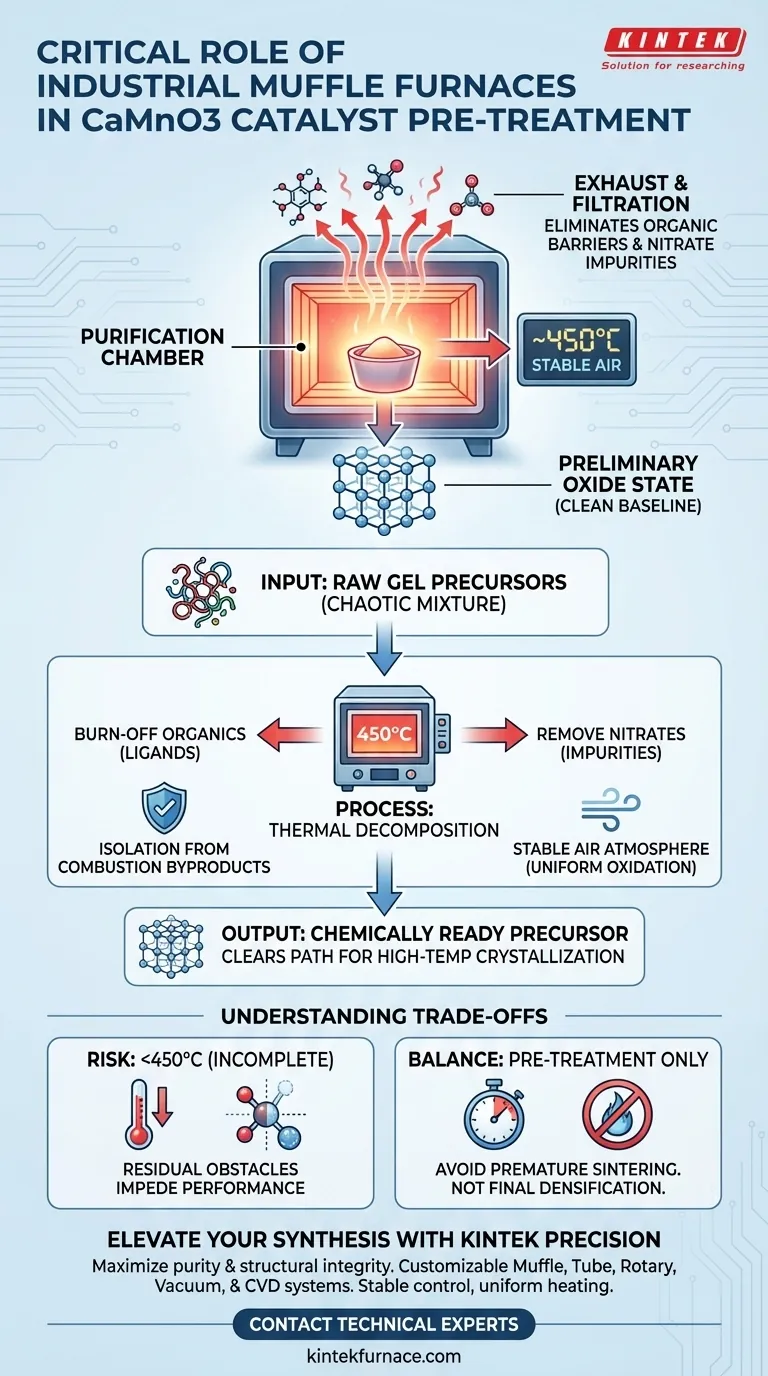
The critical role of industrial muffle furnaces in the pre-treatment of CaMnO3 catalysts is to facilitate the precise thermal decomposition of gel precursors. By maintaining a stable air atmosphere at approximately 450°C, the furnace ensures the complete removal of organic ligands and nitrate impurities. This process effectively converts the raw precursors into a preliminary oxide state, clearing the chemical path for successful high-temperature crystallization.
Core Insight The muffle furnace does not merely heat the material; it acts as a purification chamber that isolates the sample from combustion contaminants. By stripping away organic and nitrate "noise," it creates a chemically clean baseline essential for the structural integrity of the final CaMnO3 catalyst.

The Mechanics of Thermal Decomposition
Eliminating Organic Barriers
The primary function during this stage is the thorough burn-off of organic ligands.
These organic components are inherent to the gel precursors used in the initial synthesis. If left unchecked, they would interfere with the atomic arrangement required for the final catalyst structure.
Removing Nitrate Impurities
Simultaneously, the furnace drives out nitrate impurities present in the mixture.
Removing these impurities is non-negotiable, as their presence can lead to defects or inconsistent performance in the final catalytic material.
Creating the Preliminary Oxide State
The heat treatment converts the complex gel precursors into a simplified preliminary oxide state.
This transition is the bridge between a raw chemical mixture and a structured material, setting the stage for more aggressive thermal processing later.
Why Atmosphere Control Matters
Isolation from Combustion Byproducts
A defining feature of the muffle furnace is its ability to heat samples while keeping them isolated from fuel and combustion byproducts.
Unlike open-flame heating, this isolation prevents external contaminants from reacting with the CaMnO3 precursors, ensuring high purity.
Stable Air Environment
The process relies on a stable air atmosphere to facilitate uniform oxidation.
Consistency in the atmosphere ensures that the thermal decomposition occurs evenly throughout the batch, preventing localized defects.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Incomplete Decomposition
If the temperature deviates significantly below 450°C, the burn-off of organics may be incomplete.
Residual carbon or nitrates can act as "chemical obstacles," impeding the subsequent high-temperature crystallization process and degrading the catalyst's final performance.
Balancing Pre-treatment and Crystallization
It is crucial to understand that this stage is only for pre-treatment, not final densification.
Overheating at this stage could trigger premature sintering or unwanted phase changes before the material is chemically ready, disrupting the intended cycle of preparation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize the preparation of CaMnO3 catalysts, you must align your furnace parameters with your specific purity and structural requirements.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Ensure the furnace maintains a strictly isolated environment to prevent combustion byproducts from re-contaminating the precursor during ligand burn-off.
- If your primary focus is Process Efficiency: Strictly adhere to the 450°C target to maximize the speed of thermal decomposition without triggering premature crystallization.
Success in this stage is defined not just by heating the material, but by clearing the chemical obstacles that stand between a raw precursor and a high-performance catalyst.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Function | Key Parameter | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decomposition | Removal of organic ligands | ~450°C | Chemical baseline purification |
| Purification | Elimination of nitrates | Stable Air | Prevention of material defects |
| Phase Transition | Conversion to oxide state | Isolated Heating | High-purity precursor preparation |
Elevate Your Catalyst Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Maximize the purity and structural integrity of your CaMnO3 catalysts with KINTEK’s industry-leading thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific lab or industrial high-temperature needs.
Don't let impurities compromise your research. Our high-precision furnaces ensure stable atmosphere control and uniform heating for every batch.
Ready to optimize your pre-treatment process? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your unique requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Shaowei Yao, Tengwei Chen. Tandem catalysis of zeolite and perovskite for light olefins production in dehydrogenation cracking of naphtha. DOI: 10.1039/d5ra02427g
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What makes crucible furnaces suitable for high-temperature applications? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Precision
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in ZnNPs synthesis? Achieve Pure, Crystalline Zinc Oxide
- What is a batch furnace? Maximize Flexibility and Precision for Your Heat Treatment
- What is the significance of using a box-type furnace for molybdenum aluminide coating oxidation? Master Thermal Testing
- How are muffle furnaces applied in heat treatment processes? Achieve Precise Control for Superior Material Properties
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the carbonization synthesis of orange peel biochar? Precision Thermal Pyrolysis
- What are the typical laboratory applications of a muffle furnace? Essential Uses for Precise Heat Treatment
- How does the temperature range affect the choice of a muffle furnace? Ensure Precision and Protect Your Materials



















