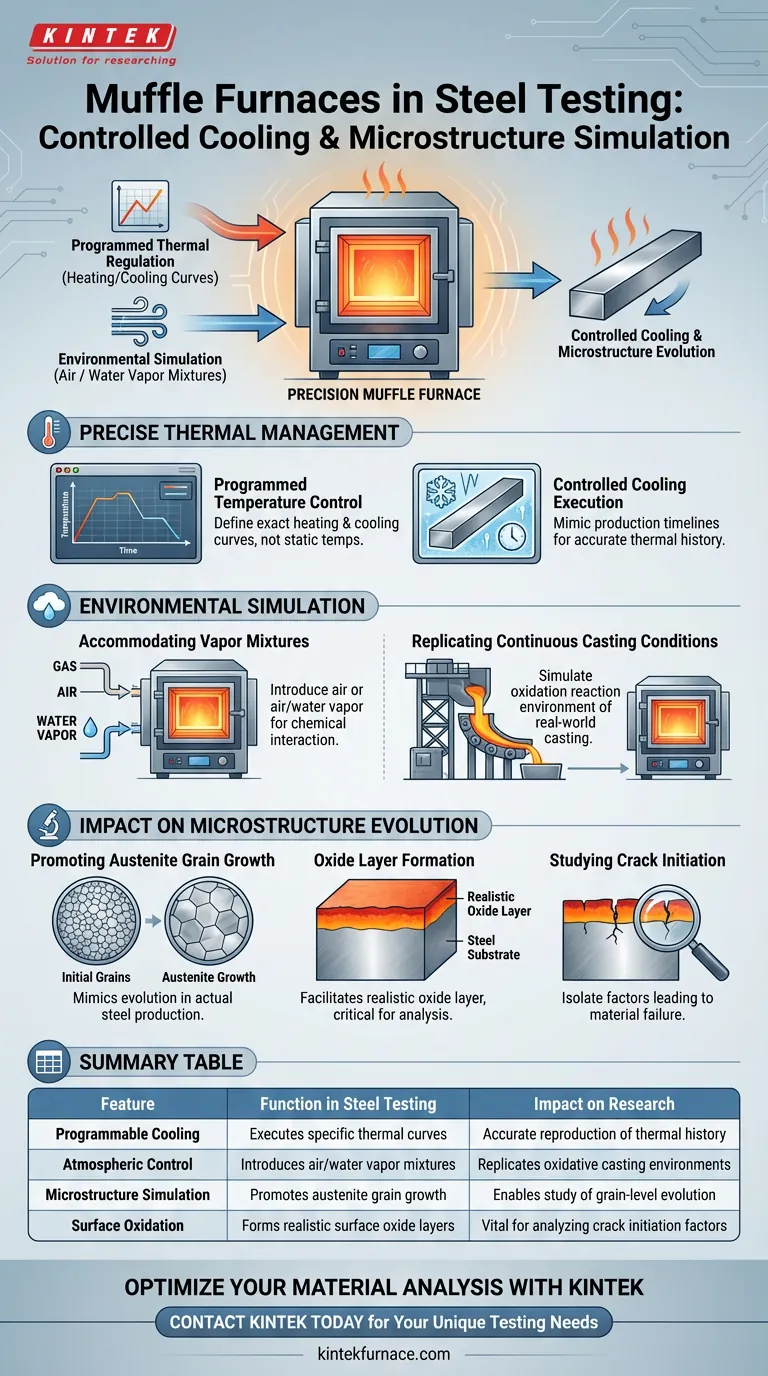
Muffle furnaces function as precision simulation tools that provide exact, programmable temperature control to regulate the cooling rates of steel specimens. Crucially, they facilitate the introduction of air or air/water vapor mixtures, enabling researchers to replicate the specific environmental conditions and oxidation reactions characteristic of industrial continuous casting.
By enabling the simultaneous control of cooling rates and oxidative atmospheres, muffle furnaces allow for the accurate reproduction of surface oxide layers and austenite grain growth, which are essential for understanding crack initiation mechanisms in steel.

Precise Thermal Management
Programmed Temperature Control
The primary function of a muffle furnace in this context is programmable thermal regulation.
This feature allows operators to define exact heating and cooling curves rather than relying on static temperatures.
Controlled Cooling Execution
During the testing phase, the furnace executes specific cooling protocols to mimic production timelines.
This ensures the specimen undergoes the exact thermal history required to study microstructure evolution accurately.
Environmental Simulation
Accommodating Vapor Mixtures
A distinct advantage of muffle furnaces is their ability to accommodate air or air/water vapor mixtures within the heating chamber.
This capability is vital for creating an environment that extends beyond simple thermal treatment to chemical interaction.
Replicating Continuous Casting Conditions
The introduction of these specific gas mixtures allows the furnace to simulate the oxidation reaction environment found in actual continuous casting processes.
This fidelity to the production environment ensures that laboratory results are applicable to real-world manufacturing scenarios.
Impact on Microstructure Evolution
Promoting Austenite Grain Growth
The specific combination of heat and atmosphere provided by the furnace promotes austenite grain growth on the specimen's surface.
This microstructural change mimics the evolution that occurs during actual steel production.
Oxide Layer Formation
The controlled presence of air and water vapor facilitates the formation of a realistic oxide layer on the steel surface.
Reproducing this layer is critical, as a sterile or vacuum environment would not yield the same surface characteristics.
Studying Crack Initiation
The ultimate goal of these combined functions is to enable the study of how the oxide layer influences crack initiation.
By replicating the exact surface conditions of production, researchers can isolate the factors leading to material failure.
Understanding the Simulation Requirements
The Necessity of Atmospheric Control
To accurately study surface cracking, temperature control alone is insufficient.
You must utilize a furnace capable of sustaining the correct oxidative atmosphere to generate valid data regarding surface integrity.
Correlation to Reality
The validity of the test results relies heavily on the furnace's ability to match the continuous casting environment.
Any deviation in the vapor mixture or cooling profile can lead to microstructures that do not reflect true production outcomes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate testing protocol, align the furnace's capabilities with your specific research objectives:
- If your primary focus is reproducing industrial conditions: Ensure the furnace is programmed to utilize air/water vapor mixtures that mimic the oxidation environment of continuous casting.
- If your primary focus is analyzing failure mechanisms: Prioritize the simulation of the oxide layer formation, as this is the critical factor influencing surface crack initiation.
Leveraging the dual capabilities of thermal programming and atmospheric control provides the most accurate insight into how steel will behave during the manufacturing process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Steel Testing | Impact on Research |
|---|---|---|
| Programmable Cooling | Executes specific thermal curves | Accurate reproduction of thermal history |
| Atmospheric Control | Introduces air/water vapor mixtures | Replicates oxidative casting environments |
| Microstructure Simulation | Promotes austenite grain growth | Enables study of grain-level evolution |
| Surface Oxidation | Forms realistic surface oxide layers | Vital for analyzing crack initiation factors |
Optimize Your Material Analysis with KINTEK
Ensure your research yields valid, production-ready data by leveraging KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer high-precision Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific oxidative atmosphere and cooling rate requirements.
Whether you are simulating continuous casting or studying material failure mechanisms, our laboratory high-temp furnaces provide the control you need to succeed. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique testing needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Investigation on the Susceptibility to Surface Crack Formation in Continuous Casting by a New In Situ Bending Test. DOI: 10.1007/s11663-025-03649-x
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the alternative names for a muffle furnace? Discover Key Terms and Design Insights
- What function does a muffle furnace serve in LaMO3 calcination? Master Perovskite Nanoparticle Synthesis
- What is a box furnace and what are its common uses? Discover Versatile High-Temperature Solutions
- What safety measures should be taken when handling thermocouples in a muffle furnace? Essential Tips for Safe Operation
- How does a muffle furnace contribute to CRP thermal treatment? Unlock High Reactivity in Recycled Powder
- What is the primary advantage of a muffle furnace compared to other types of furnaces? Superior Purity and Element Protection
- How does the programmed temperature control of a muffle furnace influence the formation of g-C3N4 semiconductors?
- What is the use of digital muffle furnace? Unlock Precise High-Temperature Processing



















