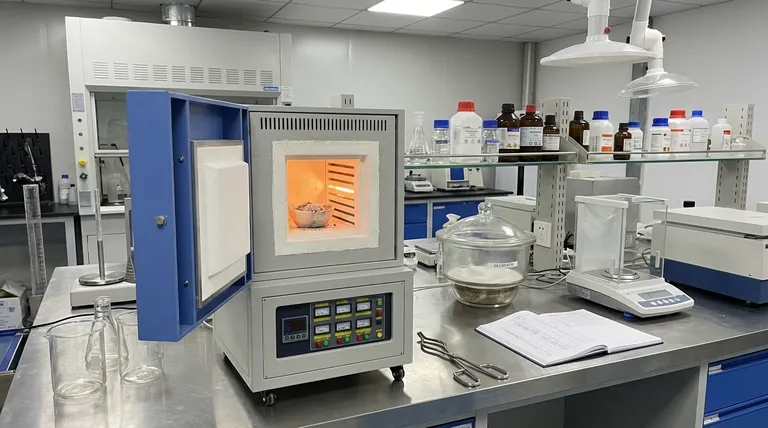
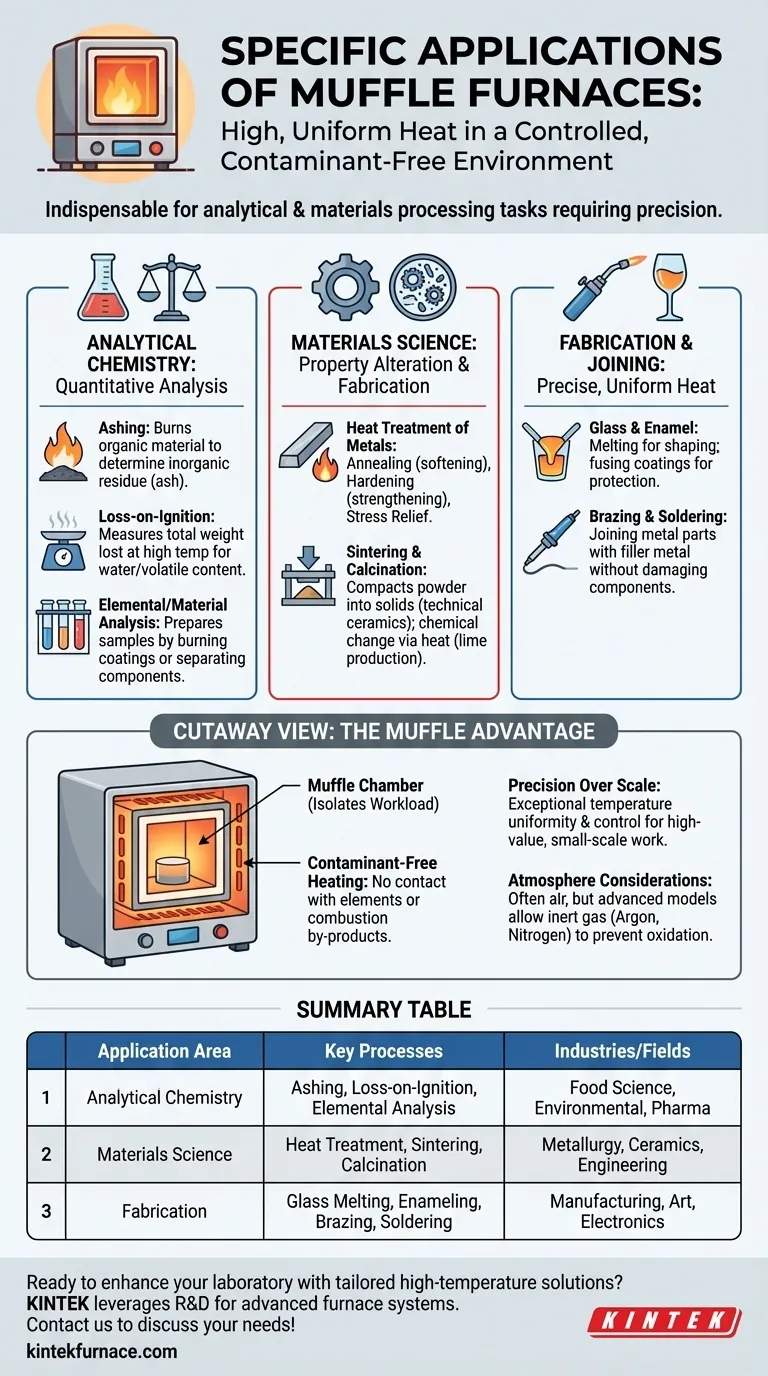
In short, muffle furnaces are indispensable tools for any process requiring high, uniform heat in a controlled and contaminant-free environment. Their applications span from fundamental chemical analysis in laboratories, such as determining the ash content of a sample, to advanced materials processing in industry, like creating technical ceramics and heat-treating metals.
A muffle furnace's true value lies in its unique ability to isolate a sample from the heating elements. This separation provides a precisely controlled, pure high-temperature environment, making it the essential tool for tasks where chemical purity and temperature uniformity are non-negotiable.

Core Applications in Analytical Chemistry
The clean heating environment of a muffle furnace is critical for quantitative analysis, where any contamination would skew the results.
Ashing and Loss-on-Ignition
Ashing is a process that burns away all organic material in a sample to determine the weight of the inorganic, non-combustible residue (ash). This is fundamental in food science, environmental testing, coal quality analysis, and the pharmaceutical industry.
Loss-on-ignition is a similar technique that measures the total weight lost from a sample when it is heated to a high temperature, often used to determine water or volatile organic content.
Elemental and Material Analysis
In metallurgy and materials science, furnaces are used to prepare samples for further analysis. This can involve burning off coatings, testing thermal degradation in polymers, or separating components based on their combustion temperatures.
Essential Processes in Materials Science and Engineering
Muffle furnaces are used to fundamentally change the physical properties of materials or to fabricate new ones from raw components.
Heat Treatment of Metals
Heat treatment involves carefully controlled heating and cooling cycles to alter a material's microstructure, thereby changing its properties. Common processes include:
- Annealing: Softening a metal and relieving internal stresses to improve ductility.
- Hardening: Increasing the hardness and strength of steel by heating and then rapidly cooling it.
- Stress Relief: Reducing internal stresses caused by manufacturing processes like welding or machining.
Sintering and Calcination
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material from powder using heat, but without melting it to the point of liquefaction. This is a primary method for producing technical ceramics and certain metal parts.
Calcination involves heating a material to induce a chemical change, such as driving off carbon dioxide from limestone to produce lime.
Fabrication and Joining
The precise, uniform heat of a muffle furnace makes it ideal for several fabrication tasks:
- Glass and Enamel: Melting glass for artistic or technical shaping, and fusing enamel coatings onto metal surfaces for a durable, protective finish.
- Brazing and Soldering: Joining metal parts together using a filler metal with a lower melting point. The furnace provides the consistent heat needed to melt the filler without damaging the components being joined.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Core Features
While incredibly versatile, a muffle furnace is a specialized tool. Understanding its defining features helps clarify its ideal use cases.
The "Muffle" Advantage: Contaminant-Free Heating
The defining feature is the "muffle"—an inner chamber that isolates the workload from the heating elements and any fuel combustion by-products. This is what prevents contamination and ensures the purity of analytical results.
Precision Over Scale
Muffle furnaces offer exceptional temperature uniformity and control, which is why they are fixtures in laboratories and for small-scale, high-value industrial production. They are not, however, designed for the large-volume melting seen in foundries, which use different types of furnaces.
Atmosphere Considerations
Most standard muffle furnaces operate in air. However, some advanced models allow for a controlled atmosphere, where the air is replaced with an inert gas like argon or nitrogen. This is crucial for heat-treating materials that would otherwise oxidize at high temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right process, identify your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is analytical testing: Your goal is quantitative measurement, so leveraging the furnace's clean, contaminant-free environment for ashing or loss-on-ignition is key.
- If your primary focus is materials processing: You need to alter a material's properties, making processes like annealing, hardening, and sintering the correct application of the furnace's precise temperature control.
- If your primary focus is fabrication or joining: The furnace's ability to provide uniform, high heat is essential for melting glass, curing enamel, or executing high-temperature brazing.
By understanding its core capabilities, you can leverage the muffle furnace not just as a source of heat, but as a precision instrument for your specific scientific or industrial goal.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Processes | Industries/Fields |
|---|---|---|
| Analytical Chemistry | Ashing, Loss-on-Ignition, Elemental Analysis | Food Science, Environmental Testing, Pharmaceuticals |
| Materials Science | Heat Treatment (Annealing, Hardening), Sintering, Calcination | Metallurgy, Ceramics, Materials Engineering |
| Fabrication | Glass Melting, Enameling, Brazing, Soldering | Manufacturing, Art, Electronics |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with tailored high-temperature solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs in analytical chemistry, materials science, and fabrication. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















