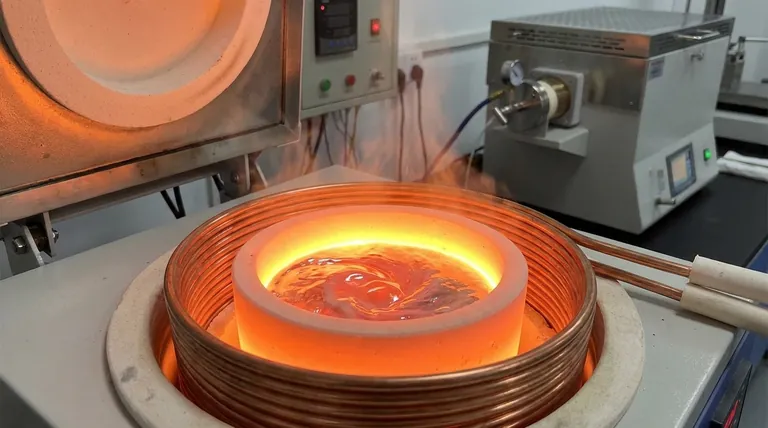
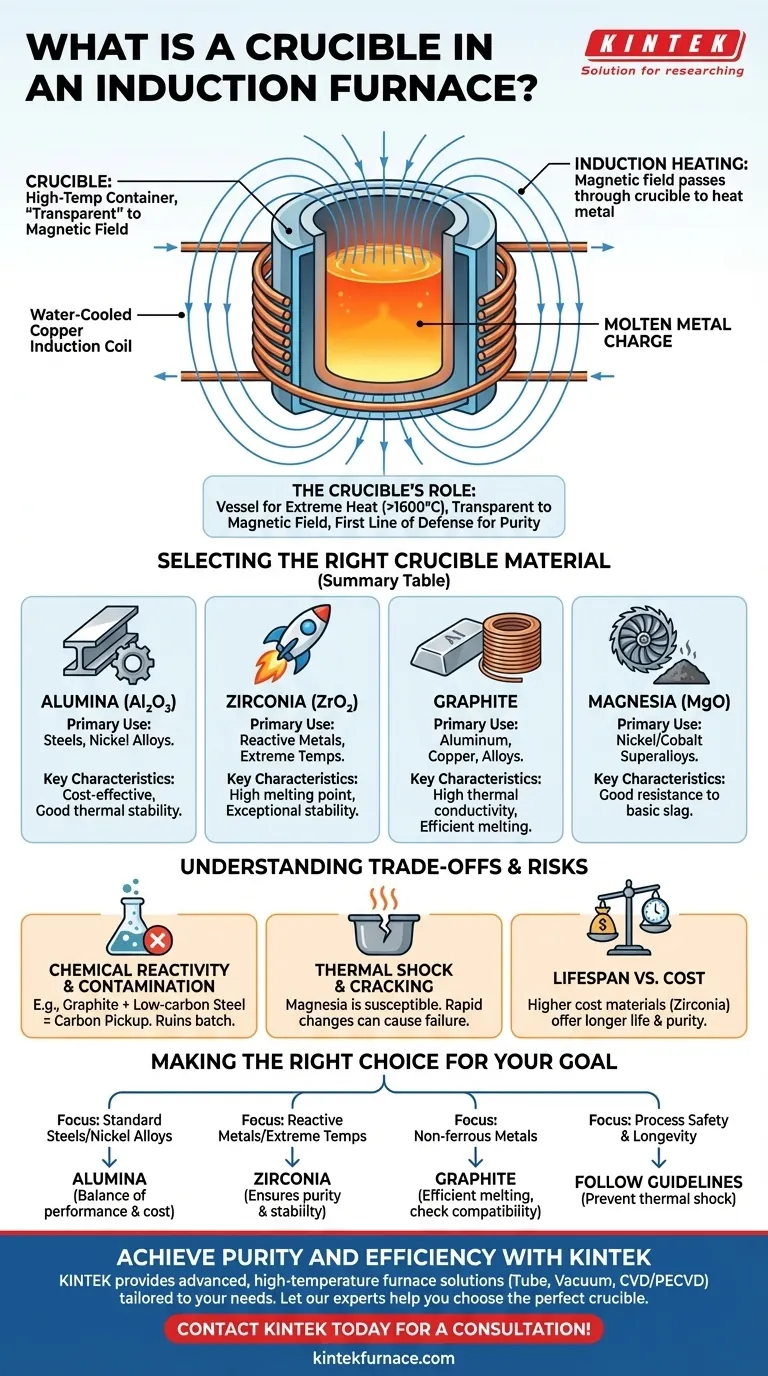
In an induction furnace, the crucible is the high-temperature container that holds the metal charge to be melted. It is designed to withstand extreme thermal stress while remaining "transparent" to the magnetic field that actually heats and melts the metal within it.
The crucible is not merely a container; it is a critical engineered component. The material it is made from directly determines the purity of the final metal, the efficiency of the melt, and the overall safety of the operation.

The Crucible's Role in the Induction Process
An induction furnace works by creating a powerful, alternating electromagnetic field. The crucible's job is to sit within this field and securely contain the metal as it transforms from a solid to a liquid state.
A Vessel for Extreme Heat
The most basic function of the crucible is to hold the metal charge. It must maintain its structural integrity at temperatures that can easily exceed 1600°C (3000°F), depending on the metal being melted.
Transparent to the Magnetic Field
Crucially, the crucible itself is not directly heated by the induction coil. The material must be an electrical insulator that allows the magnetic field to pass through it and induce an electric current directly within the metal charge. This induced current, known as an eddy current, is what generates the intense heat that causes melting.
The First Line of Defense for Purity
The crucible is in direct contact with the molten metal. Therefore, its chemical inertness is paramount. An improperly selected crucible can react with the melt, introducing impurities and compromising the final alloy's chemical composition and mechanical properties.
Selecting the Right Crucible Material
The choice of crucible material is dictated by the metal being melted, the maximum temperature required, and the potential for chemical reactions.
Alumina (Al₂O₃)
Alumina crucibles are an excellent, cost-effective choice for melting most steels and nickel-based alloys. They offer good thermal stability and are relatively inert in these applications.
Zirconia (ZrO₂)
For extremely high-temperature applications or when melting highly reactive metals (like titanium), zirconia is the superior choice. It has a much higher melting point than alumina and is exceptionally stable, though it comes at a significantly higher cost.
Graphite
Graphite is commonly used for melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum, copper, and their alloys. Its high thermal conductivity contributes to an efficient melt.
Magnesia (MgO)
Magnesia crucibles are used for specific applications, often involving the melting of nickel or cobalt-based superalloys. They provide good resistance to basic slag environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Selecting a crucible involves balancing performance, cost, and operational risk. Making the wrong choice can lead to failed melts, damaged equipment, or contaminated products.
Chemical Reactivity and Contamination
This is the most critical risk. For example, using a graphite crucible to melt low-carbon steel is a mistake, as the carbon from the crucible can dissolve into the molten steel, turning it into a high-carbon steel and ruining the batch. This is known as carbon pickup.
Thermal Shock and Cracking
Crucibles must be heated and cooled under controlled conditions. Materials like magnesia are particularly susceptible to thermal shock—cracking caused by rapid temperature changes. A cracked crucible can lead to a catastrophic failure where molten metal escapes the furnace.
Lifespan vs. Cost
More robust materials like zirconia offer longer service life and better purity but have a high initial cost. Less expensive materials may need to be replaced more frequently, increasing downtime and long-term operational costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Base your crucible selection on the specific requirements of the metal you are melting.
- If your primary focus is melting standard steels or nickel alloys: Alumina provides the best balance of performance and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is melting reactive metals at extreme temperatures: Zirconia is the necessary choice for ensuring purity and process stability, despite its higher cost.
- If your primary focus is melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum or copper: Graphite is the industry standard for efficient melting, but always verify its compatibility to avoid contamination.
- If your primary focus is process safety and longevity: Always follow the manufacturer's guidelines for heating cycles to prevent thermal shock and premature failure.
Choosing the right crucible is the foundational decision that ensures the safety, efficiency, and quality of your entire induction melting operation.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Material | Primary Use | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | Steels, Nickel Alloys | Cost-effective, good thermal stability |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | Reactive Metals, Extreme Temperatures | High melting point, exceptional stability |
| Graphite | Aluminum, Copper, Alloys | High thermal conductivity, efficient melting |
| Magnesia (MgO) | Nickel/Cobalt Superalloys | Good resistance to basic slag |
Achieve Purity and Efficiency in Your Melting Operations
Selecting the right crucible is the foundation of a successful induction melting process. KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced, high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by deep customization capabilities.
Let our experts help you choose the perfect crucible material to ensure the safety, efficiency, and quality of your operation.
Contact KINTEL today for a consultation and elevate your lab's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs



















