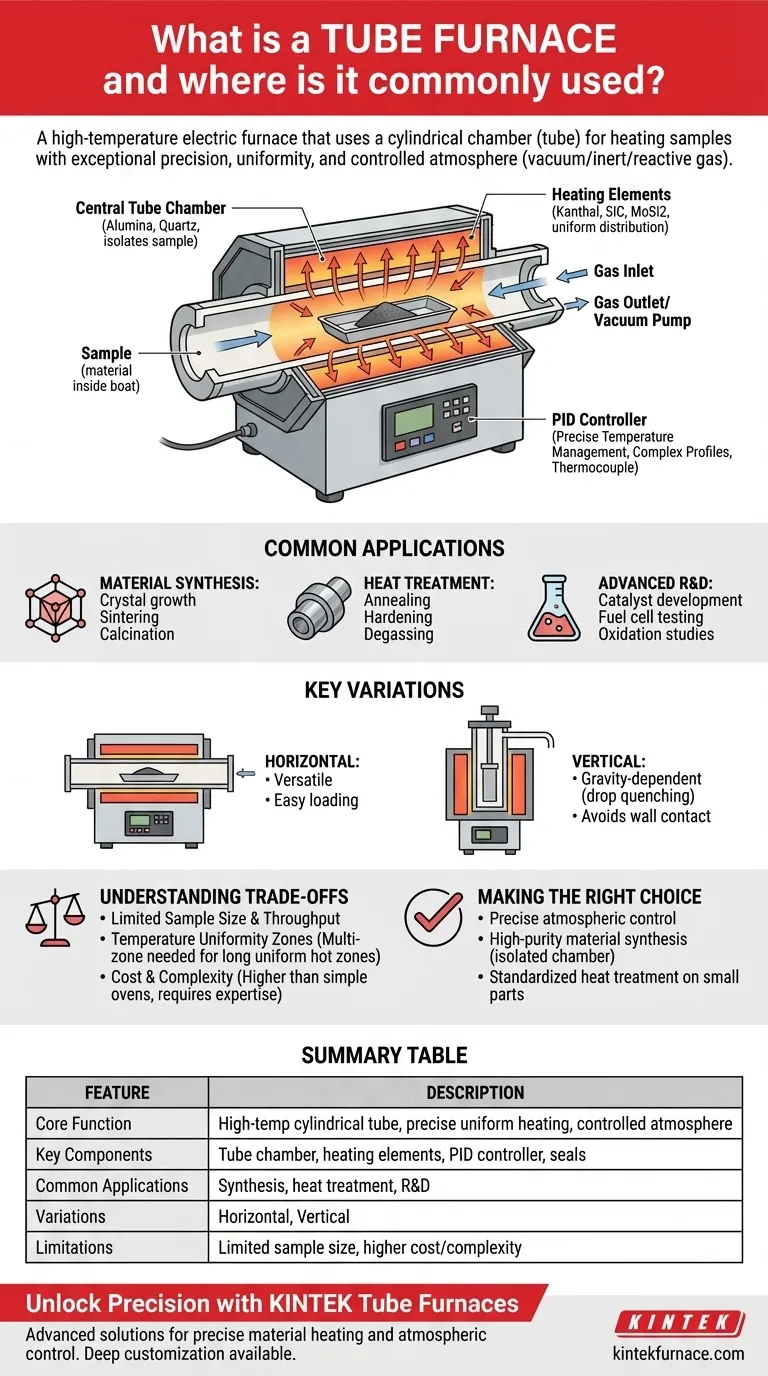
In essence, a tube furnace is a high-temperature electric furnace that uses a cylindrical chamber, or tube, to heat samples with exceptional precision and uniformity. It is a fundamental tool used across research laboratories and industrial settings for processes that demand a highly controlled thermal environment, often in conjunction with a specific atmosphere like a vacuum or inert gas.
The true value of a tube furnace is not just its ability to generate high temperatures, but its capacity to create a contained, repeatable, and precisely controlled environment. This makes it indispensable for developing and testing advanced materials where atmospheric conditions are as critical as the heat itself.
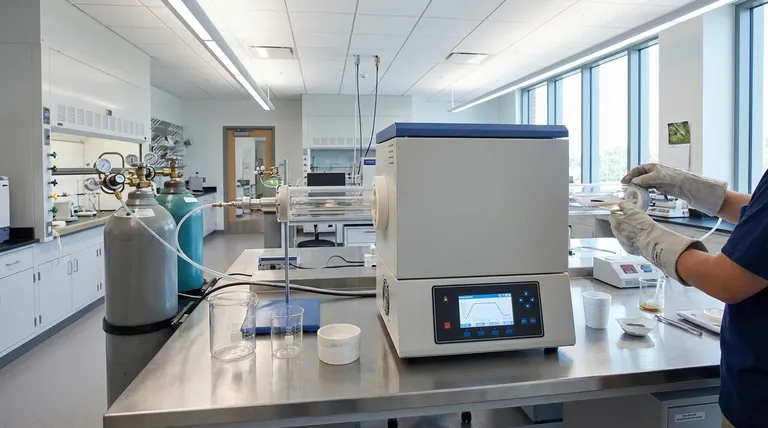

How a Tube Furnace Achieves Precision Control
A tube furnace's design is deceptively simple, but each component is critical for achieving a stable and uniform heating environment.
The Central Tube Chamber
The core of the furnace is a hollow tube, typically made from high-purity ceramic (like alumina) or quartz. This tube contains the sample and isolates it from the heating elements, allowing for the creation of a clean, controlled atmosphere inside.
The choice of tube material depends on the maximum required temperature and chemical compatibility with the sample or process gases.
The Heating Elements
Heating elements, often made of materials like Kanthal (FeCrAl), silicon carbide (SiC), or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2), surround the exterior of the tube. This configuration ensures that heat radiates inward, providing highly uniform temperature distribution along the central heating zone of the tube.
The Control System and Atmosphere
A sophisticated PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller and thermocouple allow for extremely precise temperature management. This system can execute complex heating profiles, with specific ramp rates and dwell times.
Crucially, the ends of the tube can be sealed, allowing operators to control the internal atmosphere. This enables processes under vacuum, in an inert gas (like argon or nitrogen), or in a reactive gas environment, which is impossible in a standard box furnace.
Common Applications Across Industries
The unique capabilities of a tube furnace make it a vital tool for a wide range of high-stakes applications.
Material Synthesis and Processing
Tube furnaces are essential for creating new materials. Common uses include crystal growth, the synthesis and purification of inorganic compounds, sintering of ceramics and powders, and calcination to induce phase changes in materials.
Heat Treatment and Testing
In metallurgy and materials science, tube furnaces are used for precise heat treatments. These include annealing to relieve internal stresses, hardening metals, degassing components for high-vacuum applications, and general thermal testing of material properties.
Advanced Research and Development
The ability to control both temperature and atmosphere makes tube furnaces ideal for R&D. They are used for developing catalysts, testing fuel cell components, performing diffusion and oxidation studies, and for the precise calibration of thermocouples.
Understanding Key Variations
While all tube furnaces share a core design, key structural differences adapt them for specific tasks.
Horizontal Furnaces
This is the most common configuration. Horizontal furnaces are versatile and easy to load, making them a general-purpose workhorse for many labs and processes where the sample can be placed in a boat and pushed into the center.
Vertical Furnaces
In a vertical orientation, samples are loaded from the top or bottom. This design is crucial for processes where gravity is a factor, such as drop quenching (dropping a hot sample into a liquid to cool it rapidly) or to avoid sample contact with the tube walls. They are also favored in certain crystal growth and gas reaction processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, tube furnaces have limitations that are important to recognize.
Sample Size and Throughput
By design, the tubular chamber limits the size and volume of the sample. Tube furnaces are ideal for small, high-value samples but are not suited for large-scale batch production, where a box or conveyor furnace would be more appropriate.
Temperature Uniformity Zones
A standard single-zone furnace is hottest in the center, with temperature dropping off near the ends of the tube. For processes requiring a longer, highly uniform hot zone, more complex and expensive multi-zone furnaces with independent controllers for each section are necessary.
Cost and Complexity
A tube furnace is a piece of precision scientific equipment. The cost, especially for models capable of very high temperatures or multi-zone control, is significantly higher than a simple oven. Proper operation requires an understanding of vacuum systems, gas handling, and thermal profiling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a tube furnace depends entirely on the specific requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is precise atmospheric control: A tube furnace is the definitive choice for heating materials in a vacuum, inert, or reactive gas environment.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material synthesis: The isolated chamber of a tube furnace prevents contamination from heating elements, making it ideal for creating sensitive materials like semiconductors or single crystals.
- If your primary focus is standardized heat treatment on small parts: The excellent temperature uniformity and repeatability make it perfect for developing and executing precise annealing, hardening, or coating protocols.
Ultimately, the tube furnace is the premier tool for anyone who needs to master the relationship between heat, atmosphere, and materials on a small scale.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Function | High-temperature electric furnace with a cylindrical tube for precise, uniform heating in controlled atmospheres. |
| Key Components | Tube chamber (e.g., alumina, quartz), heating elements (e.g., Kanthal, SiC), PID controller, and atmosphere seals. |
| Common Applications | Material synthesis (crystal growth, sintering), heat treatment (annealing, hardening), and R&D (catalyst development, oxidation studies). |
| Variations | Horizontal (versatile, easy loading) and vertical (gravity-dependent processes like drop quenching). |
| Limitations | Limited sample size and throughput; higher cost and complexity for multi-zone or high-temperature models. |
Unlock Precision in Your Laboratory with KINTEK Tube Furnaces
Are you working with advanced materials that demand exact temperature and atmosphere control? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Whether you're involved in material synthesis, heat treatment, or cutting-edge R&D, our tube furnaces offer superior precision, uniformity, and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution to enhance your research and industrial processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















