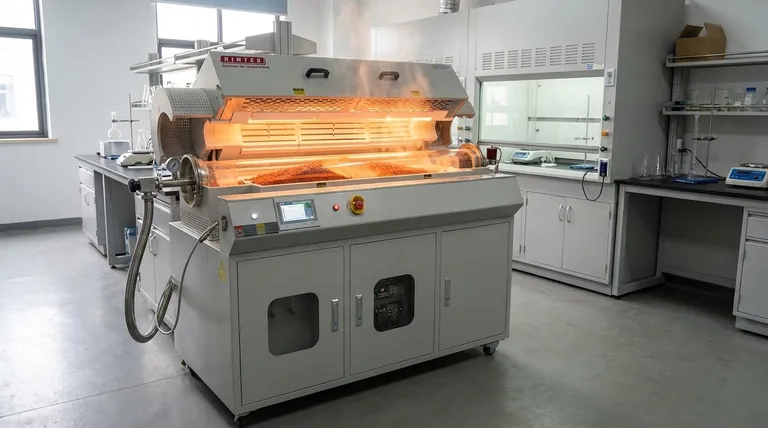
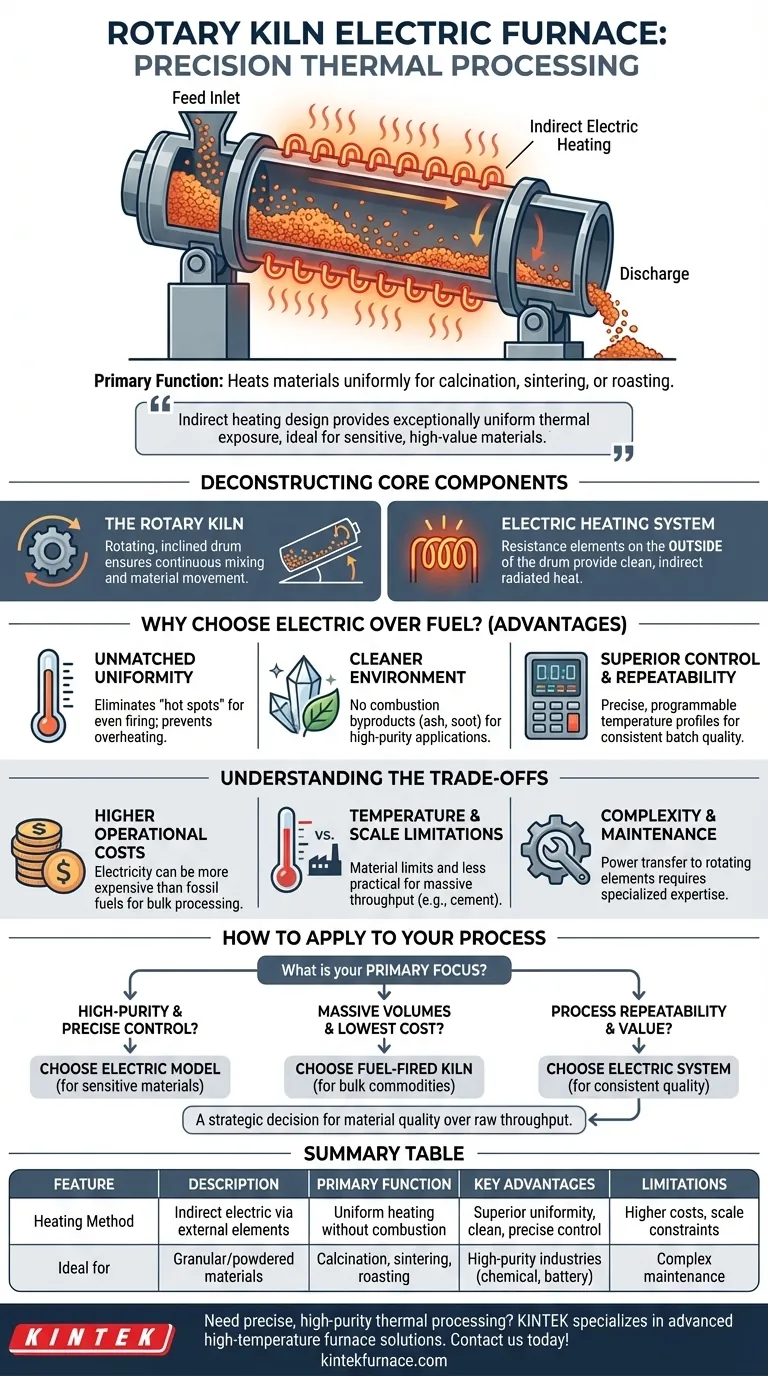
In essence, a rotary kiln electric furnace is a specialized piece of thermal processing equipment that combines a rotating, inclined cylinder with an external electric heating system. Its primary function is to heat granular or powdered materials to very high temperatures with exceptional uniformity, inducing physical changes or chemical reactions like calcination, sintering, or roasting.
While many industrial heating methods struggle with temperature consistency, the rotary kiln electric furnace separates the heating source from the material. This indirect heating design provides exceptionally uniform thermal exposure, making it the ideal choice for sensitive, high-value materials where precise control is non-negotiable.

Deconstructing the Core Components
A rotary kiln electric furnace is best understood by examining its two fundamental systems: the mechanical rotation and the electric heating. These two elements work in concert to achieve results that are difficult to replicate with other methods.
The Rotary Kiln: A Foundation of Movement
The core of the device is a long, cylindrical vessel, or drum, that is slightly inclined from the horizontal. This cylinder rotates slowly on its axis.
Material is fed into the higher end of the kiln. As the kiln rotates, the material tumbles and gradually moves down the slope toward the discharge end, ensuring every particle is continuously mixed and exposed to the heat.
The Electric Heating System: The Key to Precision
Unlike traditional fuel-fired kilns where a flame is introduced directly into the drum, an electric model uses resistance heating elements mounted on the outside of the rotating cylinder.
This is a form of indirect heating. The electric elements heat the kiln's body, which then radiates that heat evenly and consistently to the material tumbling inside. This prevents direct contact with flames or combustion byproducts.
Why Choose Electric Heating Over Traditional Fuel?
The decision to use an electric heating source is deliberate and driven by the need for a higher degree of process control. It offers distinct advantages over kilns that burn gas, oil, or coal.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
Because the heat source surrounds the kiln drum, it delivers a consistent radial temperature. This eliminates the "hot spots" and temperature gradients common in direct-fired kilns, preventing uneven firing or overheating of the material.
A Cleaner Processing Environment
With no combustion occurring inside the kiln, the material is not contaminated by ash, soot, or other byproducts of burning fuel. This is critical for applications requiring high purity, such as in the chemical, battery material, and pharmaceutical industries.
Superior Control and Repeatability
Electric heating offers precise, digital control over temperature profiles. The rate of heating, the holding temperature, and the cooling rate can be programmed and executed with high accuracy, ensuring that every batch is processed under the exact same conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the rotary kiln electric furnace is not a universal solution. Its specialized design comes with specific considerations.
Higher Operational Costs
Electricity is often a more expensive energy source per BTU than natural gas or other fossil fuels. For large-scale, bulk material processing, the operational cost of an electric kiln can be significantly higher.
Temperature and Scale Limitations
While capable of achieving very high temperatures, the materials used for electric heating elements and kiln construction can have operational limits. For applications requiring extreme temperatures or massive throughput (like cement production), large, direct-fired kilns are often more practical and economical.
Complexity and Maintenance
The system of transferring power to heating elements on a rotating body can be more complex than a simple fuel burner. Maintenance of these electrical systems requires specialized expertise.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Your choice of kiln technology must align directly with your material, budget, and quality objectives.
- If your primary focus is high-purity output and precise temperature control: The clean, indirect heating and superior uniformity of an electric model is the definitive choice for sensitive materials.
- If your primary focus is processing massive volumes at the lowest operational cost: A traditional, direct-fired fuel kiln is almost always the more economical solution for bulk commodities.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability for high-value products: The digital precision and control of an electric system will ensure consistent quality and minimize batch-to-batch variation.
Ultimately, selecting a rotary kiln electric furnace is a strategic decision to prioritize material quality and process precision over raw throughput.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Heats granular/powdered materials uniformly for calcination, sintering, or roasting. |
| Heating Method | Indirect electric heating via external elements, avoiding combustion byproducts. |
| Key Advantages | Superior temperature uniformity, clean processing, precise digital control, and repeatability. |
| Ideal Applications | High-purity industries like chemicals, battery materials, and pharmaceuticals. |
| Limitations | Higher operational costs, temperature/scale constraints, and complex maintenance. |
Need precise, high-purity thermal processing? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, designed for diverse laboratory needs. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our reliable equipment can enhance your process efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes



















