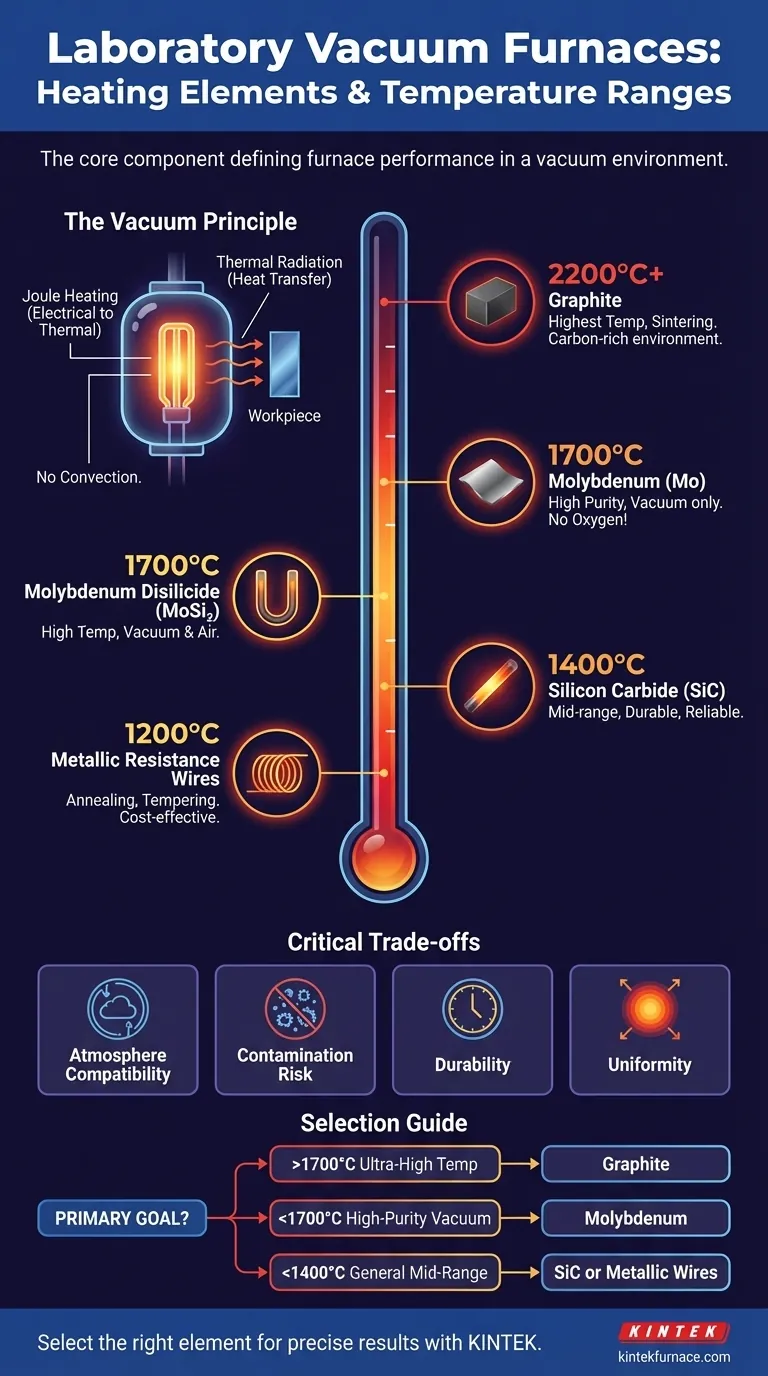
In laboratory vacuum furnaces, the heating element is the core component dictating the unit's maximum temperature and application range. The most common elements are graphite for the highest temperatures (up to 2200°C or more), refractory metals like molybdenum for high-purity applications (around 1700°C), molybdenum disilicide (1700°C), silicon carbide (1400°C), and metallic resistance wires for lower-temperature processes (1200°C).
The choice of heating element is not just about reaching a target temperature. It is a critical decision that defines the furnace's atmospheric compatibility, potential for material contamination, and ultimately, its suitability for a specific scientific or industrial process.
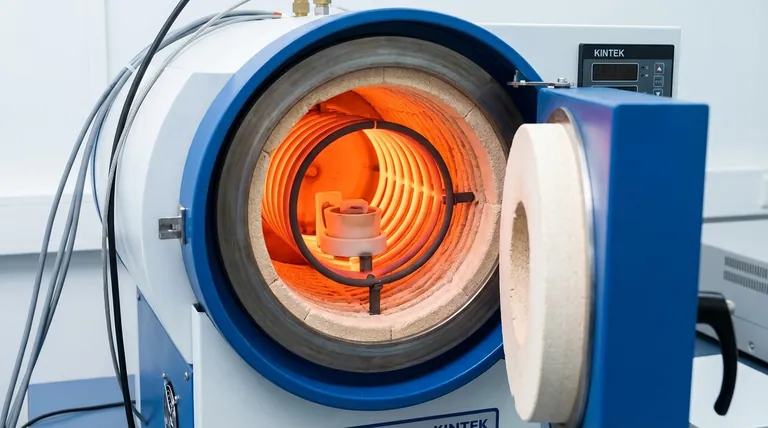

The Role of Heating Elements in a Vacuum
A heating element's job seems simple, but its function within a high-vacuum environment is highly specialized. Understanding this principle is key to appreciating the differences between element types.
Converting Electricity to Heat
All common heating elements operate on the principle of Joule heating, or resistive heating. As electrical current is passed through the element, its natural resistance converts that electrical energy into thermal energy, causing it to glow hot.
The Dominance of Radiation
In a standard furnace, heat is transferred through conduction, convection, and radiation. However, in the near-perfect vacuum of a laboratory furnace, convection is eliminated. Heat is transferred almost entirely through thermal radiation, moving from the hot element to the cooler workpiece. This makes element design and placement critical for achieving uniform temperatures.
A Breakdown of Common Heating Elements
Each material offers a unique combination of maximum temperature, atmospheric compatibility, and physical properties.
Graphite (Up to 2200°C, extending to 3000°C in some designs)
Graphite is the go-to material for the highest temperature applications, such as sintering advanced ceramics or processing refractory metals. It is robust, relatively low-cost for its performance, and has excellent thermal stability.
Molybdenum (Up to ~1700°C)
Molybdenum (Mo) is a refractory metal prized for its strength at high temperatures and its exceptional purity. It is the ideal choice for processes where any carbon contamination from graphite elements would be detrimental to the sample.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) (Up to 1700°C)
MoSi₂ elements are known for their ability to operate at high temperatures. While very common in air-fired furnaces due to a protective silica layer that forms on their surface, they are also used in vacuum environments for their high performance.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) (Up to 1400°C)
Silicon Carbide is a durable and reliable heating element for mid-range temperature applications. It is mechanically strong and offers a long service life for processes that do not require the extreme temperatures of graphite or molybdenum.
Metallic Resistance Wires (Up to 1200°C)
Alloys like nickel-chromium (NiCr) or iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) are used in wire or rod form for lower-temperature vacuum applications. They are cost-effective solutions for processes like annealing, tempering, and brazing.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Selecting an element is an exercise in balancing competing requirements. There is no single "best" material, only the most appropriate one for the task.
Atmosphere Compatibility
This is arguably the most critical factor in a vacuum furnace. Molybdenum cannot be exposed to oxygen at high temperatures as it will rapidly oxidize; it is exclusively for high-vacuum or pure, dry hydrogen atmospheres. Graphite is also used only in vacuum or inert gas, as it would combust in air.
Risk of Material Contamination
The heating element can influence the purity of the final product. Graphite elements can outgas or shed microscopic carbon particles, which can be a critical issue in semiconductor or medical-grade alloy research. Molybdenum is exceptionally clean, making it a superior choice for high-purity work.
Durability and Lifespan
The operational life of an element is affected by thermal cycling (heating and cooling) and the purity of the vacuum or process gas. Contaminants leaking into the chamber can drastically shorten the life of sensitive elements like molybdenum.
Physical Design and Uniformity
Elements may be mounted as rods arranged radially around the heating zone or as panels on the walls and door. This placement is engineered to provide the most uniform temperature field possible, ensuring the entire workpiece receives the same amount of heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Base your decision on the primary goal of your material processing work.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high temperature processing (>1700°C): Graphite is the standard choice, provided your process and material can tolerate a carbon-rich environment.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing in a high vacuum (<1700°C): Molybdenum is the ideal element due to its cleanliness and stability in a vacuum.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose mid-range applications (<1400°C): Silicon Carbide (SiC) and metallic resistance wires offer a cost-effective and highly reliable solution.
Ultimately, selecting the correct heating element is the foundational step in ensuring your vacuum furnace delivers the precise, repeatable, and clean results your work demands.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element | Max Temperature Range | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Graphite | Up to 2200°C (extends to 3000°C) | Sintering ceramics, refractory metals |
| Molybdenum | Up to ~1700°C | High-purity processes, vacuum environments |
| Molybdenum Disilicide | Up to 1700°C | High-temperature applications, vacuum and air |
| Silicon Carbide | Up to 1400°C | Mid-range temperature, durable processes |
| Metallic Resistance Wires | Up to 1200°C | Annealing, tempering, brazing |
Struggling to select the right heating element for your lab's vacuum furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your material processing with reliable, high-performance furnaces!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance



















