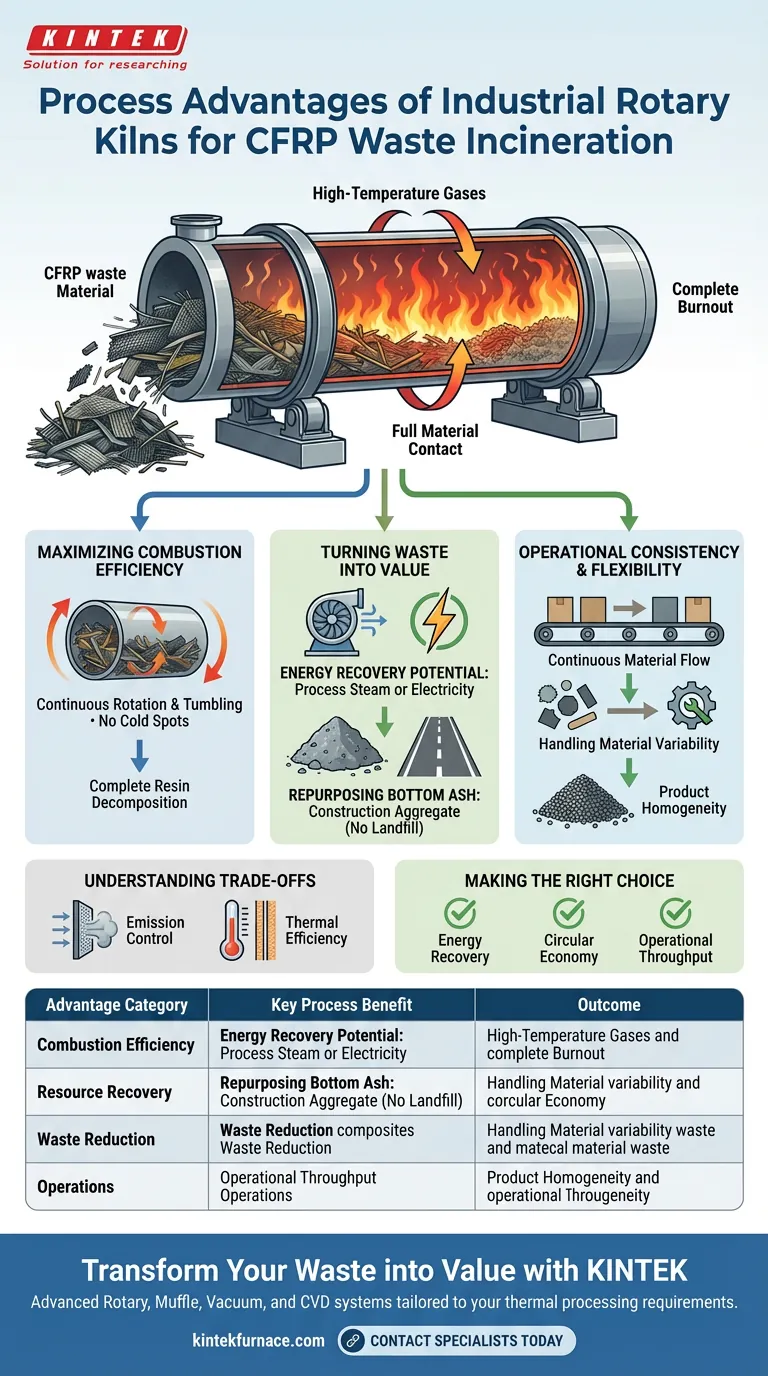
The primary process advantage of using industrial rotary kilns for Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) waste lies in the equipment's ability to ensure full material contact with high-temperature gases through continuous rotation. This mechanical action guarantees complete burnout of the complex composite matrix while simultaneously facilitating the recovery of energy in the form of steam or electricity and converting solid residue into usable construction aggregate.
While standard incineration methods often struggle with the complex composition of CFRP, the rotary kiln acts as a dual-purpose solution for disposal and recovery. It solves the "burnout" problem through constant motion while transforming the waste stream into viable energy and construction resources.
Maximizing Combustion Efficiency
The Role of Continuous Rotation
The fundamental advantage of the rotary kiln is its dynamic nature. As the kiln rotates, the CFRP waste is continuously tumbled and turned.
Achieving Full Gas Contact
This tumbling action ensures that every surface of the waste material makes contact with the high-temperature gas. This eliminates "cold spots" that often occur in static incineration, ensuring the resin matrix is completely decomposed.
Turning Waste into Value
Energy Recovery Potential
The incineration of CFRP generates significant thermal energy. Rotary kiln systems are designed to capture this heat, converting it into process steam or electricity to power facility operations.
Repurposing Bottom Ash
The process does not end with combustion. The resulting solid residue, known as bottom ash, is stabilized and collected.
Eliminating Landfill Waste
Instead of requiring disposal, this ash can be chemically suitable for use as construction aggregate. This achieves effective resource utilization and significantly reduces the volume of waste sent to landfills.
Operational Consistency and Flexibility
Continuous Material Flow
Unlike batch processing, rotary kilns allow for a constant feed of material. This supports uninterrupted production cycles, making it ideal for facilities managing high volumes of waste.
Handling Material Variability
CFRP waste streams can be inconsistent in size and composition. Rotary kilns offer high design flexibility, allowing operators to adapt the process to different waste profiles without sacrificing performance.
Product Homogeneity
The mixing action of the kiln ensures the final ash product is uniform. This homogeneity is critical if the byproduct is to be successfully resold or reused in construction applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Emission Control Requirements
Incinerating CFRP involves breaking down toxic components and resins. While kilns effectively reduce waste volume, they must be equipped with rigorous filtration and gas control systems to safely manage the resulting emissions.
Thermal Efficiency Dependencies
Modern designs are efficient, but older or poorly insulated units can suffer from heat loss. Achieving maximum thermal efficiency requires modern design standards to minimize energy waste during the high-temperature phases.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goals
To determine if a rotary kiln is the right fit for your CFRP waste management strategy, consider your specific operational targets:
- If your primary focus is Energy Recovery: Prioritize kiln designs that feature integrated boilers or turbines to maximize the conversion of incineration heat into process steam or electricity.
- If your primary focus is Circular Economy: Evaluate the kiln's ability to produce consistent, high-quality bottom ash that meets certification standards for use as construction aggregate.
- If your primary focus is Operational Throughput: Leverage the continuous heat treatment capabilities of the kiln to maintain constant material flow and eliminate downtime associated with batch processing.
By leveraging the rotary kiln’s mechanical advantages, you transform a hazardous waste liability into a consistent source of energy and raw material.
Summary Table:
| Advantage Category | Key Process Benefit | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Combustion Efficiency | Continuous rotation and tumbling | Complete resin decomposition; no cold spots |
| Resource Recovery | Thermal energy capture | Generation of process steam or electricity |
| Waste Reduction | Bottom ash stabilization | Conversion of waste into construction aggregate |
| Operations | Continuous material flow | High-volume throughput and product homogeneity |
Transform Your Waste into Value with KINTEK
Is your facility ready to optimize the recovery of CFRP and other complex materials? Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides advanced Rotary, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored to your thermal processing requirements.
Our customizable high-temperature lab and industrial furnaces ensure superior performance for energy recovery and material recycling. Partner with KINTEK to leverage our technical expertise in sustainable waste management—contact our specialists today to design a solution that meets your unique operational needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Charitidis J. Panagiotis. Recycling of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Composites-A Review. DOI: 10.48175/ijarsct-17474
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a rotary kiln electric furnace and what is its primary function? Achieve Uniform High-Temp Processing
- What industries can benefit from using electromagnetic induction rotary kilns? Boost Efficiency and Quality in Thermal Processing
- How does the design of electromagnetic induction rotary kilns contribute to operational safety? Enhance Safety with Advanced Heating Technology
- What is reduction firing and which type of kiln supports it? Unlock Unique Ceramic Colors with Gas Kilns
- How do gas and electric kilns differ in portability? Choose the Right Kiln for Your Mobile Studio
- What are some common processes carried out in rotary kilns? Unlock Efficient Material Transformation Solutions
- How does the design of a rotary kiln facilitate material movement? Optimize Material Flow for Consistent Processing
- What are the two main types of rotary kilns based on heating methods? Choose the Right Kiln for Your Process



















