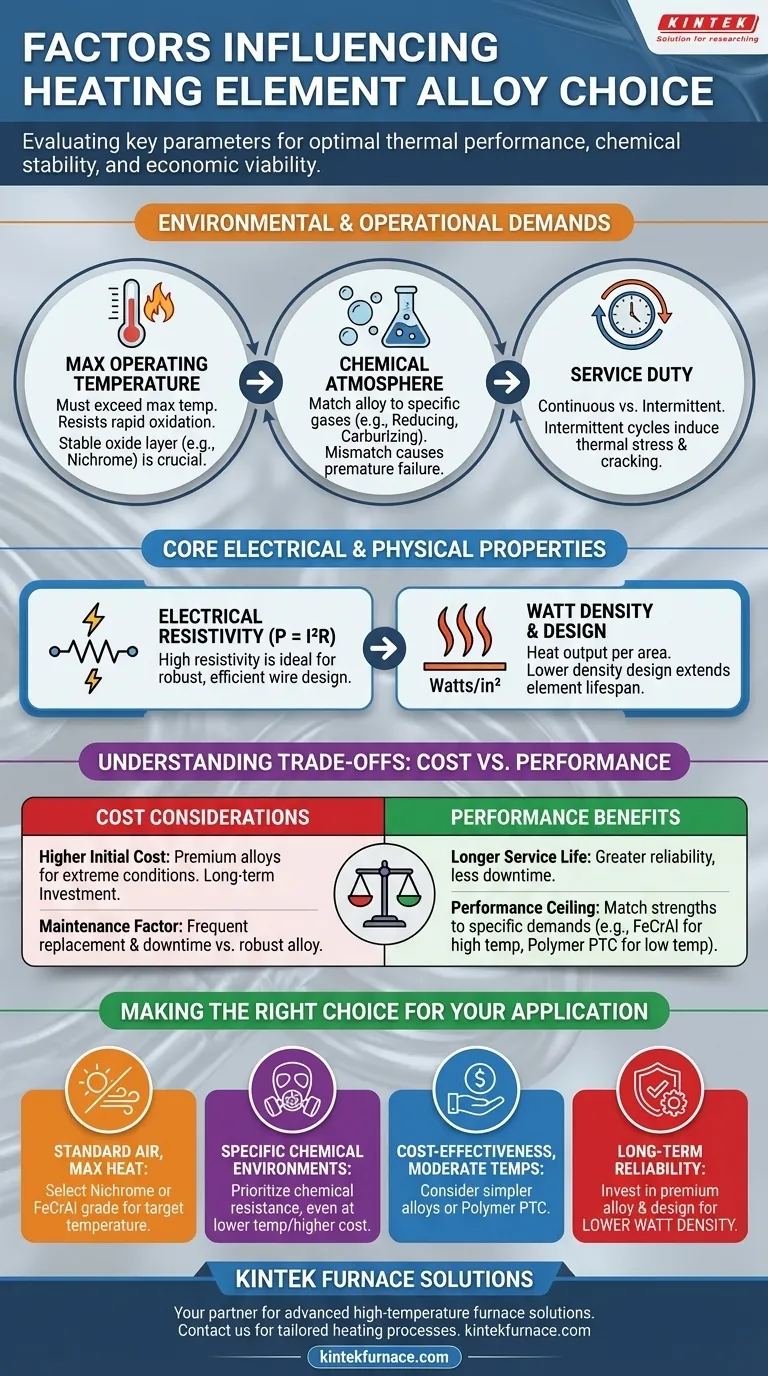
To select the correct heating element alloy, you must evaluate several critical factors. The most important are the required operating temperature, the chemical atmosphere it will operate in, and its inherent electrical resistance. Secondary considerations like service duty (continuous vs. intermittent), watt density, and overall cost also play a crucial role in the final decision.
Choosing a heating element is not about finding the "best" material, but the most suitable one for a specific operational context. The ideal alloy represents a calculated trade-off between thermal performance, chemical stability, and economic viability.

Environmental and Operational Demands
The environment where the element operates is the first and most critical filter for selecting an alloy. Mismatching the material to its environment is the most common cause of premature failure.
Maximum Operating Temperature
The alloy must have a melting point significantly higher than its maximum operating temperature. More importantly, it must resist rapid oxidation at that temperature.
As temperature increases, the rate of oxidation accelerates, forming a oxide layer that can flake off, thinning the element and eventually causing it to fail. Materials like nickel-chromium (Nichrome) are prized for their ability to form a stable, adherent oxide layer at high temperatures.
Chemical Atmosphere
An element that performs well in open air may fail quickly in a different atmosphere. The specific gases present determine the type of corrosion that will occur.
For example, a reducing atmosphere (lacking oxygen) can prevent the formation of a protective oxide layer on some alloys, while a carburizing atmosphere can cause carbon to infuse into the alloy, making it brittle. You must choose an alloy specifically rated for the chemical environment.
Service Duty (Continuous vs. Intermittent)
How the element is used profoundly impacts its lifespan. Continuous operation at a stable temperature is generally less stressful on a material.
Intermittent service, with frequent heating and cooling cycles, causes the element to expand and contract repeatedly. This thermal cycling induces mechanical stress and can cause the protective oxide layer to crack and flake off, accelerating degradation. Alloys with better fatigue resistance are required for such applications.
Core Electrical and Physical Properties
Once environmental needs are met, you must consider the inherent properties of the alloy itself to ensure it functions efficiently and can be manufactured into the desired shape.
Electrical Resistivity
A heating element works by converting electrical energy into heat through resistance (P = I²R). An ideal alloy has high electrical resistivity.
High resistance allows a shorter, more robust wire to generate the required heat. An alloy with low resistance would require an impractically long and thin wire to achieve the same heating effect, making it fragile and difficult to install.
Watt Density and Design
Watt density is the heat output per unit of surface area (watts/in² or watts/cm²). It is a critical factor in determining the element's operating temperature and lifespan.
A higher watt density means the element runs hotter, which can shorten its life. Choosing a superior alloy may allow for a higher watt density design, but for maximum longevity, it is often wise to use more or larger elements to achieve a lower watt density.
Mechanical Strength and Formability
The alloy must be ductile enough to be drawn into wire or formed into strips and coils without breaking.
Simultaneously, it must possess sufficient mechanical strength at high temperatures (known as "hot strength") to hold its shape and not sag or deform over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Performance
There is no single "best" alloy. The selection process is always a balance between achieving performance targets and managing costs.
The Cost of Longevity
Alloys designed for higher temperatures and extreme chemical resistance, such as certain iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) grades or specialized nickel alloys, are almost always more expensive.
This higher initial cost is an investment in longer service life, greater reliability, and the ability to operate under more demanding conditions.
The Maintenance Factor
A cheaper alloy may seem economical upfront but can lead to a higher total cost of ownership if it requires frequent replacement. Production downtime and labor for maintenance often outweigh the initial material savings.
Choosing a more robust alloy can significantly reduce maintenance intervals and improve operational uptime.
The Performance Ceiling
Every alloy has its limits. Nickel-chromium is an excellent default for high-temperature air heating, but it will fail in certain sulfurous atmospheres.
For lower-temperature applications, a non-metallic option like a Polymer PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) element may be more cost-effective and provide the benefit of being self-regulating. Always match the material's strengths to the application's specific demands.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Based on these factors, your decision can be guided by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum heat in a standard air atmosphere: Select a nickel-chromium (Nichrome) or iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) alloy, focusing on the grade rated for your target temperature.
- If your primary focus is operation in a specific chemical environment (e.g., reducing or carburizing): You must prioritize an alloy specifically designed for that chemical resistance, even if it has a lower temperature limit or higher cost.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for moderate temperatures: Consider simpler, less expensive alloys or non-metallic options like polymer PTC elements where appropriate.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability and minimal maintenance: Invest in a premium alloy and design for a lower watt density, as this reduces thermal stress and dramatically extends service life.
A methodical evaluation of these factors ensures you select an alloy that delivers reliable and efficient performance for its intended purpose.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | Must exceed max temp; resist oxidation (e.g., nickel-chromium forms stable oxide layer) |
| Chemical Atmosphere | Choose alloys rated for specific gases (e.g., reducing or carburizing atmospheres) |
| Electrical Resistivity | High resistivity allows shorter, robust wires for efficient heat generation |
| Service Duty | Continuous vs. intermittent use affects thermal cycling and fatigue resistance |
| Watt Density | Lower density extends lifespan by reducing thermal stress |
| Cost vs. Performance | Balance initial cost with long-term reliability and maintenance needs |
Struggling to select the right heating element alloy for your lab's unique needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your experimental requirements, delivering enhanced performance, durability, and cost-efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your heating processes and boost operational uptime!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism

















