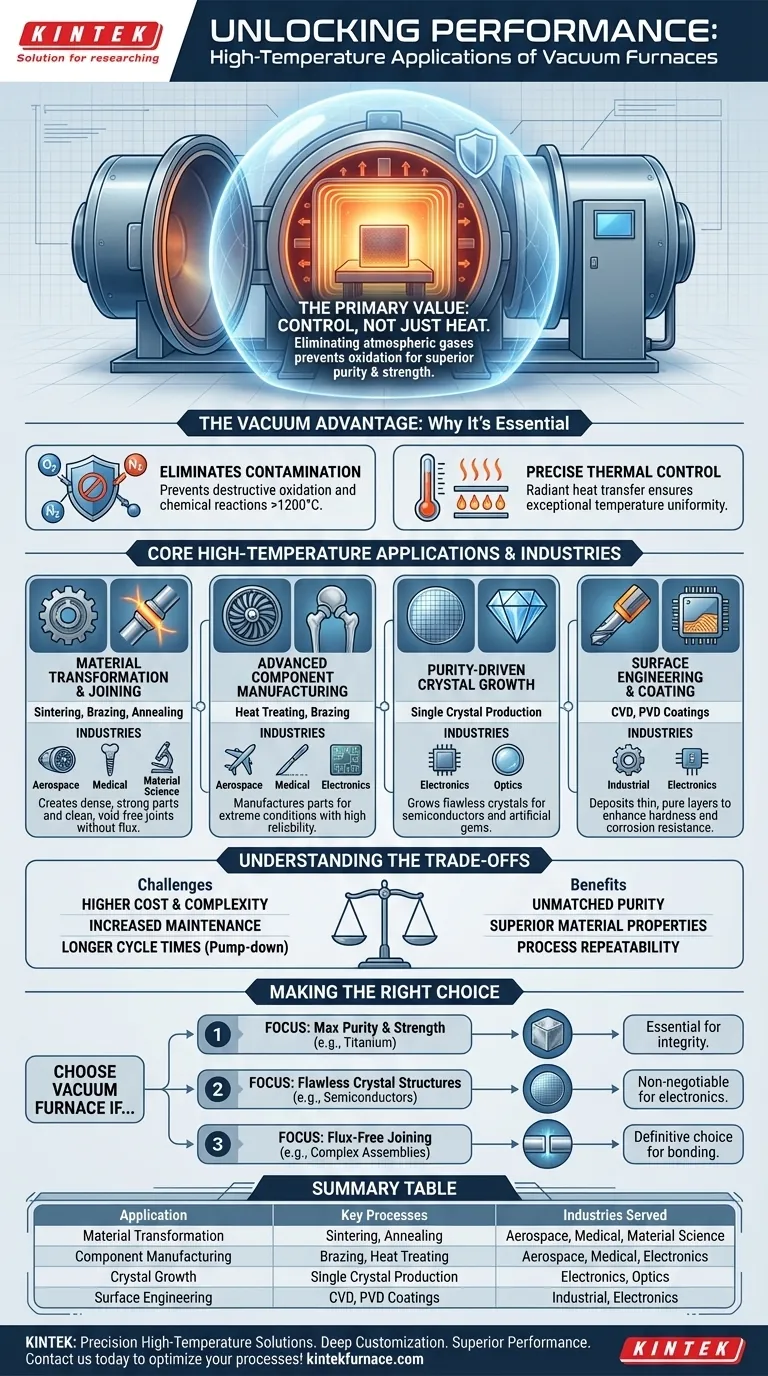
In high-temperature applications, vacuum furnaces are indispensable tools across a range of advanced industries, including aerospace, medical, electronics, and material science. They are used for processes above 1200°C such as brazing titanium alloys for jet engines, sintering biocompatible materials for medical implants, and growing flawless crystals for semiconductors and artificial gems. These operations require an environment free of atmospheric contaminants that would otherwise compromise the material's integrity at extreme temperatures.
The primary value of a vacuum furnace is not just heat, but control. By removing atmospheric gases, it eliminates unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation, enabling the creation of materials with superior purity, strength, and specific properties that are impossible to achieve in a conventional furnace.

The Fundamental Role of the Vacuum Environment
Understanding why a vacuum is necessary is key to appreciating the furnace's capabilities. At high temperatures, materials become highly reactive, and even trace amounts of atmospheric gases can cause catastrophic failures.
Eliminating Contamination and Oxidation
The most critical function of the vacuum is to remove reactive gases, primarily oxygen and nitrogen.
At temperatures exceeding 1200°C, these gases rapidly oxidize and contaminate metals and ceramics, degrading their structural, mechanical, and electrical properties. A vacuum environment prevents these destructive reactions from ever occurring.
Enabling Precise Thermal and Process Control
A vacuum provides a highly predictable and uniform environment for heating and cooling.
Without air to cause unpredictable convection currents, heat is transferred primarily through radiation, allowing for exceptional temperature uniformity across the part. This is coupled with advanced control systems that ensure processes are precise and repeatable.
Facilitating Purity-Dependent Processes
Certain processes are physically impossible in the presence of an atmosphere.
Degassing, the removal of trapped gases from within a material, requires a vacuum to pull the gases out. Similarly, processes like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) require a vacuum so that vaporized coating material can travel unimpeded to the target surface.
Core High-Temperature Applications Breakdown
The unique environment of a vacuum furnace enables several critical manufacturing and research processes. Each leverages the absence of atmosphere to achieve a specific outcome.
Material Transformation and Joining
These processes alter a material's internal structure or join separate components into a single, robust assembly.
- Sintering: Used to fuse powdered materials (metals or ceramics) into a solid mass just below their melting point. The vacuum prevents oxidation of the fine particles, resulting in a dense, strong final part.
- Brazing: Joins materials using a filler metal. Vacuum brazing creates exceptionally clean, strong, and void-free joints without the need for corrosive fluxes, which is critical for aerospace and medical components.
- Annealing: Heats and slowly cools a material to relieve internal stresses and improve ductility. In a vacuum, this can be done without causing surface discoloration or decarburization.
Advanced Component Manufacturing
High-performance industries rely on vacuum furnaces to create parts that can withstand extreme conditions.
This includes manufacturing turbine blades from titanium alloys for aerospace, biocompatible surgical implants for the medical field, and durable silicon carbide bearings for industrial machinery. The material purity achieved is directly linked to component reliability and safety.
Purity-Driven Crystal Growth
The electronics and optics industries require materials with near-perfect atomic structures.
Vacuum furnaces provide the ultra-pure environment necessary for growing large, single crystals used in semiconductor wafers and artificial gems. Any contamination would disrupt the crystal lattice and render the final product useless.
Surface Engineering and Coating
These techniques deposit thin layers of material onto a substrate to enhance its properties, such as hardness or corrosion resistance.
Processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) must be done in a vacuum. This ensures the deposited film is pure and adheres strongly to the substrate without interference from atmospheric particles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not a universal solution. Their advantages come with specific challenges that must be considered.
Higher Initial Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are significantly more expensive and complex than their atmospheric counterparts. The need for vacuum pumps, robust chamber seals, sophisticated gauges, and advanced control systems adds to the initial investment and footprint.
Potentially Longer Cycle Times
The process of pumping the chamber down to the required vacuum level adds time to every cycle. This "pump-down" phase can make the overall processing time longer compared to simply heating a part in an atmospheric furnace.
Increased Maintenance Demands
Maintaining vacuum integrity is a constant operational task. The system is sensitive to leaks, which can compromise the process and require specialized knowledge and equipment to detect and repair. Regular maintenance of pumps and seals is non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting a vacuum furnace depends entirely on whether the process demands an inert environment to ensure the final material's integrity.
- If your primary focus is maximum material purity and strength: A vacuum furnace is essential for processing reactive materials like titanium or advanced ceramics for aerospace and medical applications.
- If your primary focus is creating flawless crystal structures: A vacuum environment is non-negotiable for manufacturing semiconductors, optics, or synthetic gems where purity is paramount.
- If your primary focus is joining complex assemblies without flux: Vacuum brazing is the definitive choice for creating clean, high-strength bonds in critical components.
- If your primary focus is modifying bulk properties without surface reaction: Vacuum annealing or heat treating ensures the material's surface chemistry remains unchanged during the thermal cycle.
Ultimately, choosing a high-temperature vacuum furnace is a decision to prioritize absolute control over the material's environment to unlock its ultimate performance potential.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Processes | Industries Served |
|---|---|---|
| Material Transformation | Sintering, Annealing | Aerospace, Medical, Material Science |
| Component Manufacturing | Brazing, Heat Treating | Aerospace, Medical, Electronics |
| Crystal Growth | Single Crystal Production | Electronics, Optics |
| Surface Engineering | CVD, PVD Coatings | Industrial, Electronics |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with precision high-temperature solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced vacuum furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs, delivering superior purity, strength, and performance for industries like aerospace, medical, and electronics. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Why must sintering equipment maintain a high vacuum for high-entropy carbides? Ensure Phase Purity and Peak Density
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace for rare earth copper composites? Density & Purity
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Enhance In-Situ Composite Performance
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in CoNiCrAlY coatings? Repairing Cold-Sprayed Microstructures



















