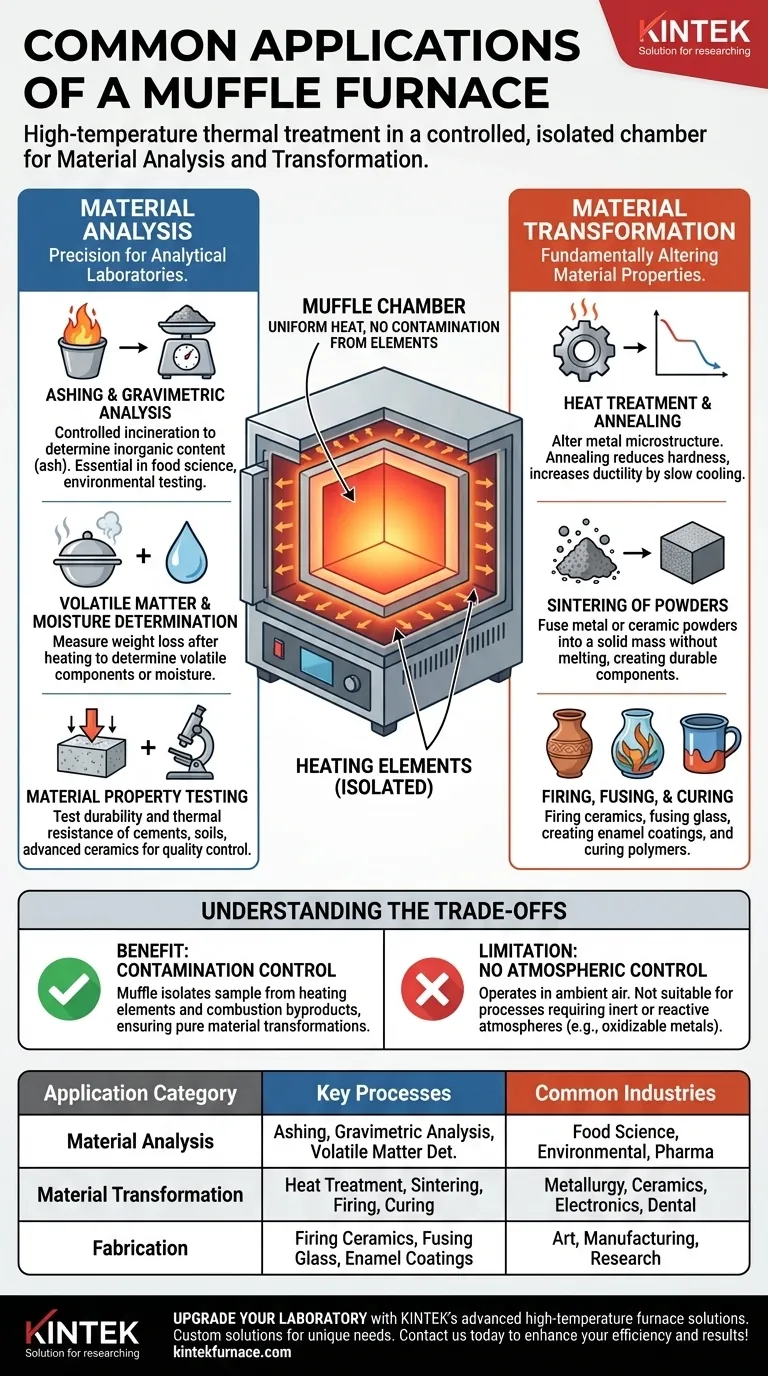
At its core, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven used for processes requiring thermal treatment in a controlled, isolated chamber. Its primary applications fall into two main categories: transforming materials and performing quantitative analysis. These range from heat-treating metals and sintering ceramics to precisely burning away organic matter from a sample to analyze the inorganic residue left behind.
The critical distinction of a muffle furnace is not simply its high heat, but its internal chamber—the "muffle." This feature isolates the sample from the heating elements, ensuring uniform temperature and preventing contamination from fuel or combustion byproducts.

Core Applications: Material Analysis
The furnace's ability to provide clean, consistent heat makes it an indispensable tool for analytical laboratories where precision is paramount.
Ashing and Gravimetric Analysis
Ashing is the process of controlled incineration, where organic material in a sample is burned away at a high temperature.
This leaves behind only the inorganic, non-combustible components (the ash), which can then be weighed and analyzed. This is a form of gravimetric analysis and is essential in food science, environmental testing, and the pharmaceutical industry.
Volatile Matter and Moisture Determination
Similarly, a muffle furnace is used to determine the amount of volatile matter in a sample like coal or biomass.
By heating the sample to a specific temperature in a covered crucible, the volatile components are driven off, and the resulting weight loss is measured. The same principle applies to determining moisture content, though typically at lower temperatures.
Material Property Testing
Muffle furnaces are used to test the durability and thermal resistance of various materials.
Engineers and material scientists test how substances like cements, soils, aggregates, and advanced ceramics behave under extreme, sustained heat, providing critical data for quality control and research.
Core Applications: Material Transformation
Beyond analysis, muffle furnaces are workhorses for fundamentally changing the physical properties of materials.
Heat Treatment and Annealing
Heat treatment refers to a group of processes used to alter the microstructure of a metal. Annealing, a common form of heat treatment, involves heating a metal and then slowly cooling it.
This process reduces hardness, relieves internal stresses, and increases the metal's ductility, making it easier to work with.
Sintering of Powders
Sintering is a process that uses heat to fuse powders—such as ceramics or metals—into a solid, coherent mass without melting them completely.
The high, uniform temperature inside a muffle furnace causes the particles to bond together, creating durable components for industries ranging from electronics to dental prosthetics.
Firing, Fusing, and Curing
In artistic and fabrication settings, muffle furnaces are used for a variety of tasks. These include:
- Firing ceramics and pottery.
- Fusing glass to create decorative pieces.
- Creating enamel coatings on metal.
- Curing specialized rubbers and polymers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A muffle furnace is a specific tool, and its advantages come with inherent limitations. Understanding these is key to using it correctly.
The Benefit: Contamination Control
The defining feature is the muffle, which separates the workload from the heating elements. In a direct-fired furnace or kiln, combustion byproducts could react with and contaminate the sample.
The muffle's design ensures the sample is only exposed to uniform radiant heat, which is critical for sensitive analytical work or achieving pure material transformations.
The Limitation: No Atmospheric Control
A standard muffle furnace operates in ambient air. This is perfectly acceptable for many materials, but it is unsuitable for processes that require an inert or reactive atmosphere.
For high-temperature treatment of metals that readily oxidize (like titanium), a specialized vacuum furnace or controlled-atmosphere furnace is necessary. The muffle furnace is for applications where contamination from heating elements is a concern, but reaction with air is not.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right process, identify your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis: You are likely performing ashing to determine the inorganic content or volatile matter of a sample for food, environmental, or chemical testing.
- If your primary focus is altering material properties: You are performing heat treatment, such as annealing metals to improve their ductility, or sintering powders to create a solid component.
- If your primary focus is fabrication or creation: You are using the furnace for firing ceramics, fusing glass, or creating enamel coatings where uniform, clean heat is paramount.
Understanding these core functions allows you to leverage the unique capabilities of a muffle furnace to achieve your precise analytical or material objective.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Common Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Material Analysis | Ashing, Gravimetric Analysis, Volatile Matter Determination | Food Science, Environmental Testing, Pharmaceuticals |
| Material Transformation | Heat Treatment, Sintering, Firing, Curing | Metallurgy, Ceramics, Electronics, Dental |
| Fabrication | Firing Ceramics, Fusing Glass, Enamel Coatings | Art, Manufacturing, Research |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable muffle, tube, rotary, vacuum, atmosphere furnaces, and CVD/PECVD systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs in material analysis and transformation. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















