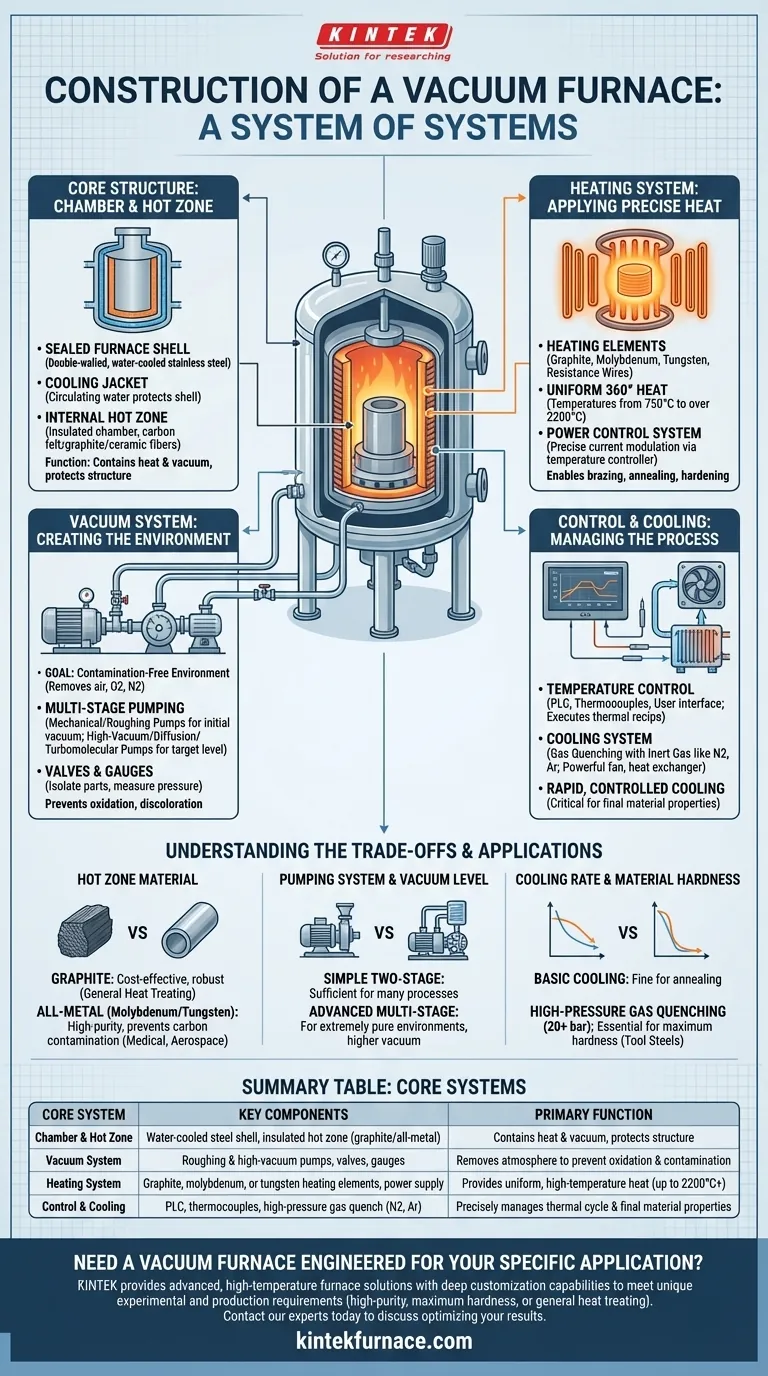
At its core, a vacuum furnace is an assembly of several critical, integrated systems. These are the sealed furnace chamber (the vessel), an internal heating system, a vacuum system to remove the atmosphere, a temperature control system to manage the thermal cycle, and a cooling system to finalize the material's properties.
A vacuum furnace is best understood not as a simple oven, but as a system of systems. Its primary function is to create a highly controlled, contamination-free environment by first removing atmospheric gases and then applying precise thermal energy.
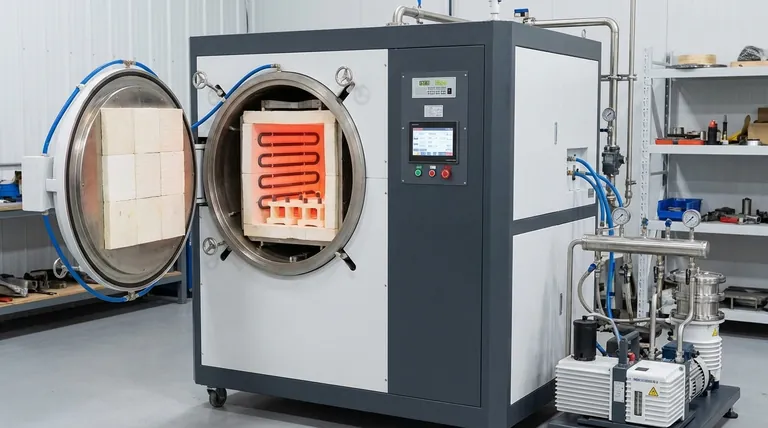

The Core Structure: Chamber and Hot Zone
A vacuum furnace's physical structure is designed for containment—both of the vacuum and the intense heat.
The Sealed Furnace Shell
The outer body, often called the vacuum chamber or vessel, is the primary barrier to the outside atmosphere. It is typically a double-walled structure fabricated from high-strength or stainless steel.
Water circulates within these double walls, forming a cooling jacket. This vital feature keeps the exterior of the furnace shell cool and protects seals, instrumentation, and the structural integrity of the vessel from the extreme internal temperatures.
The Internal Hot Zone
Inside the cooled vessel sits the hot zone. This is the insulated chamber where the heating actually occurs. Its purpose is to contain the thermal energy and direct it efficiently toward the workpiece.
The hot zone's insulation is made from materials like high-grade carbon felt, graphite paper, or ceramic fibers. This insulation prevents the immense heat from reaching and damaging the water-cooled furnace shell.
Creating the Vacuum: The Pumping System
The vacuum system is what differentiates a vacuum furnace from any other type of furnace. Its sole purpose is to remove air and other gases from the chamber before and during the heating process.
The Goal: A Contamination-Free Environment
By removing atmospheric gases—primarily oxygen and nitrogen—the furnace prevents oxidation, discoloration, and other surface reactions that would otherwise occur at high temperatures. This allows for clean, bright processing of metals and other materials.
The Pumping Mechanism
Creating a high vacuum is a multi-stage process. The system typically consists of:
- Mechanical Pumps (Roughing Pumps): These pumps do the initial work, removing the vast majority of air from the chamber to achieve a "rough" vacuum.
- High-Vacuum Pumps (Diffusion or Turbomolecular Pumps): Once the roughing pump has done its job, a secondary pump takes over to remove the remaining molecules and achieve the target high-vacuum level.
- Valves and Gauges: A series of valves isolates different parts of the system, while vacuum gauges provide the critical measurement and feedback for process control.
Applying Heat: The Heating System
The heating system generates the thermal energy required for processes like brazing, annealing, or hardening.
Heating Elements
Heating elements are positioned within the hot zone to provide uniform, 360-degree heat to the workload. The material used for these elements depends on the maximum required temperature and the chemical environment.
Common materials include graphite, molybdenum, tungsten, or specialized resistance wires. These can achieve temperatures ranging from 750°C to over 2200°C (1382°F to 3992°F).
The Power Control System
These elements are powered by a dedicated power supply system. This system, governed by the main temperature controller, precisely modulates the electrical current to the elements to control the heating rate and maintain a stable temperature.
Managing the Process: Control and Cooling
The control and cooling systems are responsible for executing the desired thermal profile and achieving the final material properties.
The Temperature Control System
This is the brain of the furnace. It consists of thermocouples (temperature sensors), a programmable logic controller (PLC), and a user interface. It executes the pre-programmed recipe, controlling heating rates, holding times (soaks), and the initiation of the cooling cycle.
The Cooling System
Controlled cooling is just as important as heating. A modern vacuum furnace uses a gas quenching system for rapid cooling.
After the heating cycle, the chamber is backfilled under pressure with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon. A powerful fan circulates this gas through the hot zone and over a heat exchanger (typically water-cooled), rapidly and uniformly removing heat from the workpiece.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The specific construction of a furnace involves choices that directly impact its performance, cost, and suitability for certain applications.
Graphite vs. All-Metal Hot Zones
A furnace with a graphite hot zone (graphite elements and carbon-felt insulation) is a robust, cost-effective workhorse for most heat-treating applications.
However, for extremely sensitive or high-purity applications like medical implants or aerospace components, an all-metal hot zone (using molybdenum or tungsten) is required. This construction prevents any possibility of carbon transfer from the furnace elements to the workpiece.
Pumping System and Vacuum Level
The level of vacuum required dictates the complexity of the pumping system. A simple two-stage system is sufficient for many processes. However, applications requiring an extremely pure environment will need a more advanced and expensive multi-stage system with turbomolecular or diffusion pumps to achieve a higher vacuum.
Cooling Rate and Material Hardness
The speed of the cooling process is a critical variable. A furnace with a basic cooling system is fine for annealing. But for hardening processes that require specific metallurgical structures, a high-pressure gas quenching system (20 bar or higher) is essential for achieving the necessary cooling rates.
Choosing the Right Construction for Your Application
The ideal furnace construction is dictated entirely by your end goal.
- If your primary focus is general heat treating (annealing, stress relieving): A standard furnace with a graphite hot zone and a basic two-stage pumping system is a reliable and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing (medical, aerospace): An all-metal hot zone is non-negotiable to prevent carbon contamination, and a high-vacuum pumping system is critical.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum hardness (tool steels): The construction must include a high-pressure gas quenching system capable of rapid, controlled cooling.
Understanding how these core systems interact is the key to selecting or operating a vacuum furnace that precisely meets your material processing goals.
Summary Table:
| Core System | Key Components | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Chamber & Hot Zone | Water-cooled steel shell, insulated hot zone (graphite/all-metal) | Contains heat & vacuum, protects structure |
| Vacuum System | Roughing & high-vacuum pumps, valves, gauges | Removes atmosphere to prevent oxidation & contamination |
| Heating System | Graphite, molybdenum, or tungsten heating elements, power supply | Provides uniform, high-temperature heat (up to 2200°C+) |
| Control & Cooling | PLC, thermocouples, high-pressure gas quench (N2, Ar) | Precisely manages thermal cycle & final material properties |
Need a Vacuum Furnace Engineered for Your Specific Application?
Whether your priority is high-purity processing for medical/aerospace components, achieving maximum hardness in tool steels, or reliable general heat treating, the precise construction of your furnace is critical.
KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced, high-temperature furnace solutions. Our deep customization capabilities allow us to tailor vacuum furnaces—including the hot zone material, pumping system, and cooling capacity—to meet your unique experimental and production requirements precisely.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can build a vacuum furnace system to optimize your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision



















