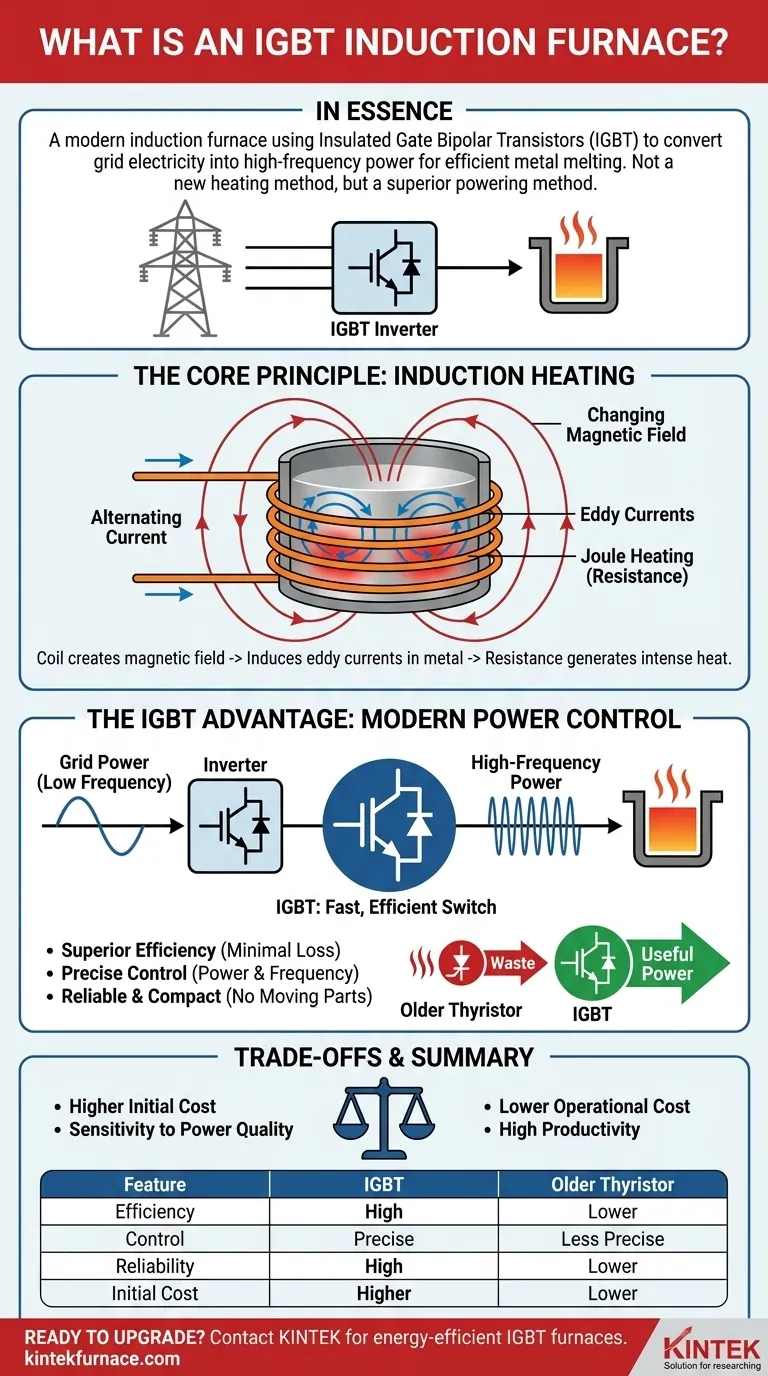
In essence, an IGBT induction furnace is a modern type of induction furnace that uses a specific electronic component—the Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT)—to manage its power supply. Instead of using older, less efficient methods, these furnaces leverage IGBTs to convert standard grid electricity into the high-frequency power needed to melt metal. This results in a more efficient, precise, and reliable heating process.
The term "IGBT" does not describe a new method of heating; it describes a superior method of powering the furnace. Understanding this distinction is key to recognizing that IGBT technology represents a significant leap forward in the efficiency and control of established induction heating principles.
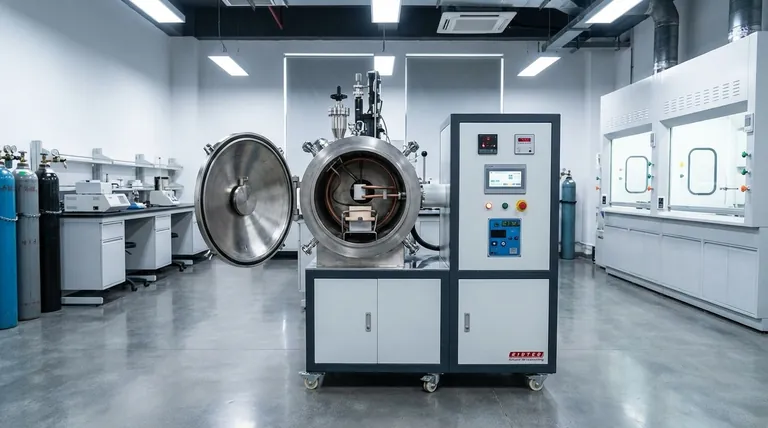

The Core Principle: How Induction Heating Works
To understand the role of the IGBT, we must first understand the fundamental process of induction heating itself. This process relies on basic principles of electromagnetism to generate heat directly within the metal.
The Induction Coil and Magnetic Field
An induction furnace uses a powerful coil of conductive tubing, typically copper. A strong alternating current (AC) is passed through this coil, which generates a rapidly changing and powerful magnetic field in the space within and around the coil.
Inducing Eddy Currents
When a conductive material, such as steel or other metals, is placed inside this magnetic field, the field induces electrical currents within the metal. These looping currents are known as eddy currents.
Resistance and Heat Generation
As these eddy currents flow through the metal, they encounter the material's natural electrical resistance. This resistance causes the material to heat up rapidly and intensely, a principle known as Joule heating. If enough power is applied, this heat is sufficient to melt the metal.
The "IGBT" Advantage: Modernizing Power Control
The magic of an IGBT furnace lies in how it creates and controls the high-frequency alternating current required for this process. This is where the IGBT component becomes critical.
What is an IGBT?
An Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) is a high-power semiconductor device that acts as an extremely fast and efficient electronic switch. Think of it as a digital light switch that can turn on and off thousands of times per second with minimal energy loss.
The Role of the Inverter
The power from the electrical grid is not at the correct frequency for efficient induction heating. The furnace's power supply uses a circuit called an inverter, with IGBTs at its heart, to convert this power. By switching on and off at a precise rate, the IGBTs "chop up" the incoming electricity and re-form it into a high-frequency AC output.
Superior Efficiency and Precision
Older technologies, like thyristor-based systems, were less efficient at this power conversion, wasting significant energy as heat. IGBTs switch with very little loss, meaning more of the electricity drawn from the grid is converted into useful power for melting metal. This speed also allows for exceptionally precise control over the furnace's power and frequency.
Reliability and Compact Design
Compared to legacy motor-generator sets or even older solid-state technologies, IGBT-based power supplies have no moving parts. This makes them far more reliable and significantly smaller, reducing the furnace's overall footprint.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While IGBT technology offers clear advantages, it's important to understand the complete picture.
Higher Initial Cost
Systems built with modern power electronics like IGBTs can have a higher upfront purchase price compared to older designs. However, this cost is often quickly recovered through lower energy consumption and higher productivity.
Sensitivity to Power Quality
Advanced electronic systems can be more sensitive to fluctuations, surges, or "dirty" power from the grid. Proper installation requires adequate circuit protection to ensure the longevity of the IGBT modules.
Complexity of Repair
While highly reliable, troubleshooting a sophisticated IGBT inverter requires specialized knowledge and equipment. Repair often involves replacing an entire module rather than a single, simple component, which can be more expensive if a failure occurs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
When evaluating furnace technology, your decision should align with your primary operational and financial goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum energy efficiency and precise melt control: The superior power conversion and responsiveness of an IGBT furnace is the definitive choice for reducing long-term operational costs.
- If your primary focus is achieving the absolute lowest upfront investment: You might consider an older thyristor-based system, but you must account for its lower efficiency, larger physical footprint, and less precise control.
- If your primary focus is reliability and process repeatability: The solid-state design and digital control of an IGBT system offer a distinct advantage over any older mechanical or analog technology.
Ultimately, choosing an IGBT-based system is an investment in modern, efficient, and highly controllable induction melting technology.
Summary Table:
| Feature | IGBT Induction Furnace | Older Thyristor Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Power Conversion Efficiency | High (Minimal Energy Loss) | Lower (More Energy Wasted as Heat) |
| Temperature & Power Control | Extremely Precise & Responsive | Less Precise |
| Reliability & Footprint | High Reliability, Compact Design | Larger Footprint, More Moving Parts |
| Initial Investment | Higher Upfront Cost | Lower Upfront Cost |
Ready to upgrade your melting process with superior IGBT technology?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides foundries and metalworking facilities with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including IGBT Induction Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique production requirements.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss how our energy-efficient and precise IGBT furnaces can reduce your operational costs and enhance your process control.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification



















