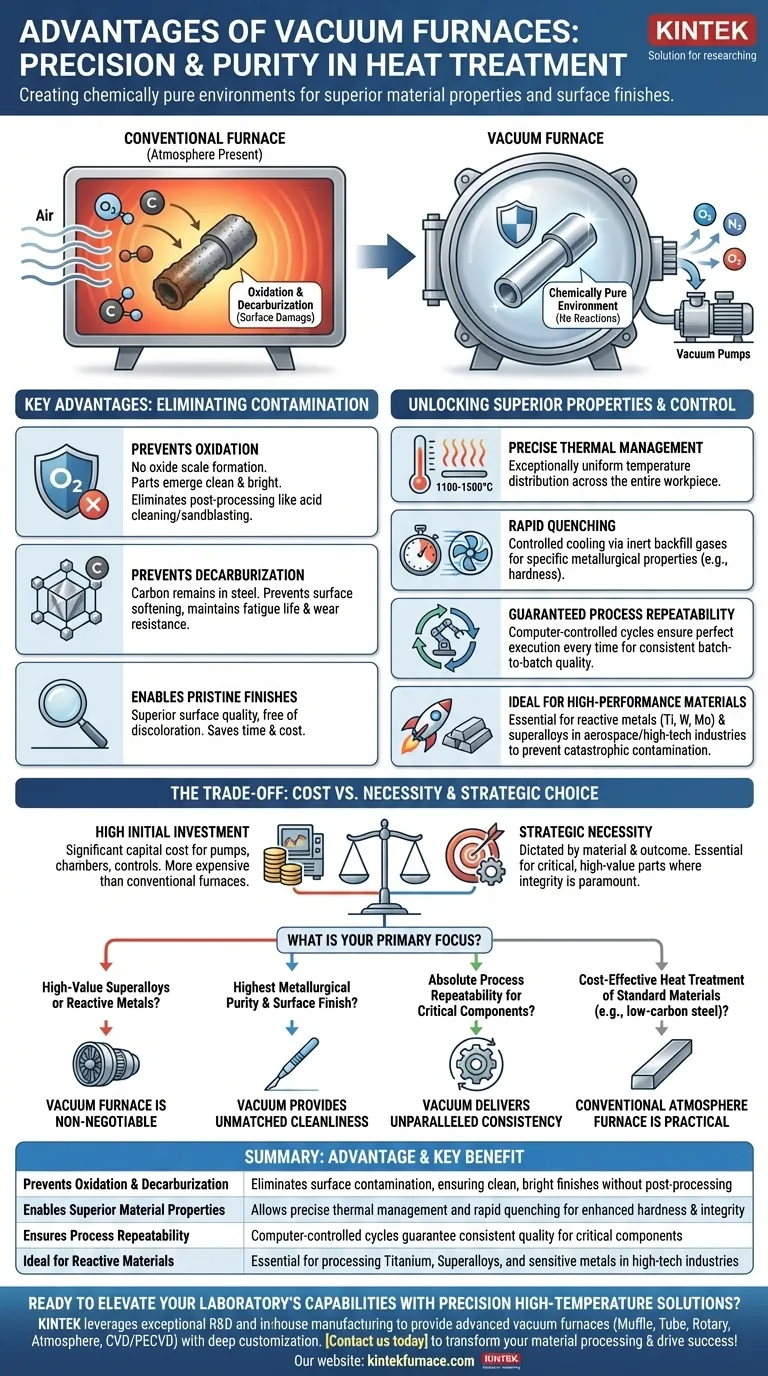
In essence, the primary advantage of a vacuum furnace is its ability to create a chemically pure environment for heat treatment. By removing air and other gases, it prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation and contamination, allowing for unparalleled control over the final properties and surface finish of a material.
While conventional furnaces simply apply heat, a vacuum furnace provides a meticulously controlled environment. This transforms heat treatment from a brute-force process into a precision tool, essential for manufacturing high-performance components where material integrity cannot be compromised.

The Core Principle: Eliminating Atmospheric Contamination
A vacuum furnace's fundamental advantage stems from what it removes: the atmosphere. This seemingly simple act has profound implications for material processing.
Preventing Oxidation and Decarburization
At high temperatures, the oxygen in the air aggressively reacts with most metals, forming a layer of oxide scale. This oxidation can ruin a component's surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
Similarly, the carbon within steel alloys can react with atmospheric gases, a process called decarburization. This depletes carbon from the surface, softening the material and reducing its fatigue life and wear resistance. A vacuum eliminates the gases responsible for these destructive reactions.
Enabling Pristine Surface Finishes
By preventing oxidation, parts emerge from a vacuum furnace clean, bright, and free of discoloration. This often eliminates the need for post-processing steps like acid cleaning, sandblasting, or machining, saving both time and cost.
Unlocking Superior Material Properties and Process Control
Removing the atmosphere is the first step. The second is leveraging that controlled environment to achieve superior results that are difficult or impossible in conventional furnaces.
Precise and Uniform Thermal Management
Vacuum furnaces offer exceptionally uniform temperature distribution, often within a very tight range (e.g., 1100-1500°C), ensuring the entire workpiece receives the same thermal treatment.
They also allow for rapid quenching (cooling) by using inert backfill gases. This controlled cooling is critical for achieving specific metallurgical properties, such as the hardness in tool steels.
Guaranteed Process Repeatability
Modern vacuum furnaces are computer-controlled, allowing for precise and highly repeatable metallurgical cycles. Every parameter—from the vacuum level to heating rates and quenching speed—is programmed and executed perfectly every time, ensuring consistent quality from batch to batch.
Ideal for High-Performance and Reactive Materials
Certain materials are impossible to process correctly in the presence of air. Reactive metals like titanium, tungsten, and molybdenum, as well as superalloys used in aerospace, require a vacuum to prevent catastrophic contamination and preserve their unique properties.
Analyzing the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Necessity
While the advantages are significant, a vacuum furnace is not always the right tool for the job. An objective evaluation requires understanding its limitations.
The High Initial Investment
Vacuum furnaces are complex machines that represent a significant capital investment. The pumps, chambers, and control systems make them considerably more cost-prohibitive than many conventional atmosphere furnaces.
Evaluating Your Specific Need
The necessity for a vacuum furnace is dictated entirely by the material and the required outcome. For general-purpose annealing of non-critical, low-carbon steel, the benefits may not justify the expense. A processor must carefully evaluate if the risk of oxidation or the need for perfect repeatability outweighs the higher cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace technology is a strategic decision based on your specific goals and material requirements.
- If your primary focus is processing high-value superalloys or reactive metals: A vacuum furnace is non-negotiable to prevent contamination and ensure material integrity.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest metallurgical purity and surface finish: The controlled vacuum environment provides unmatched cleanliness and prevents surface defects.
- If your primary focus is absolute process repeatability for critical components: The computer-controlled thermal cycles in a vacuum furnace deliver unparalleled consistency.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective heat treatment of standard materials: A conventional atmosphere furnace is often the more practical and economical solution.
By understanding these core advantages and trade-offs, you can confidently determine if a vacuum furnace is the right strategic investment for your specific processing goals.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Prevents Oxidation & Decarburization | Eliminates surface contamination, ensuring clean, bright finishes without post-processing |
| Enables Superior Material Properties | Allows precise thermal management and rapid quenching for enhanced hardness and integrity |
| Ensures Process Repeatability | Computer-controlled cycles guarantee consistent quality for critical components |
| Ideal for Reactive Materials | Essential for processing titanium, superalloys, and other sensitive metals in aerospace and high-tech industries |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's capabilities with precision high-temperature solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced vacuum furnaces, including our Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Atmosphere Furnaces, as well as CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization, we tailor our solutions to meet your unique experimental needs, ensuring superior performance, repeatability, and cost savings. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can transform your material processing and drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety



















