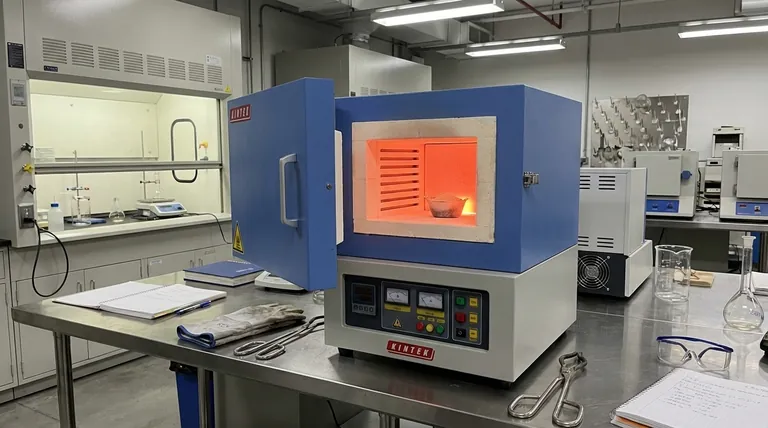
In short, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven that provides a controlled, contamination-free environment. It is used in laboratories to heat materials to extreme temperatures—often up to 1200°C (2192°F) or higher—while isolating them from the direct flame and combustion byproducts of the heat source. This ensures that any changes to the sample are a result of heat alone, not chemical reactions with fuel or gases.
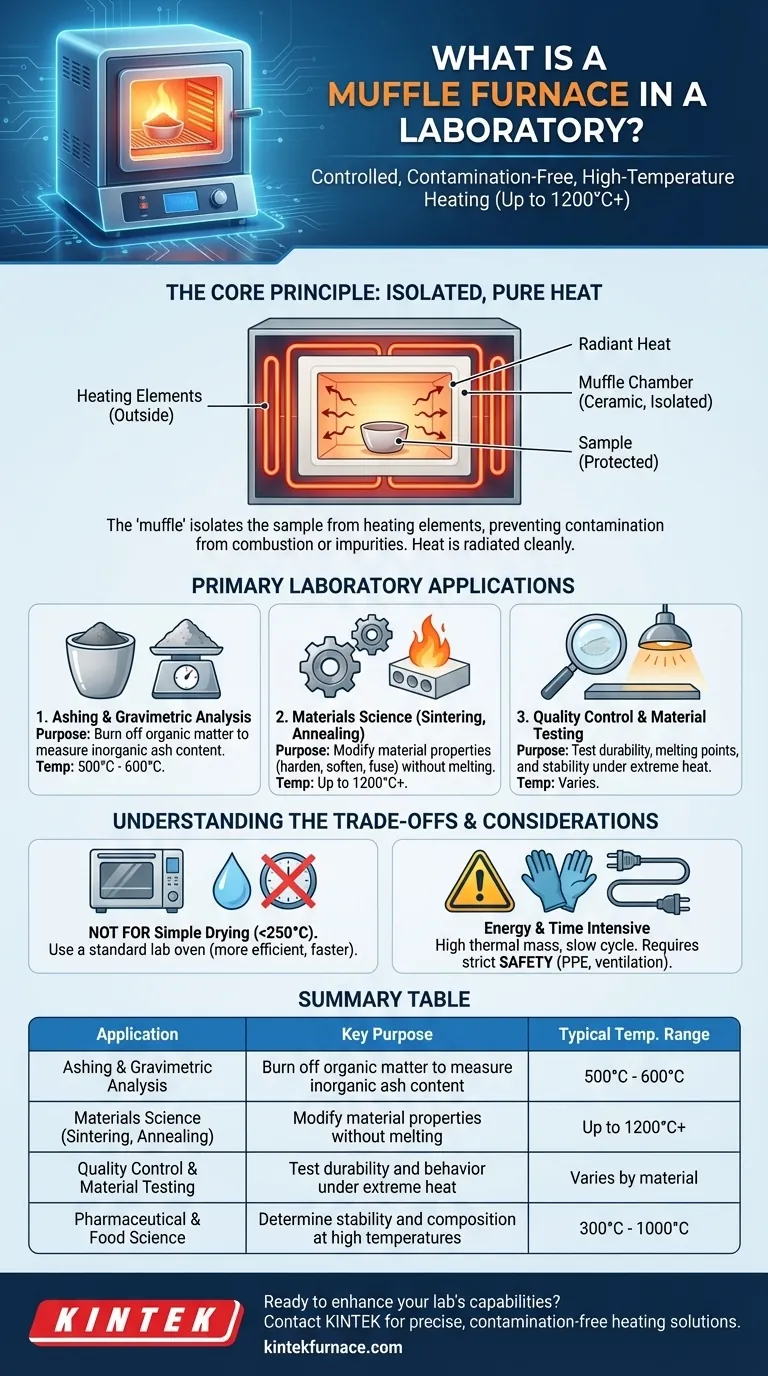
The defining feature of a muffle furnace isn't just its high heat, but its 'muffle'—an inner chamber that isolates the sample from the actual heating elements. This separation is the key to preventing contamination, which is critical for the purity and accuracy of high-temperature analytical tests and material treatments.

The Core Principle: Isolated, High-Temperature Heating
To understand the furnace's use, you must first understand its design. Unlike a simple kiln where fuel and flames might interact with the material, a muffle furnace prioritizes purity.
What is a "Muffle"?
The term muffle refers to the furnace's sealed inner chamber, typically made of a high-temperature ceramic. This chamber shields the sample inside it.
The heating elements (coils) are positioned on the outside of this muffle chamber. They heat the chamber, which then radiates heat evenly and cleanly onto the sample.
Preventing Contamination
For many scientific analyses, any external contaminant can invalidate the results. By isolating the sample, the muffle furnace prevents byproducts of combustion or impurities from the heating elements from reacting with or depositing on the material being tested.
This is essential for determining the true composition of a sample after heating.
Achieving Precise Temperatures
Standard laboratory ovens typically top out around 300°C. A muffle furnace is engineered specifically for high-temperature applications, providing stable and uniform heat distribution required for many advanced material processes and analytical methods.
Primary Laboratory Applications
The combination of high heat and a clean environment makes the muffle furnace indispensable for several key tasks.
Analytical Chemistry: Ashing and Gravimetric Analysis
The most common laboratory use is ashing. This process involves heating a sample at high temperatures (e.g., 500-600°C) to burn off all organic matter and volatile compounds.
What remains is the ash, which is the non-combustible, inorganic residue. By weighing the sample before and after ashing, analysts can precisely determine its ash content, a critical quality metric in food science, environmental testing, and pharmaceuticals. The ash can then be used for further elemental analysis.
Materials Science: Treatment and Synthesis
Muffle furnaces are central to creating and testing new materials.
Key processes include heat treatment of metals, such as annealing (to soften and relieve stress) or hardening. They are also used for sintering, a process that fuses powdered materials like ceramics or metals into a solid piece using heat without melting them.
Quality Control and Material Testing
Industries use muffle furnaces to test the durability and properties of their products. A material might be subjected to extreme temperatures to see how it behaves, ensuring it meets specifications.
This also includes determining the melting point of substances, testing the stability of pharmaceutical drugs at high temperatures, and analyzing the composition of glass and ceramics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is a specialized tool and is not always the right choice.
Not for All Heating Tasks
For simple drying of samples at low temperatures (below 250°C), a standard laboratory oven is far more efficient and appropriate. Using a muffle furnace for such a task is unnecessary and consumes significantly more energy.
Energy and Time Consumption
Due to their high thermal mass and insulation, muffle furnaces consume a large amount of electricity. They also take a considerable amount of time to reach their target temperature and, more importantly, to cool down safely. This slow thermal cycle must be factored into any laboratory workflow.
Significant Safety Considerations
Operating at temperatures that can melt metal presents obvious hazards. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE), including heat-resistant gloves and face shields, is mandatory. The area must be well-ventilated, and users must be trained on safe operating procedures to prevent severe burns and fires.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge effectively, match the tool to your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis (e.g., ash content): The muffle furnace is essential for complete and clean combustion, ensuring your results are accurate and free from contamination.
- If your primary focus is modifying material properties (e.g., metals, ceramics): This furnace is the standard tool for high-temperature processes like sintering, annealing, and hardening.
- If your primary focus is simple sample drying or moisture removal: A standard laboratory drying oven is the more efficient and cost-effective choice.
Understanding that a muffle furnace's purpose is to deliver pure, isolated heat is the key to using it correctly and effectively.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Purpose | Typical Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Ashing & Gravimetric Analysis | Burn off organic matter to measure inorganic ash content | 500°C - 600°C |
| Materials Science (Sintering, Annealing) | Modify material properties without melting | Up to 1200°C+ |
| Quality Control & Material Testing | Test durability and behavior under extreme heat | Varies by material |
| Pharmaceutical & Food Science | Determine stability and composition at high temperatures | 300°C - 1000°C |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precise, contamination-free heating?
At KINTEK, we understand that accurate results depend on reliable equipment. Our advanced muffle furnaces are engineered with exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to deliver the pure, isolated high-temperature environment your analytical and material science work demands.
Whether you're performing gravimetric analysis, sintering ceramics, or testing material durability, our solutions—including our customizable Muffle Furnaces—are designed to meet your specific experimental requirements with precision and consistency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK muffle furnace can bring superior performance and reliability to your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















