Selecting a three-zone tube furnace is a critical decision that hinges on matching the equipment's capabilities to your specific thermal processing needs. The most important factors to evaluate are the furnace's maximum temperature rating, the physical dimensions and material of the process tube, the precision and programmability of the temperature controller, and its compatibility with the required processing atmospheres.
A three-zone furnace is an investment in thermal precision. The goal is not simply to buy a heater, but to acquire a tool capable of creating a highly uniform and controllable temperature environment. Your final choice should be guided by the specific temperature profile your process demands, not just by the furnace's maximum specifications.
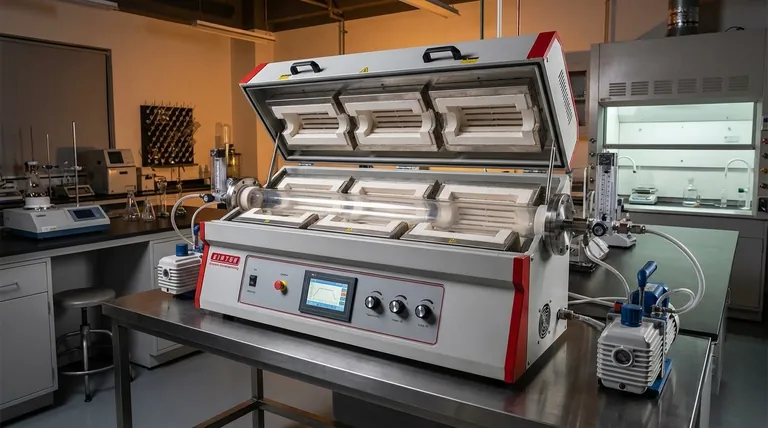

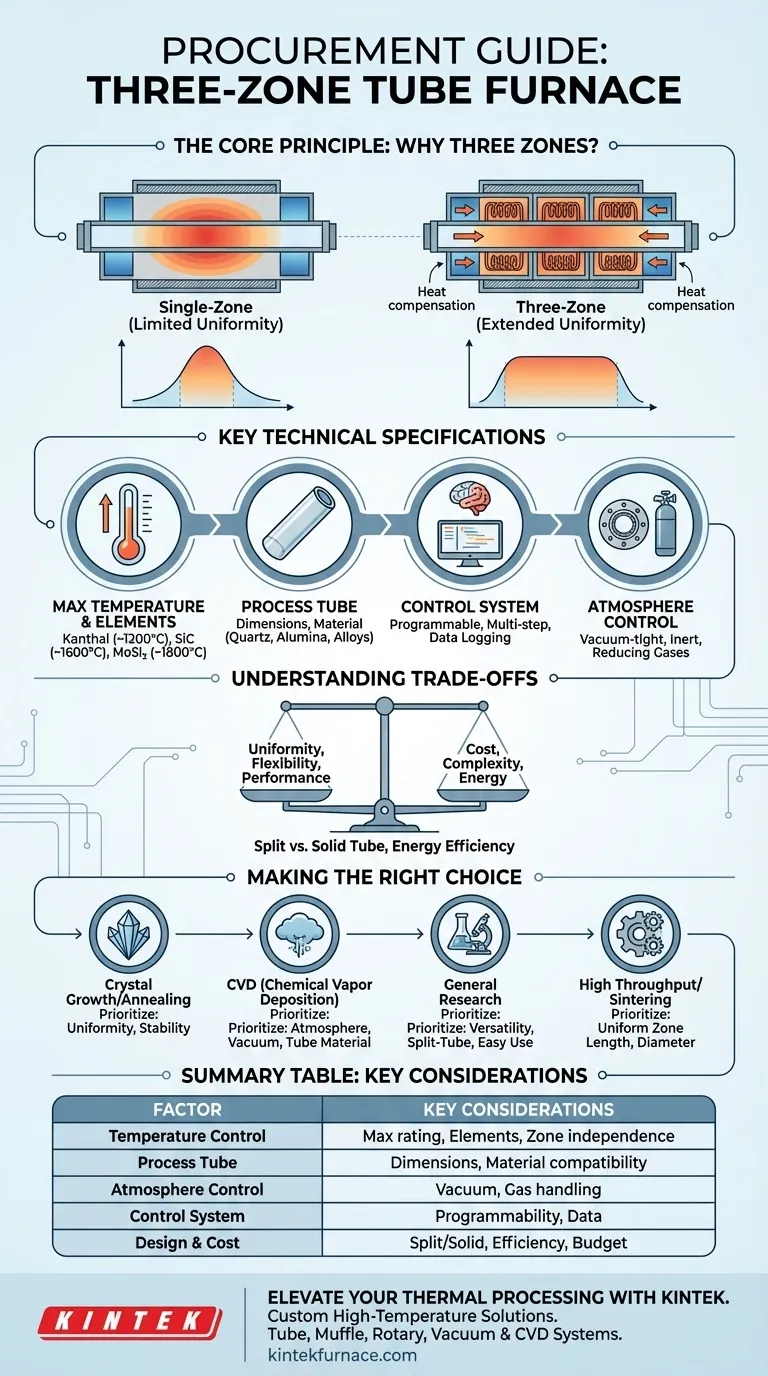
The Core Principle: Why Three Zones?
To make an informed decision, you must first understand the fundamental advantage of a three-zone design. It is engineered to solve a common problem in single-zone furnaces: heat loss at the ends of the tube.
Overcoming End-Zone Heat Loss
A standard single-zone furnace is hottest in its geometric center. The temperature naturally drops off toward the openings of the tube as heat escapes into the surrounding environment. This creates a very short region of true temperature uniformity.
How Three Zones Create Uniformity
A three-zone furnace divides the heating chamber into a large central zone flanked by two smaller end zones. Each zone has its own independent thermocouple and controller.
To create a flat, uniform temperature profile, operators set the end zones to a slightly higher temperature. This compensates for the natural heat loss, effectively creating a "thermal barrier" that keeps the central zone at the desired setpoint along a much greater length.
Beyond Uniformity: Creating Custom Profiles
The independent control also allows for more advanced applications. You can intentionally program a temperature gradient across the sample, with each zone holding a different temperature. This is essential for processes like physical vapor transport or certain types of crystal growth.
Key Technical Specifications to Evaluate
Once you understand the principle, you can assess the technical specifications in the context of your application.
Maximum Temperature and Heating Elements
The maximum operating temperature is the first filter. This capability is dictated by the heating elements used within the furnace. Common element types include:
- Kanthal (A-1): Up to ~1200°C
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): Up to ~1600°C
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2): Up to ~1800°C
Ensure the furnace's maximum rating provides a safe margin above your required processing temperature.
Process Tube Dimensions and Material
The tube's dimensions—its length and inner diameter—determine your sample capacity or throughput.
Equally important is the tube's material, which must be chosen for its temperature rating and chemical compatibility with your sample and atmosphere. Common materials include:
- Quartz: Cost-effective and excellent for many processes up to ~1100°C, but not suitable for use with alkalis.
- Alumina: A high-purity ceramic with a very high temperature rating (>1700°C) and excellent chemical resistance.
- Inconel/Alloys: Useful for applications requiring high vacuum integrity where ceramics might be too brittle.
The Control System: The Brain of the Operation
The three heating zones are only as effective as the system that controls them. A modern controller should offer multi-step programmability, allowing you to create complex thermal recipes with ramps, soaks, and controlled cooling. Look for features like real-time data logging and an intuitive user interface.
Atmosphere Control and Versatility
If your process cannot be done in ambient air, atmosphere control is non-negotiable. This requires a furnace system with vacuum-tight flanges and gas handling capabilities. Verify that the system is designed for your specific needs, whether it's flowing an inert gas (like Argon), a reducing gas (like a Hydrogen mixture), or operating under vacuum.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A perfect furnace does not exist; every choice involves balancing competing priorities.
Uniformity vs. Cost
A three-zone furnace is inherently more complex and costly than a single-zone model due to the extra controllers, thermocouples, and power wiring. You must determine if the superior temperature uniformity is essential for your process and justifies the additional investment.
Split-Tube vs. Solid-Tube Design
Many three-zone furnaces are available in a "split-tube" configuration, where the furnace body hinges open. This allows for easy placement and removal of the process tube, which is especially useful if the tube is connected to a complex external apparatus. Solid-tube designs are simpler and can be slightly more energy-efficient.
Energy Consumption
Larger furnaces and higher operating temperatures result in significant energy consumption. Consider the long-term operational costs, especially for production or continuous-use applications. The quality of the furnace's insulation will play a major role in its overall energy efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Ultimately, your application dictates the correct set of features.
- If your primary focus is high-purity crystal growth or semiconductor annealing: Prioritize the highest degree of temperature uniformity and a control system with exceptionally stable, precise programming.
- If your primary focus is chemical vapor deposition (CVD): Focus on atmosphere control capabilities, vacuum integrity of the end flanges, and a tube material compatible with your precursor gases.
- If your primary focus is general materials science research: Select a versatile furnace with a wide temperature range, a split-tube design for easy sample exchange, and an intuitive, programmable controller.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput for sintering or calcination: Carefully evaluate the uniform heated zone length and tube diameter to ensure it meets your batch size requirements.
By systematically evaluating these factors against your specific process goals, you will select a furnace that serves as a reliable and precise tool for years to come.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Max temperature rating, heating elements (e.g., Kanthal, SiC, MoSi2), zone independence for uniformity |
| Process Tube | Dimensions (length, diameter), material (e.g., quartz, alumina, Inconel) for compatibility and capacity |
| Atmosphere Control | Vacuum-tight flanges, gas handling for inert, reducing, or vacuum environments |
| Control System | Programmability, multi-step recipes, data logging, user interface |
| Design & Cost | Split-tube vs. solid-tube, energy efficiency, trade-offs with budget |
Ready to elevate your thermal processing with a custom three-zone tube furnace?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a product line including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your experimental requirements, whether for crystal growth, semiconductor annealing, CVD, or materials research.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating



















