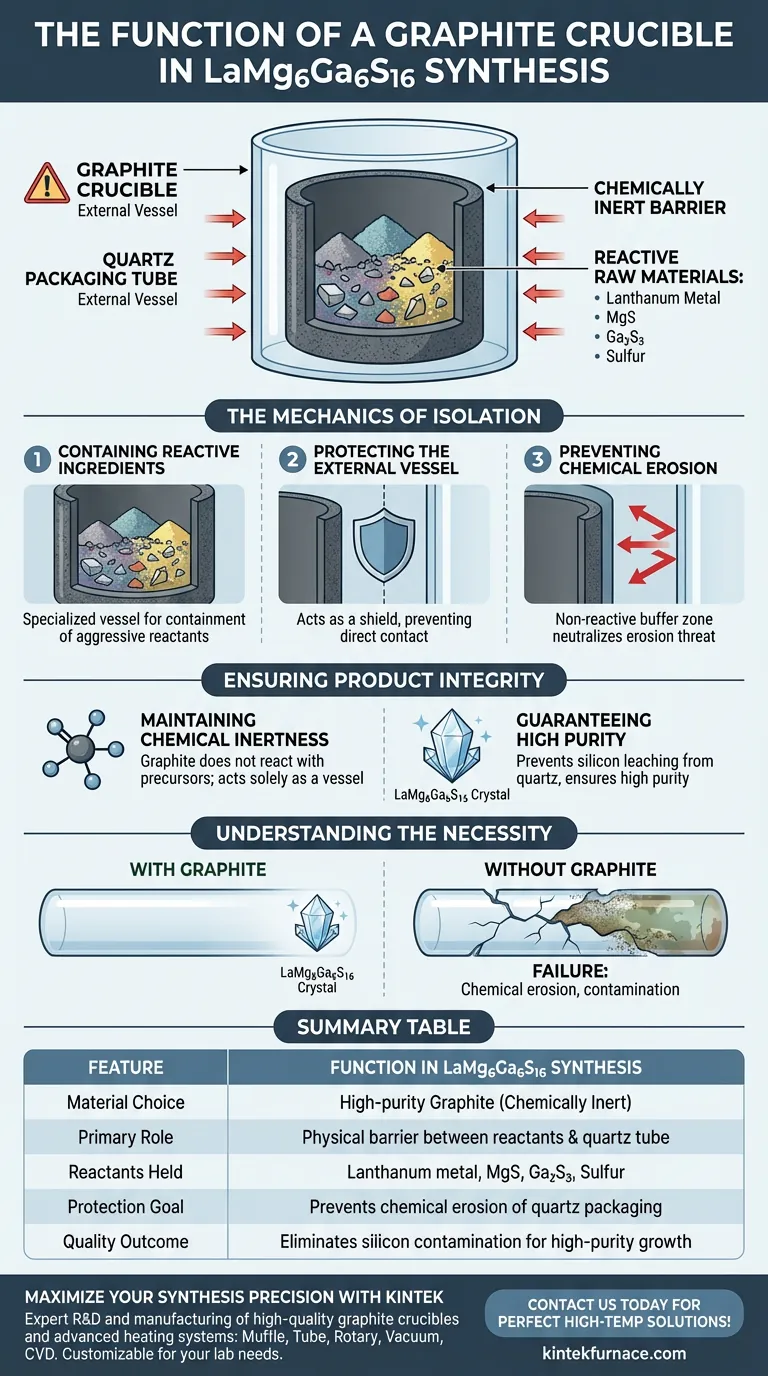
The primary function of a graphite crucible in the synthesis of LaMg6Ga6S16 is to act as a chemically inert container that isolates reactive raw materials from the external environment. Specifically, it holds the mixture of lanthanum metal, magnesium sulfide, gallium sulfide, and elemental sulfur, preventing them from coming into direct contact with the outer quartz packaging tube.
High-temperature solid-state reactions often involve aggressive reactants that can degrade standard laboratory vessels. The graphite crucible eliminates this risk by providing a robust physical barrier that prevents chemical erosion, ensuring the final crystal maintains high purity.

The Mechanics of Isolation
Containing Reactive Ingredients
The synthesis of LaMg6Ga6S16 involves a complex mixture of raw materials. These include lanthanum metal, magnesium sulfide, gallium sulfide, and elemental sulfur.
Because these materials are highly reactive, particularly under the high temperatures required for solid-state reactions, they require a specialized vessel for containment. The graphite crucible serves as this primary holder.
Protecting the External Vessel
In this specific synthesis setup, the reaction does not happen in the open air; the crucible is placed inside an external quartz packaging tube.
The graphite crucible acts as a shield between the reactants and this outer quartz tube. Without this shield, the raw materials would come into direct contact with the quartz.
Preventing Chemical Erosion
The primary danger of direct contact between the reactants and the quartz tube is chemical erosion.
At high temperatures, the sulfur-based mixture can react aggressively with quartz. The graphite creates a non-reactive buffer zone that completely neutralizes this threat.
Ensuring Product Integrity
Maintaining Chemical Inertness
Graphite is selected for this process because of its excellent chemical inertness.
It does not react with the specific precursor materials used for LaMg6Ga6S16. This ensures that the crucible acts solely as a vessel, not as a participant in the chemical reaction.
Guaranteeing High Purity
The ultimate goal of using the graphite crucible is to preserve the quality of the final product.
By preventing erosion of the quartz tube, the crucible stops silicon or other contaminants from leaching into the reaction mixture. This isolation is strictly necessary to ensure the high purity of the resulting LaMg6Ga6S16 crystals.
Understanding the Necessity
The Consequence of Omission
It is important to understand that the graphite crucible is not optional equipment in this context.
Omitting the graphite layer would likely result in the failure of the synthesis vessel. The reactants would attack the quartz, leading to structural failure of the tube and contamination of the sample.
Material Compatibility
While graphite is excellent for this specific sulfide synthesis, its utility relies on the specific chemistry of the reactants.
Its effectiveness is defined by its ability to resist these specific sulfur and metal compounds. It is the specific incompatibility between the reactants and the quartz that drives the need for this intermediate graphite layer.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When designing a synthesis protocol for complex sulfides like LaMg6Ga6S16, the choice of crucible material dictates the success of the reaction.
- If your primary focus is Product Purity: You must use a graphite liner to prevent impurities from the outer vessel from contaminating the crystal lattice.
- If your primary focus is Equipment Safety: You must use graphite to prevent the corrosive reactants from eroding and destroying the external quartz tubing.
The graphite crucible is the essential component that bridges the gap between reactive raw chemicals and a stable, high-quality crystal structure.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in LaMg6Ga6S16 Synthesis |
|---|---|
| Material Choice | High-purity Graphite (Chemically Inert) |
| Primary Role | Acts as a physical barrier between reactants and quartz tube |
| Reactants Held | Lanthanum metal, Magnesium sulfide, Gallium sulfide, Sulfur |
| Protection Goal | Prevents chemical erosion of the external quartz packaging |
| Quality Outcome | Eliminates silicon contamination for high-purity crystal growth |
Maximize Your Synthesis Precision with KINTEK
Don't let chemical erosion compromise your research. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-quality graphite crucibles and advanced heating systems—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all customizable for your unique lab needs.
Whether you are synthesizing complex sulfides or developing new materials, our precision-engineered solutions provide the thermal stability and chemical inertness your project demands. Contact us today to find the perfect high-temp solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Yu-Jie Zhang, Hongwei Yu. LaMg6Ga6S16: a chemical stable divalent lanthanide chalcogenide. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-47209-4
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How do B-type thermocouples contribute to temperature control in CaO-Al2O3-VOx slag processing? Achieve ±2 °C Precision
- What are the primary functions of high-purity graphite molds in the SPS of TiB2 ceramics? Enhance Sintering Precision
- What advantages do platinum crucibles offer for KCdCl3 sintering? Ensure Pure, Single-Phase Sample Synthesis
- How do graphite sleeves and ceramic crucibles function in induction furnaces? Key Roles in Material Synthesis
- How does a laboratory vacuum pump system contribute to the preparation process of TixNbMoTaW refractory alloys?
- What is the purpose of using a high-purity quartz boat? Ensure Sample Purity in TiO2@C High-Temp Annealing
- What is the purpose of cleaning MgO substrates for ScN growth? Optimize Your Epitaxial Film Quality
- What is the primary function of a drying oven during LLZTO preparation? Ensure Pure Phase Solid Electrolytes













