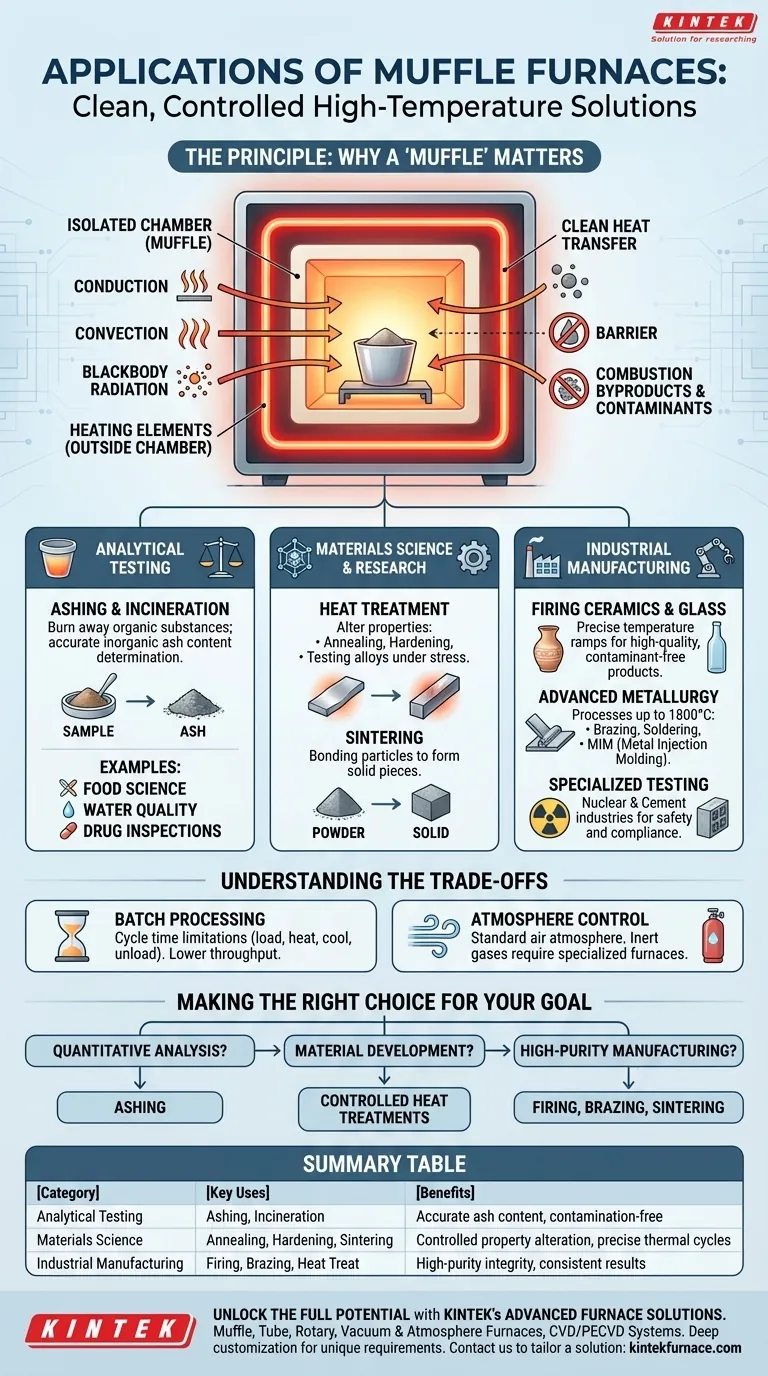
In essence, a muffle furnace is used for any high-temperature process that requires a clean, controlled environment free from the contaminants of fuel combustion. Its most common applications fall into three broad categories: analytical testing (like determining the ash content of a sample), materials science (such as heat-treating metals), and industrial manufacturing (including the firing of ceramics and glass).
The core value of a muffle furnace is its design. It uses an isolated chamber—the "muffle"—to separate the material being heated from the heating elements and any combustion byproducts. This ensures the sample's integrity is maintained, which is critical for both precise analysis and high-purity manufacturing.

The Principle: Why a "Muffle" Matters
Before examining the applications, it's crucial to understand what makes a muffle furnace unique. The design itself is the key to its utility.
The Isolated Heating Chamber
A muffle furnace contains a sealed inner chamber, or "muffle," typically made of a high-temperature ceramic. This chamber holds the sample.
The heating elements are located outside this chamber. This design completely isolates the sample from any byproducts of combustion or direct contact with the heat source.
Clean Heat Transfer
Since the sample is isolated, heat is transferred indirectly through conduction, convection, and blackbody radiation from the chamber walls.
This process guarantees that no soot, gases, or other chemical contaminants from a fuel source can react with or spoil the sample, ensuring a pure and controlled heating environment.
Core Applications in Analysis and Research
The furnace's ability to provide clean heat makes it indispensable for laboratory work where accuracy is paramount.
Ashing and Incineration
This is one of the most common uses. A sample is heated to a high temperature to completely burn away all organic substances.
Because the environment is clean, the remaining inorganic material, or ash, can be weighed accurately. This is critical for determining the ash content in food science, water quality analysis, and drug inspections.
Materials Science and Research
Researchers use muffle furnaces to alter the properties of materials through controlled heating and cooling cycles.
This includes processes like annealing (softening metal), hardening, and testing how new alloys or composites behave under extreme thermal stress.
Applications in Manufacturing and Industry
In industrial settings, consistency and product purity are key drivers for using muffle furnaces.
Firing Ceramics, Glass, and Enamels
Manufacturing high-quality ceramics and glass requires precise temperature ramps and a contaminant-free atmosphere to prevent discoloration or structural defects.
Creating enamel coatings also relies on this clean environment to ensure the coating fuses to the substrate correctly without impurities.
Advanced Metallurgy
The metallurgical industry uses muffle furnaces for sophisticated processes that require temperatures up to 1800°C (3272°F).
Key applications include heat treatment of metals like steel and copper, brazing and soldering components together, and advanced processes like sintering and debinding for metal injection molding (MIM).
Specialized Industrial Testing
Industries like cement production and the nuclear sector use muffle furnaces to process or test samples at very high temperatures. In these fields, preventing sample contamination is essential for safety, quality control, and regulatory compliance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, muffle furnaces are not the right tool for every heating task. Understanding their limitations is key to using them effectively.
Batch Processing and Cycle Time
Muffle furnaces are inherently batch-process tools. You load a sample, run the heating cycle, and then unload it. This limits throughput compared to continuous-style furnaces.
Furthermore, heating up to a high temperature and cooling down can take a significant amount of time, which impacts overall productivity.
Atmosphere Control
A standard muffle furnace operates with a normal air atmosphere inside the chamber.
If a process requires a specific atmosphere (such as inert argon or nitrogen to prevent oxidation), a more specialized and expensive vacuum or atmosphere-controlled furnace is necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge, consider what you need to achieve with high heat.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis: Use a muffle furnace for ashing to reliably determine the inorganic content of any organic material.
- If your primary focus is material development: Leverage the furnace for controlled heat treatments to test, alter, and perfect the properties of metals, ceramics, or composites.
- If your primary focus is high-purity manufacturing: Employ a muffle furnace for processes like firing ceramics, brazing, or sintering where product integrity cannot be compromised.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is the definitive tool whenever a high-temperature process demands absolute material purity and control.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Uses | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Analytical Testing | Ashing, Incineration | Accurate ash content determination, contamination-free environment |
| Materials Science | Annealing, Hardening, Sintering | Controlled material property alteration, precise thermal cycles |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Firing Ceramics, Glass, Brazing | High-purity product integrity, consistent results |
Unlock the full potential of your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions!
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Whether you're in analytical testing, materials science, or industrial manufacturing, our furnaces ensure clean, controlled environments for superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your specific needs and enhance your efficiency and precision!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















