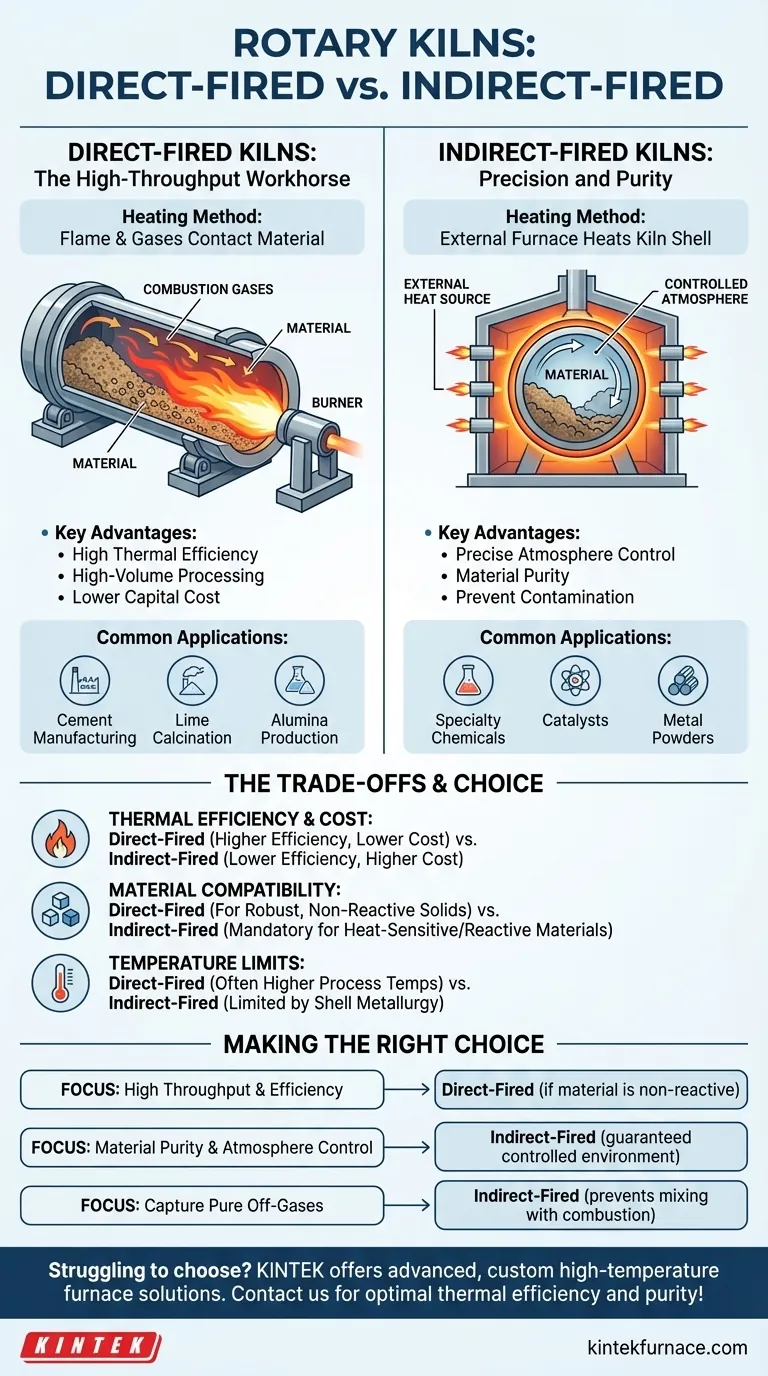
The two primary types of rotary kilns are classified by their heating method: direct-fired and indirect-fired. In a direct-fired kiln, the flame and combustion gases are in direct contact with the material being processed. In an indirect-fired kiln, an external furnace heats the kiln shell, and that heat is transferred through the wall to the material inside, which never touches the combustion gas.
The choice between direct and indirect heating is not about preference; it is dictated by the chemical nature of your material. The central question is whether the material can tolerate direct exposure to combustion byproducts or if it requires the controlled, pure environment that only indirect heating can provide.

Direct-Fired Kilns: The High-Throughput Workhorse
A direct-fired kiln is the most common configuration, valued for its thermal efficiency and ability to process large volumes of material at high temperatures.
The Principle of Direct Contact
In this design, a burner fires a flame directly into the kiln drum, either at the discharge end (counter-current flow) or the feed end (co-current flow). The hot combustion gases flow through the entire length of the kiln, tumbling with and transferring heat directly to the material.
This method is highly effective for transferring energy quickly and efficiently.
Key Advantage: Thermal Efficiency
Because heat is generated and released directly inside the processing chamber, very little energy is lost. This makes direct-fired kilns the most energy-efficient option for reaching and maintaining high process temperatures.
Common Applications
Direct-fired kilns are used for robust, non-reactive bulk solids. They are the industry standard for processes like cement manufacturing, lime calcination, and alumina production, where the material is not negatively affected by the chemical composition of the flue gas.
Indirect-Fired Kilns: Precision and Purity
Indirect-fired kilns, sometimes called calciners, are specialized tools designed for processes where material purity and atmosphere control are paramount.
The Principle of External Heating
The rotary drum is enclosed within a stationary furnace or equipped with an external heating jacket. Burners heat the outside of the drum's shell, and this heat conducts through the metal wall to the material tumbling inside.
This design creates a complete separation between the heating source and the process material.
The Critical Advantage: Atmosphere Control
Because the material is in a sealed environment, the internal atmosphere can be precisely controlled. It can be inert (e.g., nitrogen), reducing (e.g., hydrogen), or oxidizing (e.g., oxygen), preventing unwanted chemical reactions, contamination, or oxidation of the final product.
Common Applications
Indirect kilns are essential for processing heat-sensitive specialty chemicals, catalysts, and certain metal powders. They are also used when off-gases released by the material itself must be captured in a pure form, without being mixed with combustion gases.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Efficiency vs. Purity
Choosing the correct kiln type requires balancing process goals with physical and financial limitations.
Thermal Efficiency and Cost
Direct-fired kilns are more thermally efficient and generally have a lower capital cost for a given throughput. Indirect kilns lose some heat from the external furnace to the surrounding environment and have higher construction complexity, making them more expensive.
Material Compatibility
This is the most critical factor. If your material reacts with oxygen, carbon dioxide, or water vapor at high temperatures, a direct-fired kiln is not a viable option. An indirect-fired kiln is mandatory for protecting product integrity in these cases.
Temperature and Mechanical Limits
Indirect kilns have an upper temperature limit determined by the metallurgical properties of the rotating shell, which must withstand both the high heat and mechanical stresses. Direct-fired kilns can often achieve higher process temperatures as the shell is not the primary point of heat transfer.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your material and process goals will dictate the correct kiln technology.
- If your primary focus is high-volume throughput and thermal efficiency: A direct-fired kiln is the default choice, assuming your material is not reactive with flue gas.
- If your primary focus is material purity and atmosphere control: An indirect-fired kiln is the only option to guarantee a controlled, non-contaminated environment.
- If you need to capture pure off-gases from your material: An indirect-fired kiln is necessary to prevent the process gas from mixing with combustion products.
Understanding this fundamental difference in heating methods is the first step toward specifying the right equipment to achieve your process goals.
Summary Table:
| Kiln Type | Heating Method | Key Advantages | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct-Fired | Flame and gases directly contact material | High thermal efficiency, lower cost, high throughput | Cement, lime calcination, alumina production |
| Indirect-Fired | External furnace heats kiln shell | Precise atmosphere control, material purity, no contamination | Specialty chemicals, catalysts, metal powders |
Struggling to choose the right rotary kiln for your material processing needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including custom rotary kilns. Our expertise ensures optimal thermal efficiency and purity for your specific applications. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your process efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing



















