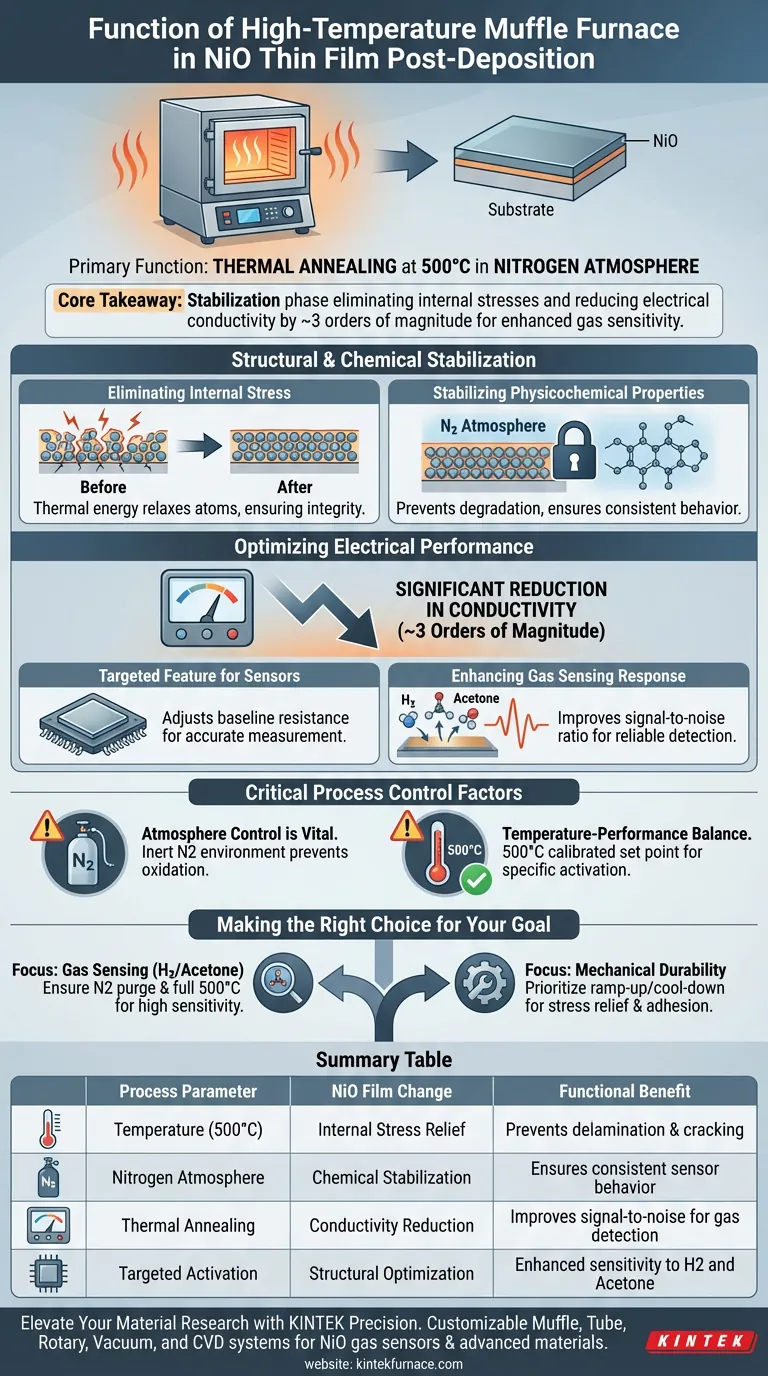
The primary function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in this context is to perform thermal annealing. Specifically, for Nickel Oxide (NiO) thin films, this involves subjecting the deposited material to a temperature of 500°C in a nitrogen atmosphere. This step is not merely for drying; it is a critical activation process that fundamentally alters the film's internal structure to prepare it for high-performance applications.
Core Takeaway The muffle furnace treatment serves as a stabilization phase that eliminates internal film stresses and reduces electrical conductivity by approximately three orders of magnitude. This modification is essential for optimizing the material's sensitivity to gases like hydrogen and acetone.
Structural and Chemical Stabilization
Eliminating Internal Stress
Freshly deposited thin films often contain significant internal mechanical stresses. These stresses arise from the deposition process itself and can lead to delamination or cracking if left untreated.
The thermal energy provided by the muffle furnace allows the atoms within the NiO film to relax. This eliminates these residual stresses, ensuring the mechanical integrity of the film on the substrate.
Stabilizing Physicochemical Properties
Beyond mechanical stress, the film's chemical structure requires stabilization. Heating the film in a controlled nitrogen atmosphere locks in the desired physicochemical properties.
This prevents the material from drifting or degrading over time, ensuring that the sensor behaves consistently during repeated use.
Optimizing Electrical Performance
Significant Reduction in Conductivity
One of the most drastic changes induced by this process is the modification of electrical transport properties. The annealing treatment reduces the electrical conductivity of the NiO film by approximately three orders of magnitude.
While high conductivity is desired in some electronics, for NiO gas sensors, this reduction is a targeted feature. It adjusts the baseline resistance of the material to a range where gas interactions can be measured accurately.
Enhancing Gas Sensing Response
The ultimate goal of these structural and electrical adjustments is to improve sensor utility. The treated NiO films demonstrate a significantly enhanced response to specific gases, particularly:
- Hydrogen
- Acetone
By optimizing the baseline electrical parameters, the signal-to-noise ratio improves, making the detection of these gases more reliable.
Critical Process Control Factors
Atmosphere Control is Vital
It is crucial to note that this process is performed in a nitrogen atmosphere. Unlike annealing in air (which contains oxygen), a nitrogen environment is inert.
Using the wrong atmosphere in the muffle furnace could lead to unwanted oxidation states or surface reactions that would alter the sensor's selectivity, negating the benefits of the thermal treatment.
The Temperature-Performance Balance
The specific temperature of 500°C is a calibrated set point.
In broader thin film processing, insufficient temperatures fail to induce the necessary atomic relaxation or crystallization. Conversely, excessive temperatures can degrade the film or cause unwanted diffusion between the film and the substrate. Adherence to the specific 500°C parameter is essential for replicating the NiO results described.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When configuring your post-deposition process for NiO films, consider your end application:
- If your primary focus is Gas Sensing (H2/Acetone): Ensure your furnace is purged with nitrogen and reaches the full 500°C to achieve the necessary drop in conductivity for high sensitivity.
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Durability: Prioritize the annealing ramp-up and cool-down cycles to maximize stress relief and prevent thermal shock, ensuring the film remains adhered to the substrate.
Correct usage of the muffle furnace turns a raw, unstable deposition into a precise, highly sensitive functional material.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | NiO Film Change | Functional Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (500°C) | Internal Stress Relief | Prevents delamination and cracking |
| Nitrogen Atmosphere | Chemical Stabilization | Ensures consistent sensor behavior |
| Thermal Annealing | Conductivity Reduction | Improves signal-to-noise for gas detection |
| Targeted Activation | Structural Optimization | Enhanced sensitivity to H2 and Acetone |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your thin film applications with high-performance thermal processing. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems.
Whether you are optimizing NiO gas sensors or developing advanced functional materials, our lab high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique temperature and atmospheric requirements. Ensure precise structural stabilization and electrical optimization for your target customers today.
Ready to achieve superior results? Contact us today to find your custom furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- I. Hotový, Fadi Dohnal. Preparation of laser induced periodic surface structures for gas sensing thin films and gas sensing verification of a NiO based sensor structure. DOI: 10.2478/jee-2024-0004
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What atmosphere control options are available in advanced muffle furnaces? Master Materials Processing with Precision
- How is the chamber temperature displayed in the muffle furnace? Get Accurate Readings for Your Lab
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace necessary for evaluating the ash content of banana powder?
- Why are muffle furnaces not suitable for low-temperature applications? Discover the High-Temperature Design Limits
- What is the function of a laboratory furnace in fire-resistant material testing? Ensure Precise EN 1363-1 Compliance
- What is the function of a muffle furnace during catalyst calcination? Master Biomass-to-Catalyst Transformation
- What is the primary application of a laboratory muffle furnace in the preparation of Co2SnO4 nanocubes? Expert Guide
- What role do auxiliary equipment like fans and sprayers play in a box furnace? Enhance Precision and Efficiency in Heat Treatment



















