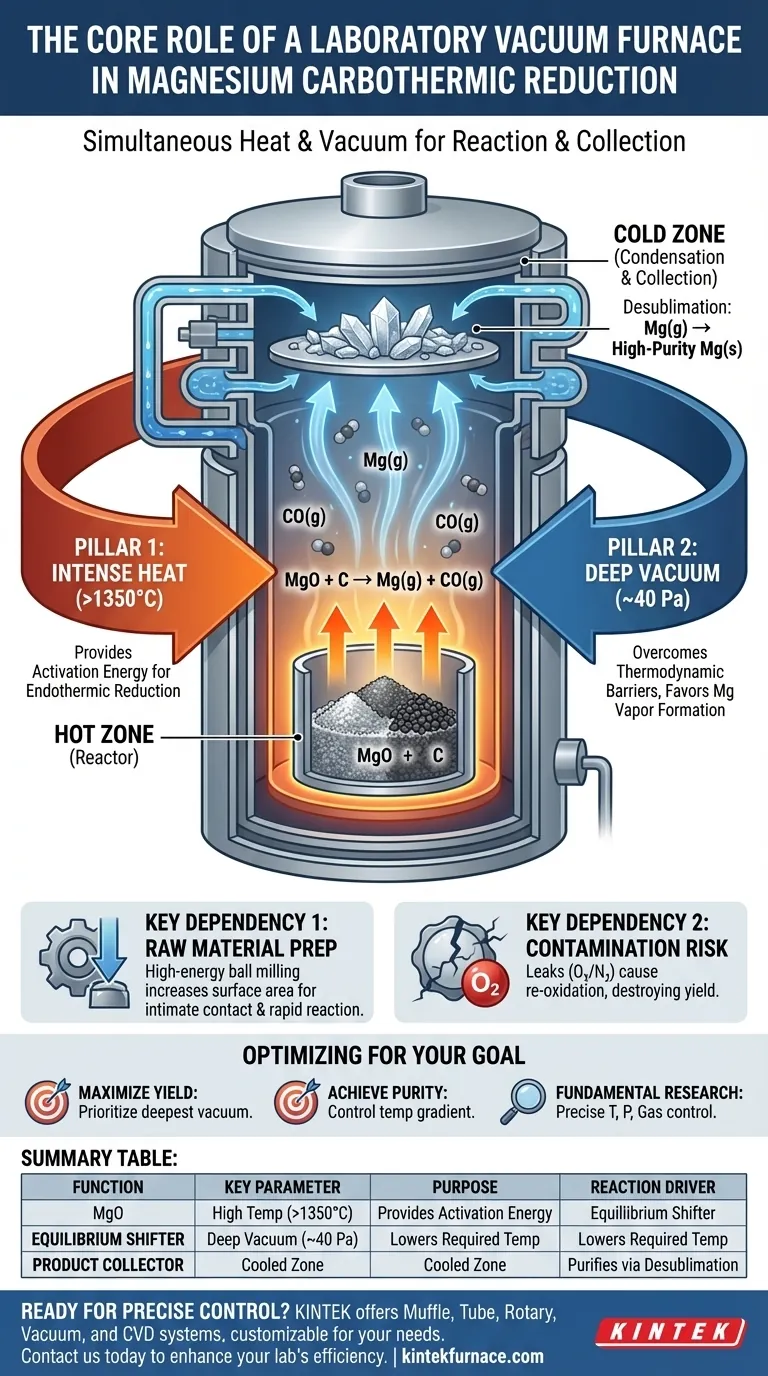
At its core, the laboratory vacuum furnace's role is to simultaneously create two extreme and non-negotiable conditions: the intense heat needed to initiate the reaction and the deep vacuum required to make the reaction thermodynamically favorable and allow the product to form. It is both the reactor and the collection vessel in one integrated system.
The vacuum furnace is not merely a high-temperature oven. It is an environment-engineering tool that fundamentally alters reaction thermodynamics, making the carbothermic reduction of magnesium oxide feasible at manageable temperatures while also serving as the apparatus for purifying and collecting the final product.

The Two Pillars: High Temperature and Deep Vacuum
The success of the carbothermic reduction process hinges entirely on the furnace's ability to precisely control two key physical parameters. These are not independent variables; they work together to drive the reaction forward.
Providing Activation Energy with Heat
The chemical reduction of magnesium oxide (MgO) with carbon is an endothermic process. It requires a significant input of energy to break strong chemical bonds.
The furnace must heat the reactants to temperatures exceeding 1350°C to provide this necessary activation energy and get the reaction started at a meaningful rate.
Overcoming Thermodynamic Barriers with Vacuum
This is the most critical function of the furnace. At atmospheric pressure, the reaction MgO + C → Mg(g) + CO(g) requires impractically high temperatures. A vacuum changes this entire equation.
By reducing the pressure inside the furnace to a high vacuum (e.g., 40 Pa), the system's equilibrium is shifted. According to Le Chatelier's principle, lowering the pressure favors the side of the reaction that produces more moles of gas. Here, it strongly favors the formation of gaseous magnesium and carbon monoxide.
This vacuum environment significantly lowers the required reaction temperature, making the entire process more energy-efficient and achievable in a laboratory setting. It also creates a clear, unobstructed path for the magnesium vapor to travel.
More Than a Reactor: The Furnace as a Distillation System
The furnace’s design serves a dual purpose. It's not just for creating the product but also for separating and purifying it in the same process step.
The Hot Zone: Generating Magnesium Vapor
Deep inside the furnace, a crucible holds the finely-milled mixture of magnesium oxide and a carbon source. This is the "hot zone," where the high temperature and vacuum drive the reduction reaction, converting the solid reactants into magnesium vapor.
The Cold Zone: Condensation and Collection
The furnace is engineered with cooled surfaces, typically a water-cooled lid and the internal furnace body. As the hot magnesium vapor rises from the crucible, it makes contact with these surfaces.
Because the temperature of these surfaces is well below the freezing point of magnesium, the vapor undergoes desublimation, rapidly solidifying directly from a gas into a high-purity solid. This process efficiently separates the pure magnesium from any unreacted materials or impurities left in the crucible.
Understanding the Key Dependencies
The furnace does not operate in isolation. Its effectiveness is directly tied to other parts of the process and requires careful management of its operating conditions.
The Importance of Raw Material Preparation
The reaction inside the furnace can only be as efficient as the materials put into it. Pre-processing the reactants, often through high-energy ball milling, is a critical preparatory step.
This milling process dramatically increases the surface area and ensures intimate contact between the magnesium oxide and carbon particles, which is foundational for a rapid and complete reaction once inside the furnace.
The Risk of Contamination
Maintaining vacuum integrity is paramount. Any leaks that allow air (specifically oxygen or nitrogen) into the chamber can be catastrophic to the process.
Oxygen will instantly re-oxidize the valuable magnesium vapor, turning it back into magnesium oxide and destroying the product yield.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The precise operation of the vacuum furnace depends on the desired outcome of the experiment or production run.
- If your primary focus is maximizing yield: Prioritize maintaining the deepest and most stable vacuum possible to continuously drive the reaction equilibrium toward the products.
- If your primary focus is achieving high purity: Carefully control the temperature gradient between the crucible (hot zone) and the condensation surfaces (cold zone) to manage the rate of desublimation.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: Utilize precise controls for temperature, pressure, and any inert gas flow to systematically study evaporation and condensation behaviors under different conditions.
Ultimately, the vacuum furnace is the indispensable tool that manipulates fundamental principles of physics and chemistry to produce magnesium through this advanced method.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Function | Key Parameter | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Reaction Driver | High Temperature (>1350°C) | Provides activation energy for the endothermic reduction reaction. |
| Equilibrium Shifter | Deep Vacuum (~40 Pa) | Lowers required temperature by favoring magnesium vapor formation. |
| Product Collector | Cooled Condensation Zone | Purifies magnesium via desublimation from vapor to solid. |
Ready to Achieve Precise Control in Your High-Temperature Processes?
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, including specialized lab vacuum furnaces ideal for demanding applications like carbothermic reduction. All our systems are customizable to meet your unique research and production needs.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and ensure high-purity results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today



















