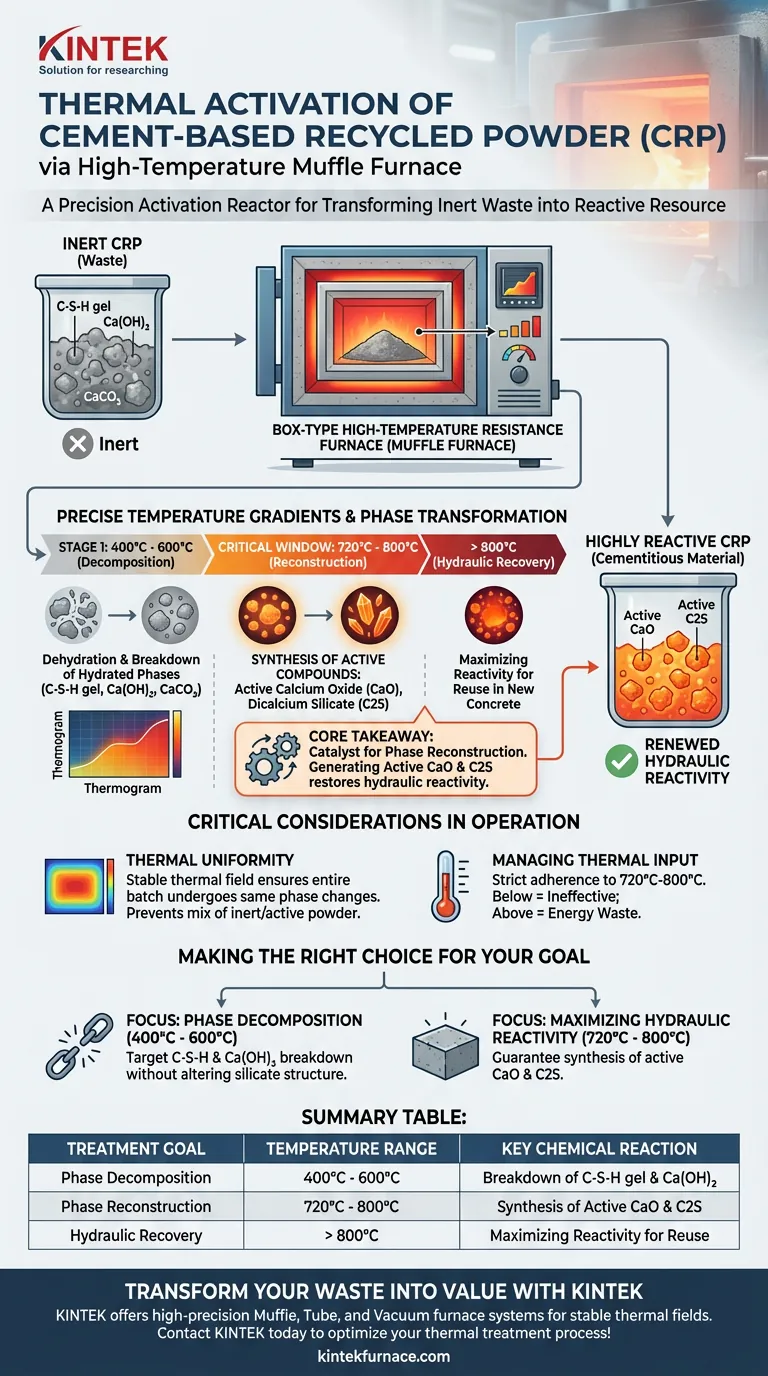
A box-type high-temperature resistance furnace functions as a precision activation reactor for Cement-based Recycled Powder (CRP). It provides a strictly controlled calcination environment that thermally decomposes inert hydrated phases within the waste powder. By applying specific temperature gradients, the furnace drives chemical transformations that convert low-activity waste into highly reactive cementitious material.
Core Takeaway: The Muffle furnace is not merely a heating device; it is the catalyst for phase reconstruction. By targeting the critical 720°C to 800°C window, it facilitates the generation of active Calcium Oxide (CaO) and Dicalcium Silicate (C2S), fundamentally restoring the hydraulic reactivity of the recycled powder.

The Mechanics of Thermal Activation
Precise Temperature Gradients
The primary contribution of the Muffle furnace is its ability to maintain exact temperature stages. This is essential for CRP, which requires a multi-step thermal treatment rather than a single blast of heat.
Commonly applied gradients include 400°C, 600°C, and 800°C. Each stage targets specific chemical bonds within the powder, ensuring a uniform transition of the material’s structure.
Decomposition of Hydrated Phases
Before reactivity can be restored, the stable, inert structures formed during the cement's original service life must be broken down.
The high-temperature environment triggers the thermal decomposition of C-S-H gel (Calcium Silicate Hydrate). Simultaneously, it breaks down calcium hydroxide and calcium carbonate present in the recycled matrix.
Chemical Transformation and Reactivity
The Critical Temperature Window
While decomposition occurs at lower temperatures, the regeneration of high-value chemical activity is temperature-specific.
The most critical reactions occur between 720°C and 800°C. The Muffle furnace must sustain this high-energy environment to push the material past simple dehydration and into phase transformation.
Formation of Active Compounds
Within this specific high-temperature window, the furnace facilitates the formation of active calcium oxide (CaO) and dicalcium silicate (C2S).
These compounds are the key to the material's renewed utility. Their formation significantly enhances the chemical activity of the powder, allowing it to react hydraulically again when mixed with water in new concrete formulations.
Critical Considerations in Furnace Operation
The Importance of Uniformity
The "box-type" design of the Muffle furnace is crucial for creating a stable thermal field.
Just as in the heat treatment of alloys or ores, thermal uniformity ensures that the entire batch of powder undergoes the same phase changes. Inconsistent heating would lead to a mix of inert and active powder, degrading the overall performance of the recycled material.
Managing Thermal Input
Operators must strictly adhere to the identified temperature ranges.
Failing to reach the 720°C threshold prevents the formation of active CaO and C2S, rendering the process ineffective for activity enhancement. Conversely, precise control prevents unnecessary energy expenditure once the optimal phase transformation is achieved.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of Cement-based Recycled Powder, align your furnace settings with your specific chemical objectives.
- If your primary focus is Phase Decomposition: Set temperature gradients at 400°C and 600°C to target the breakdown of C-S-H gel and calcium hydroxide without fully altering the silicate structure.
- If your primary focus is Maximizing Hydraulic Reactivity: Ensure the furnace reaches and stabilizes between 720°C and 800°C to guarantee the synthesis of active CaO and C2S.
The Muffle furnace transforms CRP from a passive waste product into an active chemical resource through precise thermal re-engineering.
Summary Table:
| Treatment Goal | Temperature Range | Key Chemical Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Phase Decomposition | 400°C - 600°C | Breakdown of C-S-H gel and calcium hydroxide |
| Phase Reconstruction | 720°C - 800°C | Synthesis of active CaO and Dicalcium Silicate (C2S) |
| Hydraulic Recovery | > 800°C | Maximizing reactivity for reuse in new concrete |
Transform Your Waste into Value with KINTEK
Precise thermal activation is the difference between inert waste and high-performance recycled materials. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-precision Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum furnace systems designed to maintain the stable thermal fields required for complex phase transformations in CRP and other cementitious materials.
Whether you need customizable temperature gradients or specialized atmosphere control, our systems are engineered to meet your unique lab research and production needs. Contact KINTEK today to optimize your thermal treatment process!
Visual Guide
References
- Jianglin Li, Jianhe Xie. Effect of the Pretreatment on the Properties of Cement-Based Recycled Powder. DOI: 10.3390/coatings14010107
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is a muffle furnace commonly used for in laboratories? Essential for High-Temperature Material Processing
- What role does a Muffle Furnace play in 1100°C oxidation experiments? Precision Thermal Control for Coatings
- Why is a high-temperature box resistance furnace essential for failure analysis? Master TGO Growth and Isothermal Testing
- What role does a box muffle furnace play during the pre-carbonization stage of sugarcane bagasse? Expert Insights
- What is the main drawback of muffle furnaces regarding inert gas dispersion? Learn How to Ensure Uniform Atmosphere
- What is the use of muffle furnace in laboratory? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Heat for Accurate Analysis
- In what way is a muffle furnace used for the quantitative analysis of rice husk components? Essential Ashing Guide
- What is the temperature of a muffle oven? A Guide to Choosing the Right Range for Your Lab



















