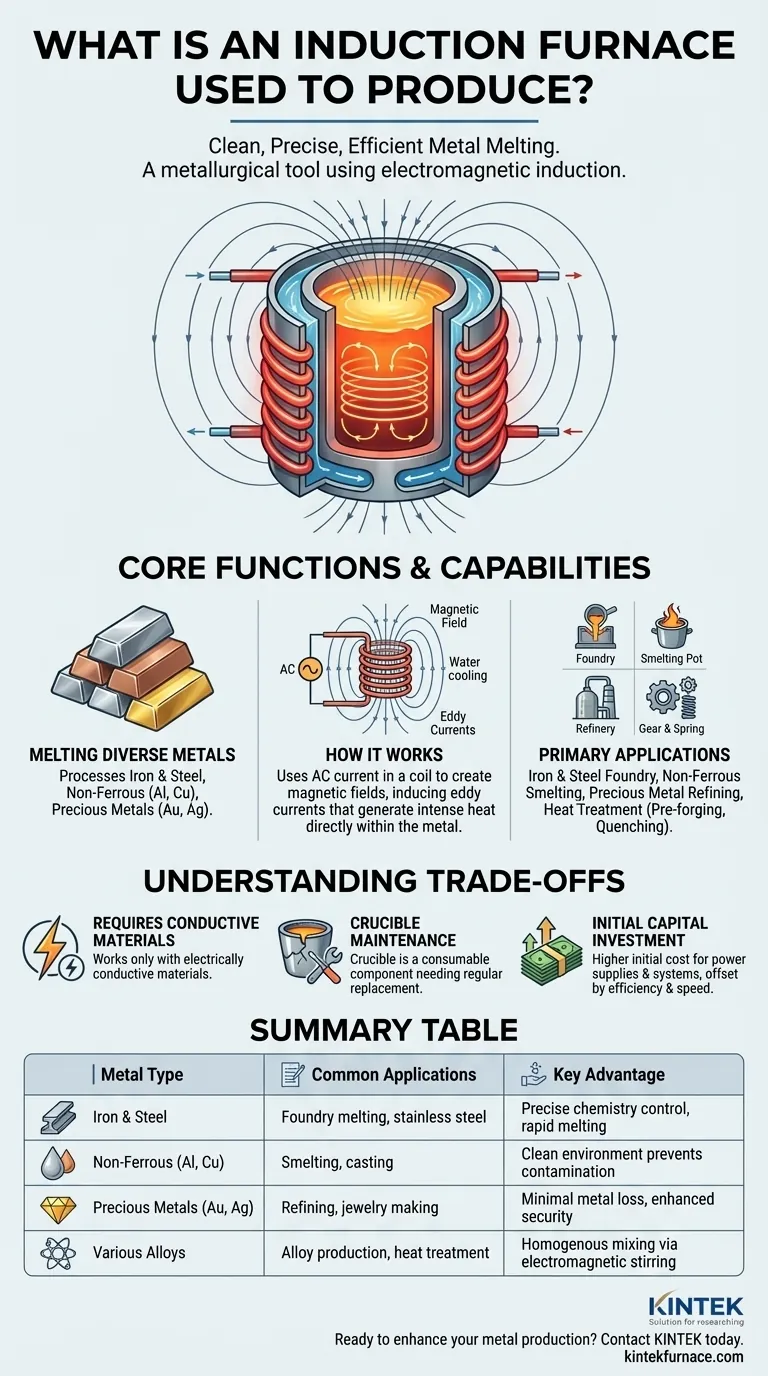
At its core, an induction furnace is used to melt metal. It can process a wide range of materials, including iron and steel, copper, aluminum, and precious metals like gold and silver. The furnace leverages clean, efficient electrical power to turn solid metal into a liquid state for casting, alloying, or further refining.
An induction furnace isn't just a heater; it's a precise metallurgical tool. Its primary function is to melt metals using electromagnetic induction, a process that offers superior control, cleanliness, and material consistency compared to traditional fuel-fired furnaces.
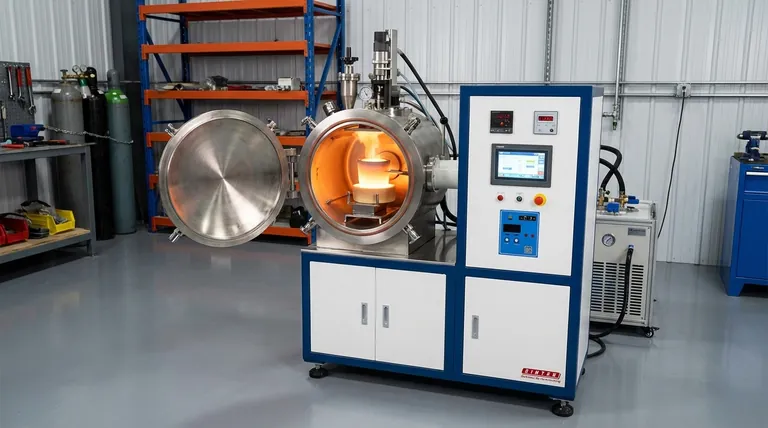

How an Induction Furnace Works: The Principle of Clean Heat
The technology's effectiveness comes from its ability to generate heat directly within the metal itself, without any external flame or heating element making contact. This core principle is what provides its unique advantages.
The Role of the Magnetic Field
An induction furnace uses a water-cooled copper coil through which a high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed. This current generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space within the coil, where the metal to be melted (the "charge") is placed.
Generating Heat Through Eddy Currents
This fluctuating magnetic field penetrates the conductive metal charge and induces electrical currents within it, known as eddy currents. As these currents swirl through the metal, they encounter electrical resistance, which generates immense heat and causes the metal to melt.
The Benefit of Electromagnetic Stirring
A valuable secondary effect of the magnetic field is that it creates a stirring action within the molten metal bath. This natural, hands-off mixing is critical for producing homogenous alloys, ensuring that all added elements are distributed uniformly for a consistent final product.
The Primary Applications of Induction Furnaces
The versatility and control offered by induction technology make it suitable for a wide range of metallurgical tasks, from bulk melting to high-precision work.
Melting Iron and Steel
Induction furnaces are workhorses in foundries for melting iron and producing various grades of steel, including stainless steel. Their speed and ability to control melt chemistry are essential for meeting precise specifications.
Smelting Non-Ferrous Metals
The process is highly effective for melting metals like aluminum and copper. The clean melting environment prevents contamination from combustion byproducts, which is crucial for maintaining the purity and electrical conductivity of these metals.
Refining Precious Metals
For high-value materials like gold and silver, induction heating is the preferred method. The precise temperature control minimizes metal loss through vaporization, and the self-contained process enhances security and accountability.
Beyond Melting: Heat Treatment
Induction heating is also used for applications that don't involve complete melting. This includes pre-forging heating, where a metal billet is brought to a specific temperature before being shaped, and quenching and tempering of steel parts to achieve desired hardness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction technology is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Requirement for Conductive Materials
The heating principle relies on inducing electrical currents within the charge. Therefore, the material being heated must be electrically conductive. This makes induction furnaces unsuitable for melting most non-conductive materials like glass or certain ceramics unless a conductive crucible is used to act as the heating element.
The Lifespan of the Crucible
The furnace is lined with a refractory material, forming a crucible that contains the molten metal. This crucible is exposed to extreme thermal stress and chemical erosion from the melt. It is a consumable component that requires regular inspection and periodic replacement, representing a significant operational cost.
Initial Capital Investment
The high-frequency power supplies, precision-engineered copper coils, and required water-cooling systems make the initial cost of an induction furnace higher than that of a simple fuel-fired furnace. However, this is often offset by higher efficiency, faster melt times, and superior product quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use an induction furnace is driven by the need for quality, speed, and control.
- If your primary focus is high-purity alloys or precious metals: An induction furnace is ideal due to its clean, non-contact heating and ability to operate in a controlled atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is rapid, efficient melting: The direct heating of induction provides faster melt cycles and greater energy efficiency compared to traditional methods.
- If your primary focus is producing homogenous, well-mixed alloys: The natural electromagnetic stirring action ensures a uniform, high-quality final product without mechanical intervention.
Understanding the principle of electromagnetic induction makes it clear why this technology is a cornerstone of modern metallurgy and high-performance material production.
Summary Table:
| Metal Type | Common Applications | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Iron & Steel | Foundry melting, stainless steel production | Precise chemistry control, rapid melting |
| Non-Ferrous (Al, Cu) | Smelting, casting | Clean environment prevents contamination |
| Precious Metals (Au, Ag) | Refining, jewelry making | Minimal metal loss, enhanced security |
| Various Alloys | Alloy production, heat treatment | Homogenous mixing via electromagnetic stirring |
Ready to enhance your metal production with superior melting technology?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced thermal solutions for diverse laboratories and foundries. Our expertise in high-temperature furnace technology, including induction systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique melting and heat treatment requirements.
Whether you are processing precious metals, developing new alloys, or need rapid, efficient melting, we can provide a solution tailored for quality, speed, and control.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss how our induction furnace solutions can benefit your operation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification



















