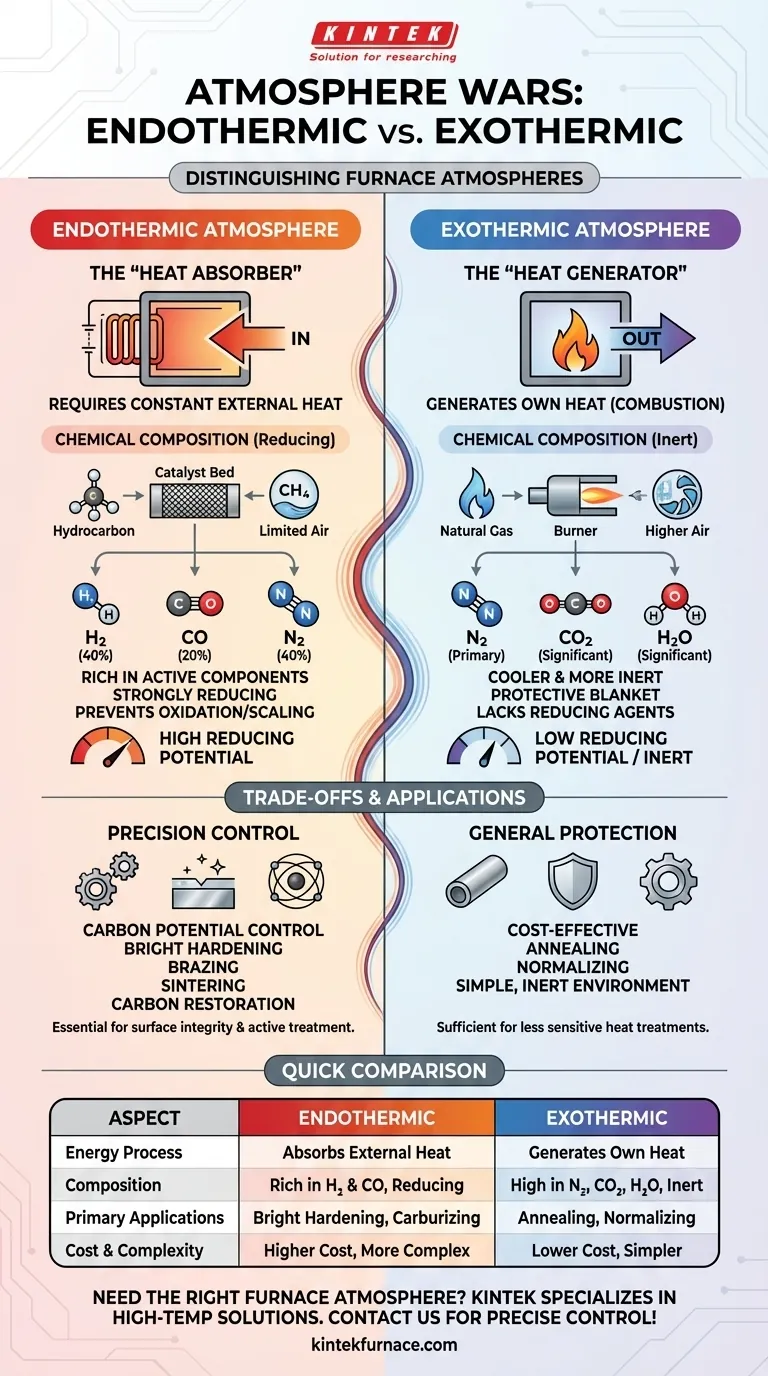
At its core, the distinction between an endothermic and an exothermic atmosphere lies in their relationship with energy. An endothermic atmosphere requires a constant input of external heat to sustain its chemical reaction, while an exothermic atmosphere generates its own heat as a byproduct of combustion.
The choice between these two atmospheres is not about thermal efficiency but about the resulting chemical composition. An endothermic atmosphere is chemically active and used for precise surface treatments, whereas an exothermic atmosphere is simpler and primarily used for general oxidation prevention.
The Core Difference: Energy and Reaction
The terms "endothermic" and "exothermic" refer to how each gas generation process handles thermal energy. This fundamental difference dictates the equipment needed, the cost of operation, and the final composition of the gas.
Endothermic: The "Heat Absorber"
An endothermic atmosphere is created by reacting a hydrocarbon gas (like natural gas) with a very limited amount of air over a heated catalyst.
The reaction absorbs heat from an external source, such as an electrically heated chamber, to "crack" the hydrocarbon molecules. This process is necessary to produce a gas rich in chemically active compounds.
Exothermic: The "Heat Generator"
An exothermic atmosphere is the product of a more complete combustion process, using a higher air-to-gas ratio than its endothermic counterpart.
This reaction releases heat, much like a standard burner. It does not require continuous external heating once initiated, making the generation process simpler and often less expensive.
A Tale of Two Compositions
The energy process directly creates two very different atmospheres, each with a unique chemical makeup suited for specific metallurgical tasks.
Endothermic Gas: Chemically Active and Reducing
Because it's formed with insufficient air for full combustion, endothermic gas is rich in active components. A typical composition is roughly 40% Nitrogen (N₂), 40% Hydrogen (H₂), and 20% Carbon Monoxide (CO).
The high concentration of hydrogen and carbon monoxide makes the atmosphere strongly reducing. This means it actively removes oxygen from the environment, preventing the metal surface from oxidizing or scaling during high-temperature treatment.
Exothermic Gas: Cooler and More Inert
In contrast, the more complete combustion of an exothermic reaction produces a gas that is primarily nitrogen, with significant amounts of carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water vapor (H₂O).
While it still displaces oxygen, it lacks the high concentration of reducing agents found in endothermic gas. It serves as a protective blanket rather than an active surface treatment agent.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Applications
Choosing the right atmosphere involves balancing process requirements against cost, complexity, and safety.
Endothermic Applications: Precision Control
The reducing nature of endothermic gas makes it essential for processes where surface integrity is paramount. Its carbon potential can also be precisely controlled to add carbon to steel (carburizing) or prevent its loss (decarburization).
Common uses include bright hardening, brazing, sintering of powdered metals, and carbon restoration for steel parts.
Exothermic Applications: General Protection
Exothermic atmospheres are a cost-effective choice when the primary goal is simply to prevent heavy scaling, and a perfectly "bright" or unaltered surface is not critical.
It is often used for less sensitive processes like annealing or normalizing of steel and non-ferrous metals, where a simple, inert environment is sufficient.
Key Pitfalls to Avoid
The most common mistake is a mismatch between the atmosphere and the goal. Using an exothermic atmosphere for a process that requires active decarburization prevention will result in a failed part.
Conversely, using a more expensive and complex endothermic system for simple annealing is inefficient. The presence of high CO and H₂ in endo gas also introduces significant safety considerations regarding toxicity and flammability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection should be dictated entirely by the desired metallurgical outcome for your component.
- If your primary focus is a bright, scale-free finish or active carbon control: Endothermic gas is the necessary choice due to its high concentration of reducing agents.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose oxidation prevention at a lower cost: Exothermic gas provides a simple and effective protective blanket for less sensitive heat treatments.
- If your primary focus is operational simplicity and safety: Exothermic generators are mechanically simpler and produce a less hazardous gas mixture.
Ultimately, understanding the chemical capability of each atmosphere is the key to selecting the correct tool for your specific heat treatment objective.

Summary Table:
| Aspect | Endothermic Atmosphere | Exothermic Atmosphere |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Process | Absorbs external heat | Generates its own heat |
| Chemical Composition | Rich in H₂ and CO, reducing | High in N₂, CO₂, and H₂O, inert |
| Primary Applications | Bright hardening, carburizing, sintering | Annealing, normalizing, general protection |
| Cost and Complexity | Higher cost, more complex | Lower cost, simpler |
Need the right furnace atmosphere for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With deep customization, we ensure precise control for your unique experiments. Contact us today to enhance your heat treatment processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















