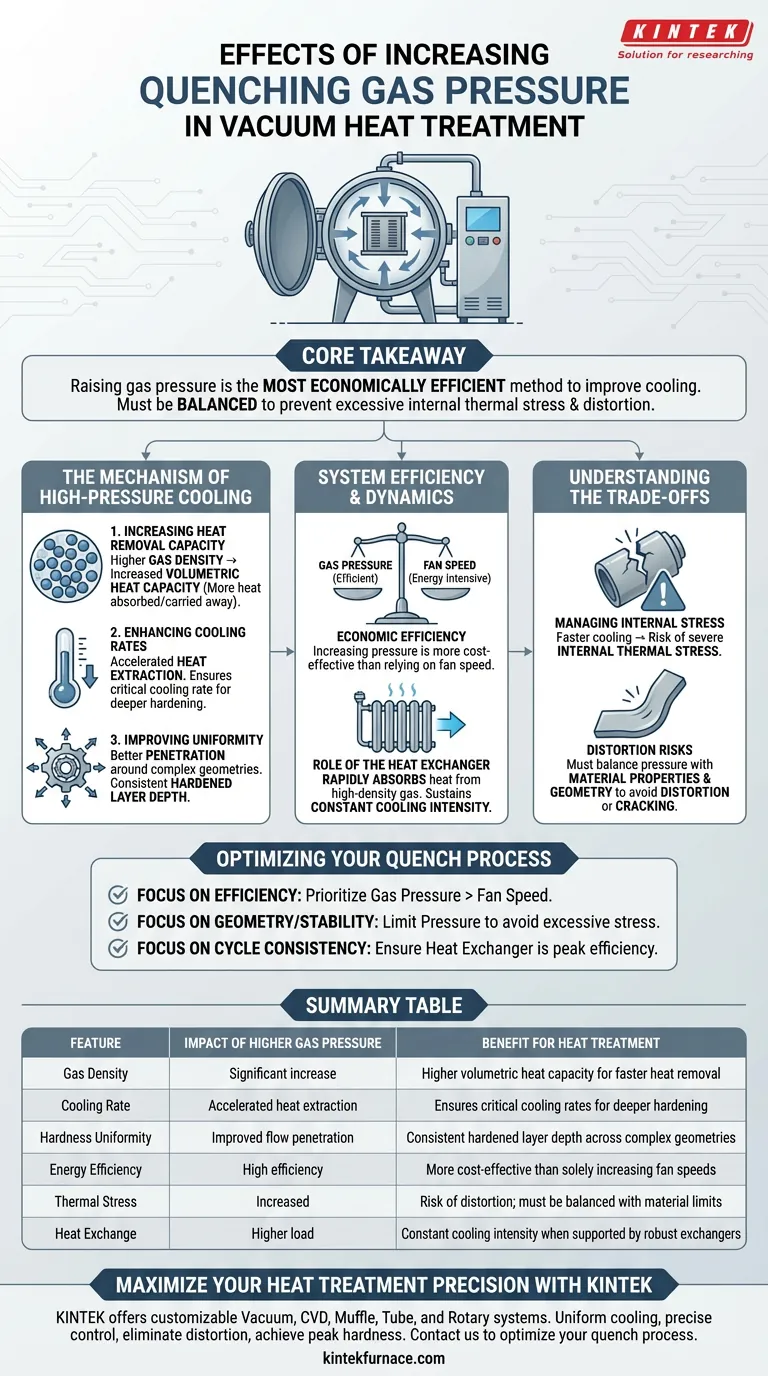
Increasing the quenching gas pressure directly enhances the cooling capacity of the system by raising the gas density and volumetric heat capacity. This allows the gas to absorb and remove significantly more heat from the workpiece per unit of time, resulting in a faster overall cooling rate and a more uniform hardened layer depth.
Core Takeaway Raising gas pressure is the most economically efficient method to improve cooling performance compared to increasing fan speed. However, this increased intensity must be carefully balanced to prevent excessive internal thermal stress that could damage the workpiece.

The Mechanism of High-Pressure Cooling
Increasing Heat Removal Capacity
The primary physical change driven by higher pressure is an increase in gas density.
As density rises, the volumetric heat capacity of the quenching medium increases. This means that for every cubic meter of gas circulating over the hot parts, a larger amount of thermal energy can be absorbed and carried away.
Enhancing Cooling Rates
Because the gas can carry more heat, the overall cooling rate of the workload accelerates significantly.
This rapid heat extraction is essential for materials that require fast quenching to transform the microstructure correctly. It ensures that the critical cooling rate is met not just at the surface, but deeper into the part.
Improving Uniformity
Higher pressure facilitates better penetration and flow around complex geometries.
This promotes a more uniform hardened layer depth across the entire workpiece. Consistency in the hardened layer translates directly to predictable mechanical performance and durability of the treated part.
System Efficiency and Dynamics
Economic Efficiency vs. Fan Speed
To improve cooling capacity, operators generally have two levers: increasing fan speed or increasing gas pressure.
Research indicates that increasing gas pressure is more economically efficient than solely relying on higher fan speeds. Achieving the same cooling effect through fan speed alone often requires disproportionate energy consumption compared to pressurization.
The Role of the Heat Exchanger
The benefits of high pressure rely heavily on the system's ability to shed the heat once it is removed from the workpiece.
The heat exchanger must rapidly absorb the heat carried by the high-density gas. It ensures the gas circulating back into the furnace chamber remains at a low initial temperature, sustaining constant cooling intensity throughout the cycle.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Managing Internal Stress
While faster cooling is generally desired for hardness, it introduces a significant risk.
Excessive cooling rates caused by very high pressure can generate severe internal thermal stress within the workpieces.
Distortion Risks
If the pressure is not matched to the material's properties and the part's geometry, this stress can lead to distortion or even cracking.
The goal is to find the maximum pressure that achieves the required metallurgical properties without exceeding the structural limits of the part during the thermal shock of quenching.
Optimizing Your Quench Process
To effectively manage your vacuum high-pressure gas quenching system, align your pressure settings with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Prioritize increasing gas pressure over fan speed to maximize cooling capacity with better energy economics.
- If your primary focus is part geometry and stability: Limit the pressure to a level that achieves hardness without inducing excessive thermal stress that causes distortion.
- If your primary focus is cycle consistency: Ensure your heat exchanger is functioning at peak efficiency to maintain the cooling intensity provided by the higher pressure.
Optimization is found at the intersection of maximum cooling speed and minimum part distortion.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Impact of Higher Gas Pressure | Benefit for Heat Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Density | Significant increase | Higher volumetric heat capacity for faster heat removal |
| Cooling Rate | Accelerated heat extraction | Ensures critical cooling rates for deeper hardening |
| Hardness Uniformity | Improved flow penetration | Consistent hardened layer depth across complex geometries |
| Energy Efficiency | High efficiency | More cost-effective than solely increasing fan speeds |
| Thermal Stress | Increased | Risk of distortion; must be balanced with material limits |
| Heat Exchange | Higher load | Constant cooling intensity when supported by robust exchangers |
Maximize Your Heat Treatment Precision with KINTEK
Don't let inefficient cooling compromise your material integrity. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers cutting-edge Vacuum, CVD, Muffle, Tube, and Rotary systems, all fully customizable to your specific high-pressure gas quenching requirements. Whether you are treating complex aerospace components or industrial tools, our high-temp furnaces provide the uniform cooling and precise control needed to eliminate distortion while achieving peak hardness.
Ready to optimize your quench process? Contact us today to discover how our tailored solutions can enhance your laboratory or production efficiency.
Visual Guide
References
- Zaiyong Ma, Jingbo Ma. Research on the uniformity of cooling of gear ring parts under vacuum high-pressure gas quenching. DOI: 10.1088/1742-6596/3080/1/012130
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum furnace prevent oxidation of metals? Unlock Purity and Strength in Heat Treatment
- What are the advantages of vacuum furnaces? Achieve Pristine Material Processing and Control
- Why is a laboratory vacuum oven with nitrogen protection used for alumina dehydration? Ensure High-Purity Surfaces
- How do controlled atmospheres and automated temperature cycles in a sintering furnace impact alloy quality?
- How does vacuum sintering improve dimensional tolerances? Achieve Uniform Shrinkage and Precision
- What is vacuum brazing and what materials does it primarily join? Discover High-Purity Joining for Superior Bonds
- How does a vacuum furnace provide precise temperature control? Achieve Unmatched Thermal Accuracy for Your Lab
- Why is it necessary to use a vacuum drying oven for Silicon Carbide slurry? Enhance Purity and Green Body Density



















