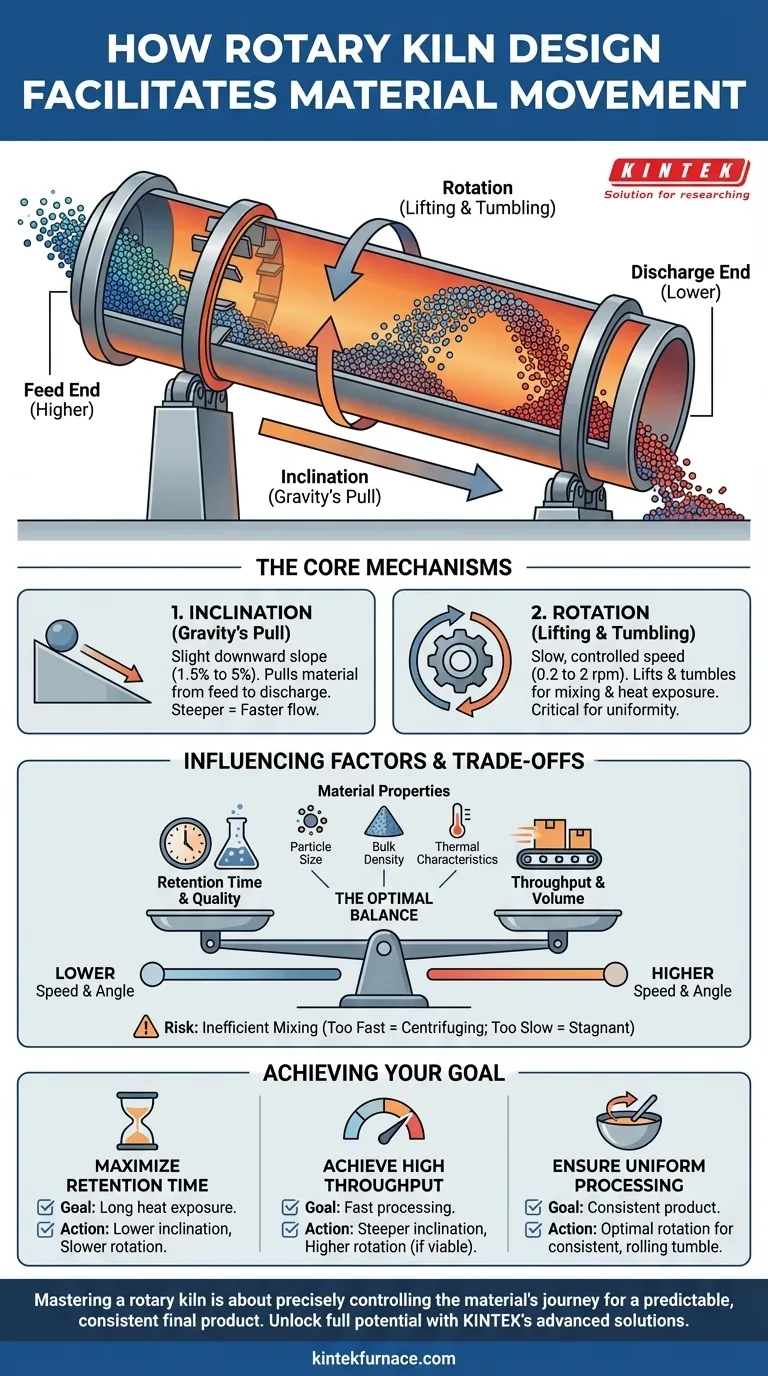
At its core, a rotary kiln's design facilitates material movement through a simple yet highly effective combination of two primary forces: gravity and mechanical tumbling. The long, cylindrical vessel is set at a slight downward angle, and as it rotates slowly, material is continuously lifted and then tumbles forward, creating a controlled, cascading flow from the feed end to the discharge end.
The genius of the rotary kiln is not just that it moves material, but that it does so in a way that guarantees continuous mixing and uniform exposure to heat. This controlled transport is the fundamental principle that enables consistent physical and chemical transformations.
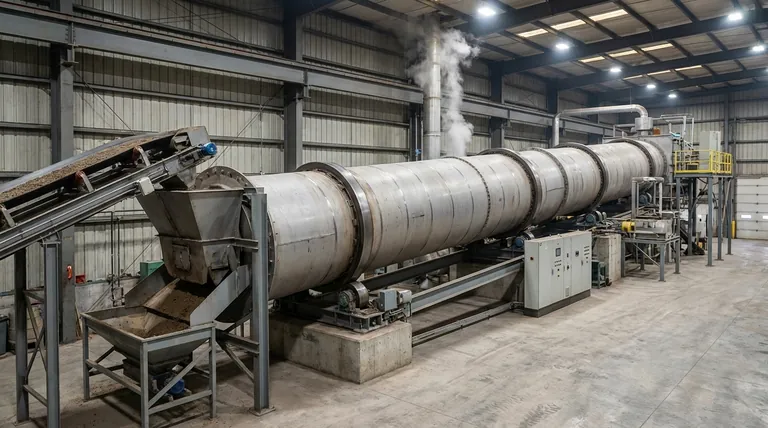

The Core Mechanisms of Material Transport
The movement of material, or "charge," through a rotary kiln is not accidental. It is the result of two intentionally designed physical characteristics working in concert.
The Role of Inclination (Gravity's Pull)
A rotary kiln is always installed with a slight downward slope, typically ranging from 1.5% to 5%.
This inclination ensures that gravity constantly acts on the material, pulling it from the higher feed end toward the lower discharge end. The steeper the angle, the faster the material will naturally want to travel through the kiln.
The Function of Rotation (Lifting and Tumbling)
The kiln rotates on its longitudinal axis at a very slow, controlled speed, usually between 0.2 and 2 revolutions per minute (rpm).
This rotation lifts the material up the side of the kiln wall. Once the material reaches a certain height—determined by its angle of repose—it tumbles back down toward the bottom of the kiln bed. Because the kiln is inclined, each tumble results in a small amount of forward progress.
This constant lifting and tumbling action is critical for mixing the material thoroughly, ensuring that new surfaces are constantly exposed to the kiln's internal atmosphere and heat source.
How Material Properties Influence Movement
The kiln's design provides the framework for movement, but the specific characteristics of the material being processed dictate how it will behave inside the kiln and influence design parameters.
Particle Size and Bulk Density
Materials with a wide particle size distribution may segregate during tumbling, with larger particles moving differently than finer ones.
High bulk density materials require more energy to lift and tumble, often necessitating more robust drives and support structures for the kiln. Conversely, pelletized feeds are uniform and can allow for smaller kiln diameters.
Thermal and Chemical Characteristics
The material's thermal properties, such as its resistance to heating (specific heat) and its ability to transfer heat (thermal conductivity), determine the necessary retention time.
To achieve a longer retention time for materials that heat slowly or require extensive chemical reactions, the kiln's inclination or rotation speed must be decreased. This slows the material's forward progress, giving it more time inside the hot zone.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing a rotary kiln involves balancing competing operational goals. The primary trade-off is between throughput and retention time.
Adjusting Speed vs. Angle
Increasing either the rotation speed or the inclination angle will increase the rate at which material moves through the kiln, thereby increasing throughput.
However, this comes at the cost of reduced retention time. This can be detrimental if the material requires a specific duration of heat exposure to complete its chemical or physical transformation.
The Risk of Inefficient Mixing
If the rotation speed is too high, material may begin to "centrifuge," sticking to the kiln wall instead of tumbling. This eliminates mixing and leads to poor heat transfer and non-uniform product.
If the speed is too low, the kiln may not achieve the tumbling action required for proper mixing, resulting in a stagnant bed of material with inefficient heat exposure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The operational parameters of a rotary kiln must be set based on the desired outcome for the specific material being processed.
- If your primary focus is maximizing retention time: Opt for a lower inclination angle and a slower rotation speed to ensure the material spends the maximum possible time in the kiln.
- If your primary focus is achieving high throughput: Use a steeper inclination angle and a higher rotation speed, provided the required material transformation can be completed in a shorter time.
- If your primary focus is ensuring uniform processing: Prioritize a rotation speed that creates a consistent, rolling tumble, which is the key to thorough mixing and even heat distribution.
Ultimately, mastering a rotary kiln is about precisely controlling the material's journey to achieve a predictable and consistent final product.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | Function | Key Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Inclination | Uses gravity to pull material from feed to discharge end | Slope: 1.5% to 5% |
| Rotation | Lifts and tumbles material for mixing and forward movement | Speed: 0.2 to 2 rpm |
| Material Properties | Influence movement and kiln design adjustments | Particle size, bulk density, thermal characteristics |
| Trade-offs | Balance throughput vs. retention time for optimal processing | Adjust speed and angle based on goals |
Unlock the full potential of your material processing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with rotary kilns and other systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and consistency. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency



















