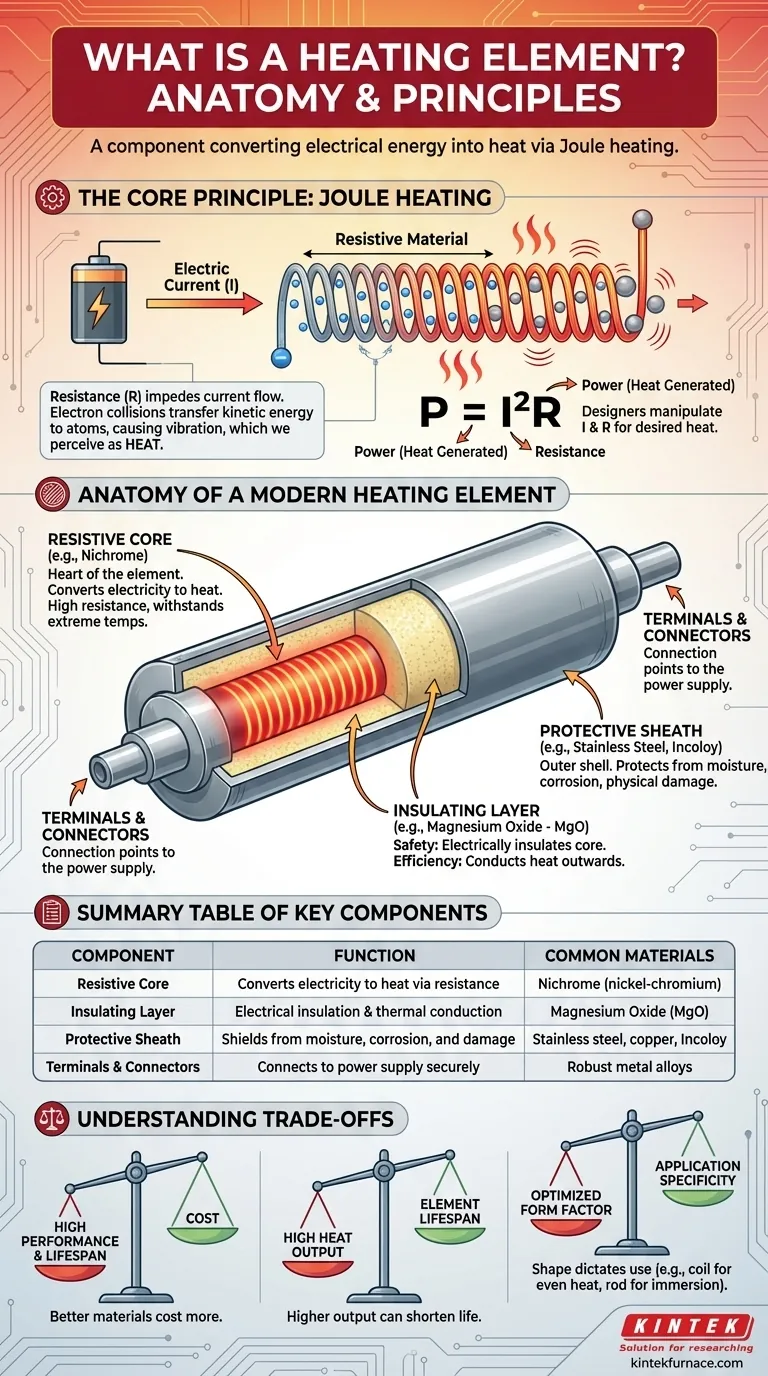
In short, a heating element is a component specifically designed to convert electrical energy into heat. This transformation happens through a principle known as Joule heating, where the material's natural resistance to electrical current generates thermal energy. A complete element is more than just a wire; it's a carefully assembled system including a resistive core, electrical insulation, and a protective outer casing.
The crucial insight is that a heating element is not merely a material that gets hot, but an engineered system. Its effectiveness and safety depend on the precise interplay between its conductive core, its insulating layer, and its protective sheath.

The Core Principle: How Joule Heating Works
To understand a heating element, you must first understand the fundamental process that makes it function. This process, called Joule or resistive heating, is the deliberate use of electrical resistance.
From Electricity to Heat
When an electric current flows through any conductor, the moving electrons collide with the atoms that make up the material. These interactions are not perfectly smooth.
The Role of Resistance
Resistance is the property of a material that impedes the flow of electric current. In a heating element, a material with high resistance is chosen intentionally.
These collisions transfer kinetic energy from the electrons to the atoms, causing the atoms to vibrate more intensely. This increased atomic vibration is what we perceive as heat.
The Formula for Heat Generation
This relationship is described by Joule's first law, often expressed as P = I²R. This means the heat generated (Power, P) is directly proportional to the resistance (R) and the square of the current (I). Designers manipulate these factors to produce the desired amount of heat.
Anatomy of a Modern Heating Element
A functional heating element is a composite structure where each component serves a critical purpose for safety, efficiency, and durability.
The Resistive Core
This is the heart of the element. It is typically a wire or ribbon made from a specialized alloy, like Nichrome (nickel-chromium), which is selected for its high electrical resistance and its ability to withstand extreme temperatures without oxidizing or melting. Its sole job is to get hot when electricity passes through it.
The Insulating Layer
Surrounding the resistive core is a layer of dielectric material. A common choice is Magnesium Oxide (MgO) powder, which is packed tightly around the core. This layer has two vital functions:
- Safety: It electrically insulates the hot core, preventing the current from shorting out to the element's outer casing.
- Efficiency: It is an excellent thermal conductor, ensuring the heat generated in the core is transferred efficiently outwards rather than being lost.
The Protective Sheath
The sheath is the element's outer shell, which encases the core and insulation. It protects the internal components from moisture, corrosion, and physical damage. The sheath material is chosen based on the application, such as stainless steel or copper for water heaters or Incoloy for high-temperature industrial processes.
Terminals and Connectors
These are the practical connection points. They are robust metal leads or terminals that allow the heating element to be securely connected to the main power supply of the appliance or system.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The design of a heating element is a balance of competing factors. Understanding these compromises is key to appreciating why they are engineered for specific tasks.
Material Selection vs. Cost
High-performance alloys that can operate at very high temperatures for thousands of hours are significantly more expensive than simpler materials. The choice of resistive core and sheath is a direct trade-off between the required performance, lifespan, and the final cost of the product.
Heat Output vs. Element Lifespan
Generating more heat requires either pushing more current through the element or using a higher-resistance material. Both of these actions increase the thermal and electrical stress on the components, which can shorten the element's operational life. Aggressive heating cycles can lead to premature failure.
Form Factor vs. Application
The shape of an element—whether it's a straight rod, a coil, or a flat strip—is critical for performance. A coiled element in an oven provides even heat over a large area, while a straight, rigid element is ideal for immersion in a liquid. Using the wrong shape for the job results in inefficient heating and potential hot spots that can damage the element.
How Design Dictates Application
The specific combination of materials, size, and shape determines an element's ideal use case. The final design is always tailored to a specific goal.
- If your primary focus is rapid, high-temperature air heating: The design prioritizes a resistive core with a very high melting point and superior oxidation resistance, often with fins attached to the sheath to radiate heat effectively.
- If your primary focus is uniform surface heating: The design emphasizes the element's form factor, shaping it into a precise coil or pattern to ensure even heat distribution across a plate or surface.
- If your primary focus is safety in a liquid environment: The design centers on a seamless, corrosion-resistant sheath and a high-integrity insulating layer to prevent any electrical leakage into the liquid.
By understanding these individual components, you see the heating element not as a simple part, but as a sophisticated device engineered for precise and reliable thermal control.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Resistive Core | Converts electricity to heat via resistance | Nichrome (nickel-chromium) |
| Insulating Layer | Provides electrical insulation and thermal conduction | Magnesium Oxide (MgO) |
| Protective Sheath | Shields from moisture, corrosion, and damage | Stainless steel, copper, Incoloy |
| Terminals and Connectors | Connects to power supply securely | Robust metal alloys |
Need a custom heating solution for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your thermal processes with reliable, tailored equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan


















