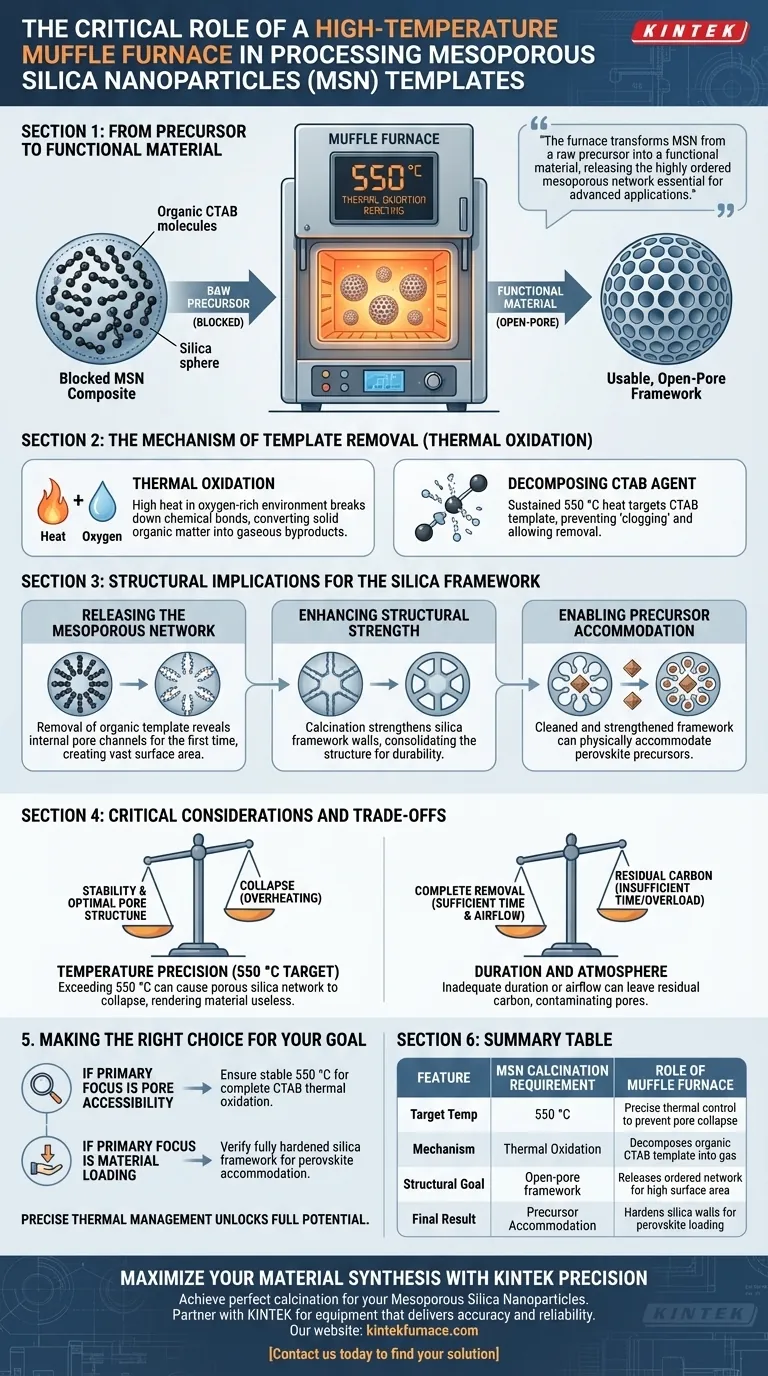
The high-temperature muffle furnace serves as the definitive tool for activating Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (MSN) through calcination. Its primary function is to execute a thermal oxidation reaction at 550 °C, which completely decomposes the organic template agent (CTAB) trapped within the material. This process is the singular step that transitions the silica from a blocked composite into a usable, open-pore framework.
The muffle furnace transforms MSN from a raw precursor into a functional material. By utilizing precise thermal oxidation to eliminate organic blockages, it releases the highly ordered mesoporous network essential for advanced chemical applications.
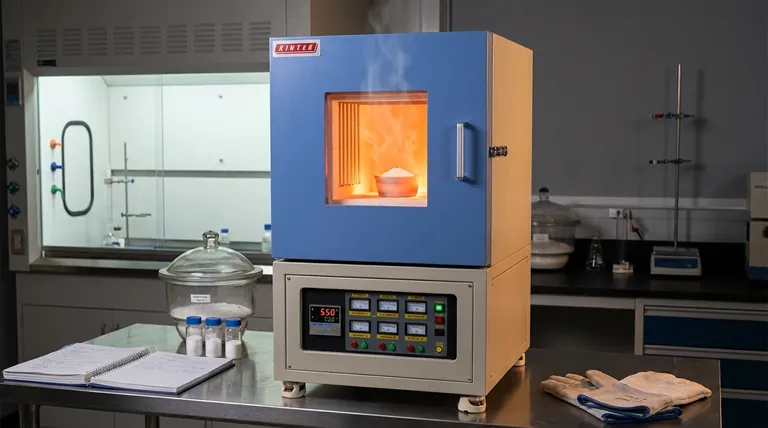

The Mechanism of Template Removal
The core function of the muffle furnace in this context is to act as a controlled reactor for decomposition. It does not merely dry the sample; it chemically alters it through heat.
Thermal Oxidation
The furnace facilitates thermal oxidation, a process where high heat in an oxygen-rich environment breaks down chemical bonds.
This reaction is critical for converting solid organic matter into gaseous byproducts that can escape the silica matrix.
Decomposing the CTAB Agent
The specific target of this heat treatment is CTAB (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide), the organic template agent used to shape the nanoparticles during synthesis.
Without the furnace's sustained 550 °C heat, the CTAB would remain inside the particles, effectively "clogging" the system.
Structural Implications for the Silica Framework
Beyond cleaning the material, the high-temperature treatment physically alters the silica's architecture to ensure it is robust enough for use.
Releasing the Mesoporous Network
The removal of the organic template reveals the internal pore channels for the first time.
This step "releases" the highly ordered network, creating the vast surface area that defines the utility of mesoporous silica.
Enhancing Structural Strength
Calcination strengthens the walls of the silica framework.
By consolidating the silica structure, the furnace ensures the nanoparticles have the structural strength required to withstand subsequent processing steps.
Enabling Precursor Accommodation
A cleaned and strengthened framework is a prerequisite for downstream applications.
Specifically, this process prepares the MSN to physically accommodate perovskite precursors, which would be impossible if the pores were still blocked by the organic template.
Critical Considerations and Trade-offs
While the muffle furnace is essential, the process requires strict adherence to parameters to avoid damaging the delicate nanostructure.
Temperature Precision vs. Structural Collapse
The target temperature of 550 °C is specific to this material's stability.
Exceeding this temperature can cause the porous silica network to collapse, reducing the surface area and rendering the material useless.
Duration and Atmosphere
The oxidation process relies on sufficient airflow and time.
If the furnace is overloaded or the duration is too short, residual carbon from the CTAB may remain, contaminating the pores and interfering with future chemical loading.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your MSN processing, you must focus on the specific outcome of the calcination phase.
- If your primary focus is Pore Accessibility: Ensure the furnace maintains a stable 550 °C to guarantee the complete thermal oxidation and removal of the CTAB template.
- If your primary focus is Material Loading: Verify that the calcination cycle has fully hardened the silica framework so it can successfully accommodate perovskite precursors without degrading.
Precise thermal management is the key to unlocking the full potential of mesoporous materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | MSN Calcination Requirement | Role of Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Target Temp | 550 °C | Precise thermal control to prevent pore collapse |
| Mechanism | Thermal Oxidation | Decomposes organic CTAB template into gas |
| Structural Goal | Open-pore framework | Releases ordered network for high surface area |
| Final Result | Precursor Accommodation | Hardens silica walls for perovskite loading |
Maximize Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Ready to achieve perfect calcination for your Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles? Contact us today to find your solution.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your laboratory's unique high-temperature processing needs. Our furnaces ensure the precise thermal oxidation and structural integrity required to transform raw precursors into advanced functional materials. Partner with KINTEK for equipment that delivers the accuracy and reliability your research demands.
Visual Guide
References
- Jiaze Wu, Kai Huang. Generative Synthesis of Highly Stable Perovskite Nanocrystals via Mesoporous Silica for Full‐Spectrum White LED. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202507240
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What personal protective equipment (PPE) is recommended for benchtop furnace use? Ensure Lab Safety with Proper Gear
- Why is the temperature control precision of a box-type muffle furnace critical when converting precursors to ZnCo2O4?
- What are some typical applications of muffle furnaces? Essential Uses in Labs and Industry
- How do high-temperature muffle furnaces and ceramic crucibles ensure accuracy? Achieve Precise Alloy Oxidation Data
- What is the role of a laboratory high-temperature furnace in LLZO crystal phase regulation? Optimize Li-Ion Electrolytes
- What heating systems can Muffle Furnaces use? Choose Electric or Gas for Optimal Performance
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in preparing expanded graphite? Achieve High-Efficiency PCM Carriers
- What role do muffle furnaces play in materials research? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment for Your Lab



















