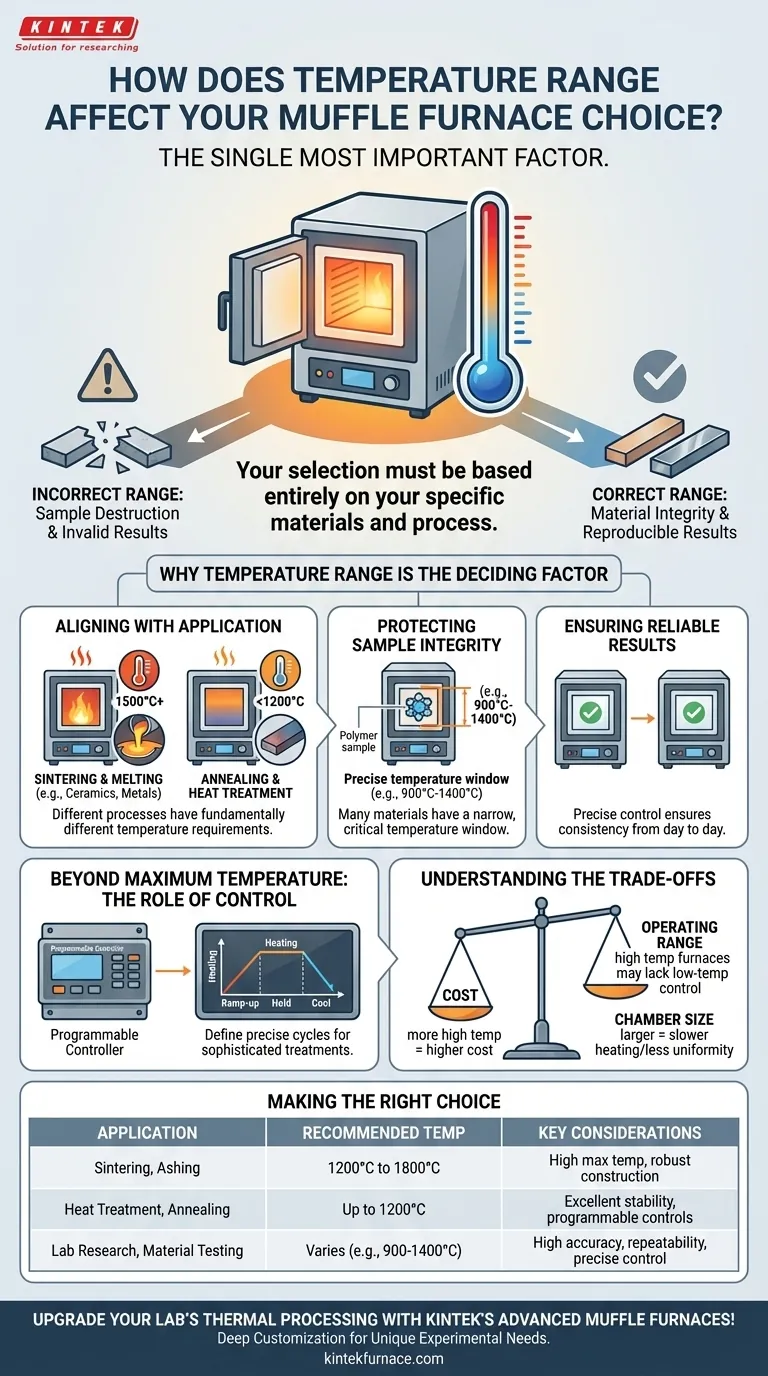
To put it simply, the required temperature range is the single most important factor when choosing a muffle furnace. Your selection must be based entirely on the specific materials you will be heating and the process you are performing. Choosing a furnace with an incorrect temperature range will not only fail to produce the desired result but can actively destroy your samples and invalidate your research or quality control.
The core decision is not just about finding a furnace that can reach a maximum temperature. It is about selecting a furnace that can precisely maintain the specific temperatures your application demands, ensuring the integrity of your material and the reproducibility of your results.

Why Temperature Range is the Deciding Factor
A muffle furnace is a tool for controlled thermal processing. Its entire value proposition rests on its ability to deliver a specific amount of heat for a specific duration. Mismatched temperature capabilities render the instrument useless for your intended task.
Aligning Temperature with Your Application
Different thermal processes have fundamentally different temperature requirements. There is no one-size-fits-all solution.
For example, processes like sintering ceramics or melting metals demand very high temperatures, often exceeding 1500°C. In contrast, processes like annealing or general heat treatments may only require a lower-to-mid range, typically below 1200°C.
Protecting Sample Integrity
Many materials have a narrow, critical temperature window for successful processing. Exceeding this window can be catastrophic.
Certain materials, such as specific polymer compounds, require a precise range (e.g., 900°C to 1400°C) for testing. Operating outside this range can cause the sample to disintegrate, melt improperly, or become contaminated, making your results unreliable.
Ensuring Reliable and Reproducible Results
The goal of any scientific or industrial process is consistency. The ability to precisely control the temperature is what ensures your results today will be the same as your results tomorrow.
A furnace that struggles to maintain a setpoint or has poor uniformity introduces variables that undermine the validity of your work. The right temperature range is the foundation of reproducible outcomes.
Beyond Maximum Temperature: The Role of Control
A furnace’s maximum temperature rating is only a headline specification. True utility comes from how well it can be controlled across its entire operating range.
The Function of the Temperature Controller
At its core, the system uses a thermometer to monitor the chamber temperature and a controller to adjust power to the heating elements. This feedback loop is what maintains the temperature you set.
The Power of Programmable Cycles
Modern furnaces feature programmable controllers that manage the entire heating process. This is a critical feature for any complex application.
These controllers allow you to define precise heating cycles, including:
- Ramp-up rates: How quickly the furnace heats to the target temperature.
- Hold times (or soaks): How long the furnace stays at the target temperature.
- Cooling periods: The rate at which the furnace is allowed to cool down.
This level of automation is essential for sophisticated heat treatments and ensuring that each sample undergoes the exact same thermal profile.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace involves balancing performance with cost and practicality. Simply choosing the model with the highest temperature is often a mistake.
The Cost of Higher Temperatures
As the maximum operating temperature increases, so does the cost. Furnaces capable of reaching 1700°C or higher require more exotic (and expensive) heating elements and more advanced insulation materials. They also consume significantly more energy.
Overlooking the Operating Range
A furnace designed for very high temperatures (e.g., 1800°C) may not offer fine control or stability at lower temperatures (e.g., 300°C). Always verify that the furnace performs well across the entire range you need, not just at its peak.
Chamber Size and Heating Dynamics
While a secondary consideration, chamber size is linked to temperature performance. A larger chamber will take longer to heat up and can have a harder time maintaining perfect temperature uniformity from corner to corner. Ensure the chamber is large enough for your samples, but not excessively so.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your primary process as your guide to narrow down the options and make a confident selection.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature sintering or ashing: Prioritize furnaces with a high maximum temperature (1200°C to 1800°C) and robust construction.
- If your primary focus is heat treatment, tempering, or annealing: Focus on furnaces with excellent temperature stability and programmable controls in the low-to-mid range (up to 1200°C).
- If your primary focus is precise lab research or material testing: Select a furnace with a versatile range and a highly accurate, programmable controller to ensure absolute repeatability across experiments.
By matching the furnace's temperature capabilities to your specific process, you build the foundation for accurate and successful work.
Summary Table:
| Application | Recommended Temperature Range | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Sintering, Ashing | 1200°C to 1800°C | High max temperature, robust construction |
| Heat Treatment, Annealing | Up to 1200°C | Excellent stability, programmable controls |
| Lab Research, Material Testing | Varies (e.g., 900°C to 1400°C) | High accuracy, repeatability, precise control |
Upgrade your lab's thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced muffle furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Ensure precise temperature control and protect your materials—contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your research and quality control processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating



















