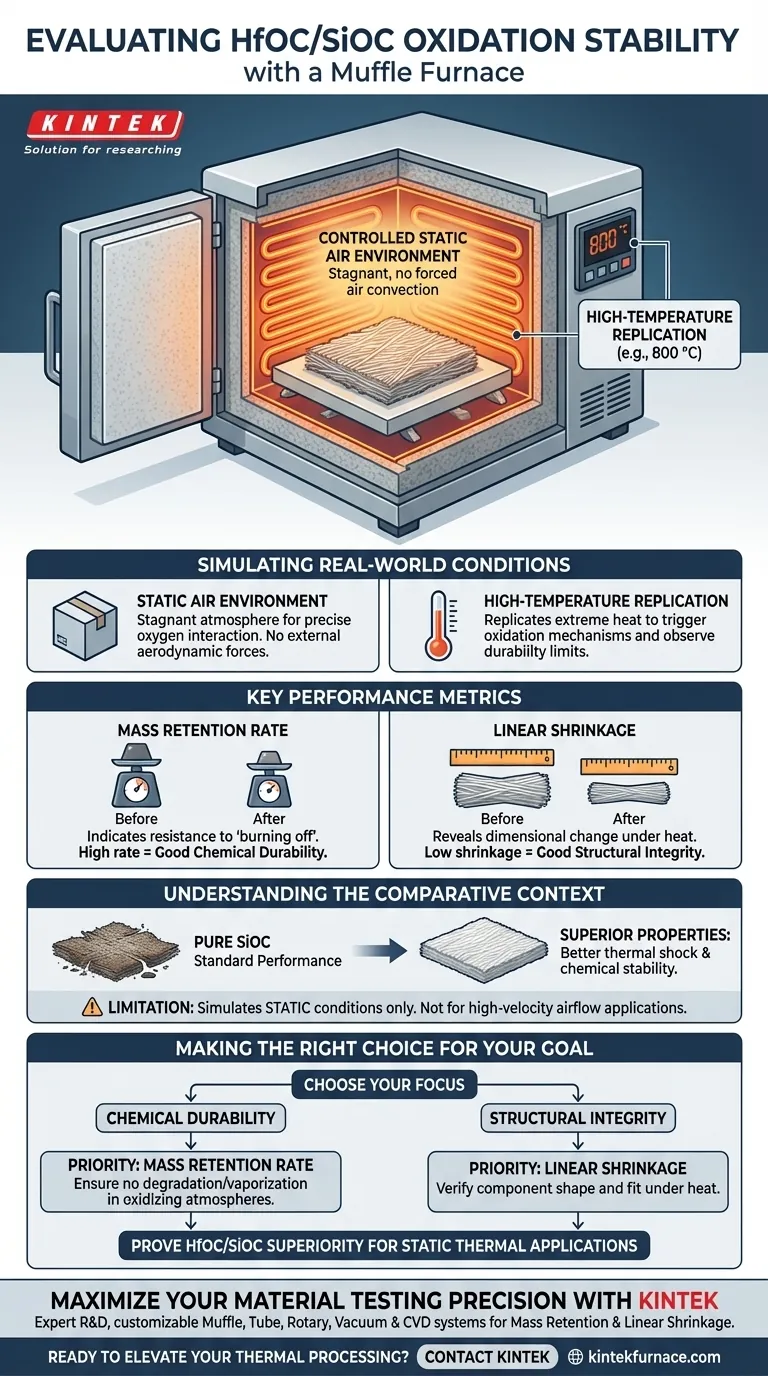
A muffle furnace provides a controlled, static air environment specifically designed to simulate high-temperature service conditions. By subjecting HfOC/SiOC fiber mats to this environment at temperatures such as 800 °C, researchers can isolate the material's response to oxidation without the interference of forced air convection.
The muffle furnace creates a baseline environment to objectively quantify physical stability. It is the primary tool for verifying that HfOC/SiOC composites offer superior thermal shock resistance and chemical stability compared to standard pure SiOC fibers.

Simulating Real-World Conditions
The Static Air Environment
The defining characteristic of the muffle furnace in this context is the provision of static air.
Unlike flow-through systems, this environment simulates conditions where the atmosphere around the material is stagnant. This allows for a precise evaluation of how the material interacts with oxygen when not subjected to external aerodynamic forces.
High-Temperature Replication
To accurately assess oxidation stability, the furnace must replicate the extreme heat of actual service environments.
Tests are frequently conducted at specific high-temperature benchmarks, such as 800 °C. This thermal load is sufficient to trigger oxidation mechanisms, allowing researchers to observe the material's durability limits.
Key Performance Metrics
Measuring Mass Retention
One of the primary indicators of oxidation stability is the mass retention rate.
By weighing the HfOC/SiOC fiber mats before and after the controlled heating cycle, researchers calculate how much material remains. A high retention rate indicates that the composite resists degrading or "burning off" into volatile oxides.
Assessing Linear Shrinkage
Dimensional stability is just as critical as chemical stability.
The muffle furnace test measures linear shrinkage, which reveals if the fiber mat contracts under heat. Low shrinkage rates suggest that the material maintains its structural integrity and shape despite the thermal stress.
Understanding the Comparative Context
Benchmarking Against SiOC
The ultimate goal of this testing is to establish a clear comparison with other materials.
The data derived from the muffle furnace is used to verify that HfOC/SiOC composites possess superior properties relative to pure SiOC fibers. Without this controlled comparison, the specific advantages of the HfOC formulation—specifically regarding thermal shock resistance—cannot be objectively validated.
The Limitation of Static Testing
While valid for many applications, it is important to recognize that a muffle furnace simulates static conditions.
If the intended end-use application involves high-velocity airflow or rapid pressure changes, static air testing may not capture all relevant failure modes. It is best used to determine fundamental chemical stability and thermal resistance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the value of muffle furnace testing for HfOC/SiOC materials, focus on the specific metric that aligns with your engineering requirements:
- If your primary focus is Chemical Durability: Prioritize the mass retention rate data to ensure the material does not degrade or vaporize in oxidizing atmospheres.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Analyze the linear shrinkage results to verify the component will maintain its shape and fit within an assembly under heat.
Use this environment to prove that your HfOC/SiOC composite outperforms standard SiOC alternatives in harsh, static thermal applications.
Summary Table:
| Condition/Metric | Description | Importance for HfOC/SiOC |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Static Air (Non-convective) | Simulates stagnant service conditions to isolate oxidation effects. |
| Temperature | Typically 800 °C | Replicates high-heat service environments to trigger oxidation. |
| Mass Retention | Weight loss measurement | Quantifies chemical durability and resistance to degradation. |
| Linear Shrinkage | Dimensional change | Evaluates structural integrity and resistance to thermal stress. |
Maximize Your Material Testing Precision with KINTEK
Ensure your advanced composites meet the highest standards of oxidation stability and thermal resistance. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides a comprehensive range of high-temperature lab equipment, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Whether you are evaluating mass retention or linear shrinkage of fiber mats, our furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research and industrial needs.
Ready to elevate your thermal processing? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace solution and discover why leading researchers trust our precision equipment.
Visual Guide
References
- Arijit Roy, Gurpreet Singh. Preparation and characterization of HfOC/SiOC composite powders and fibermats <i>via</i> the polymer pyrolysis route. DOI: 10.1039/d5ra02006a
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the common transport methods used in Muffle Furnaces? Choose the Right System for Your Lab
- How does a Box Resistance Furnace function for nanocellulose films? Master the Stabilization Phase for Better Films
- What role does a box muffle furnace play in life sciences? Unlock Precise Mineral Analysis in Research
- What safety features are included in muffle furnaces? Ensure Operator Protection and Lab Safety
- How does a bench-top high-temperature furnace ensure the quality of the ceramic layer? Master CCT for Ti6242 Alloy
- What specific functions must an industrial electric furnace perform for concrete fire testing? Master Thermal Cycles
- What are some specific applications of muffle furnaces? Unlock Precision in Heat Treatment and Analysis
- What are the different types of muffle furnaces based on heating elements? Choose the Right One for Your Lab



















