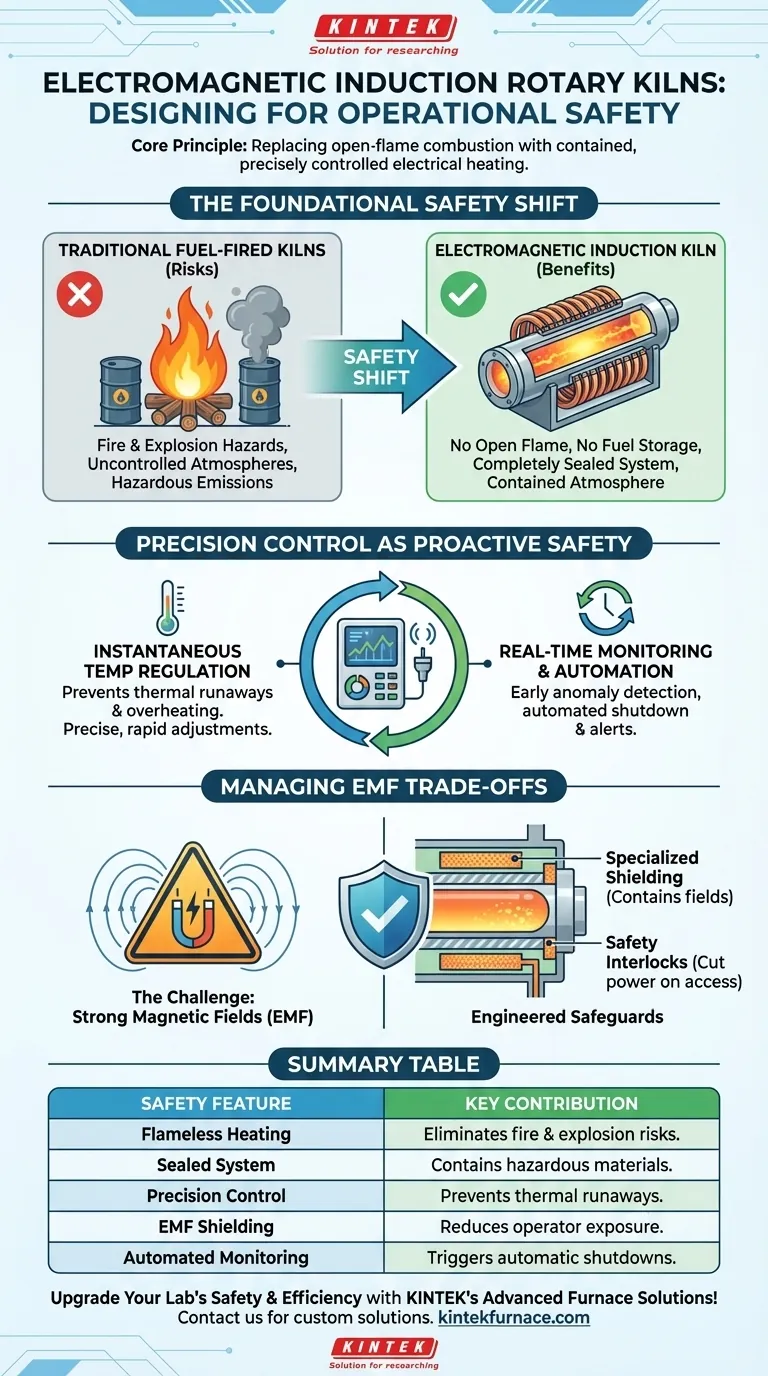
At its core, the design of an electromagnetic induction rotary kiln enhances operational safety by fundamentally replacing open-flame combustion with a contained, precisely controlled electrical heating method. This shift eliminates entire categories of risk associated with fuel storage, combustion byproducts, and thermal instability, while its advanced control systems provide proactive monitoring and automated safeguards.
The primary safety advantage of an electromagnetic induction kiln is not just a single feature, but a systemic change in the heating principle itself. By moving from combustion to electricity, the design inherently removes the hazards of fire, explosion, and uncontrolled atmospheres common in traditional fuel-fired kilns.

The Foundational Safety Shift: From Combustion to Induction
The most significant safety contributions stem from the decision to use electromagnetic induction as the heat source. This choice has cascading benefits throughout the entire system design.
Eliminating Open Flames and Fuel Hazards
Traditional kilns rely on direct or indirect firing with gas, oil, or coal. This introduces inherent risks that induction heating completely avoids.
Induction heating generates heat directly within the material or a susceptor inside the kiln tube using a magnetic field. This means there is no open flame, no fuel lines, and no need for large-scale fuel storage on-site, drastically reducing the risk of fires and explosions.
Containing the Process Atmosphere
Because induction heating requires no oxygen for combustion, the kiln can be a completely sealed system. The reference to "sealed ends for atmosphere control" is a critical safety feature this enables.
This containment prevents the escape of hazardous dust, toxic off-gassing from the processed material, or the release of specific controlled atmospheres (like nitrogen or argon) into the operator environment.
Precision Control as a Proactive Safety Mechanism
Electromagnetic induction is an electrical process, lending itself to a level of control that is difficult to achieve with combustion.
Instantaneous Temperature Regulation
The power to the induction coils can be adjusted instantaneously, allowing for extremely precise and rapid temperature control. This prevents thermal runaways and material overheating, which can damage equipment and create hazardous situations.
Advanced control systems constantly monitor temperature and can make micro-adjustments in real-time, ensuring the process stays within safe operational parameters without manual intervention.
Real-Time Monitoring and Automation
Modern induction kilns are integrated with sophisticated sensors and PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems. These systems provide early detection of any operational anomalies.
Should an issue arise, such as a change in motor load or a temperature deviation, the system can trigger an automated shutdown or alert operators long before the problem escalates into a safety incident.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Managing Electromagnetic Fields (EMF)
While induction technology eliminates many traditional hazards, it introduces a new consideration that must be properly managed: electromagnetic fields.
The Nature of Induction and EMF
The process of inducing a current to generate heat inherently creates a strong magnetic field around the induction coils. Unmitigated exposure to high levels of EMF can be a health concern for personnel.
Engineered Safeguards: Shielding and Interlocks
To address this, induction kilns are designed with engineered protective measures. This includes specialized shielding materials built into the kiln's housing that contain the magnetic fields.
Furthermore, safety interlocks are often used on access panels. If a panel is opened during operation, the power to the coils is immediately cut, ensuring operators are not exposed to active fields. These measures ensure the kiln complies with all regulatory standards for workplace safety.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The safety features of an induction kiln are not just incidental; they are a direct result of its core technology. When evaluating this option, consider how these design aspects align with your primary objectives.
- If your primary focus is eliminating fire and explosion risk: The flameless, electrical heating design of an induction kiln is an inherently safer choice than any fuel-fired alternative.
- If your primary focus is processing hazardous or air-sensitive materials: The ability to operate a completely sealed system provides superior containment and operator protection.
- If your primary focus is process stability and automation: The advanced, real-time controls offer proactive safety by preventing deviations before they become critical failures.
Ultimately, the design of an electromagnetic induction kiln translates directly into a more predictable, contained, and fundamentally safer thermal processing environment.
Summary Table:
| Safety Feature | Key Contribution |
|---|---|
| Flameless Heating | Eliminates fire and explosion risks from fuel combustion |
| Sealed System | Contains hazardous materials and prevents toxic gas release |
| Precision Control | Prevents thermal runaways with real-time temperature adjustments |
| EMF Shielding | Reduces electromagnetic field exposure for operator safety |
| Automated Monitoring | Detects anomalies early and triggers automatic shutdowns |
Upgrade your laboratory's safety and efficiency with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems tailored to your unique needs. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for enhanced operational safety and performance. Contact us today to discuss how our products can benefit your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules



















