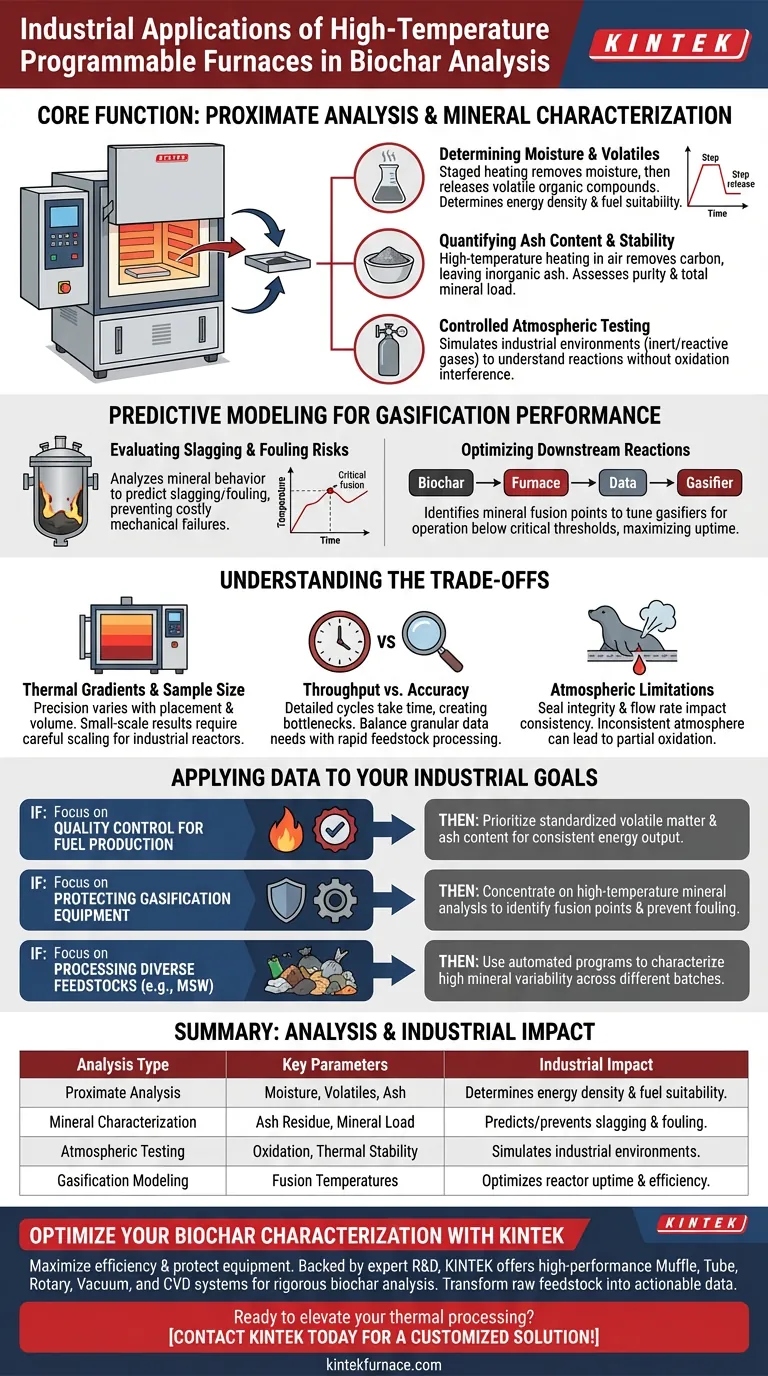
High-temperature programmable furnaces are the primary instruments for conducting proximate analysis, which involves the precise quantification of moisture, volatile matter, and ash content within biochar samples. By automating thermal cycles and controlling the gaseous environment, these furnaces enable industrial operators to assess mineral composition and predict how biochar will behave during high-stakes thermochemical processes like gasification.
Programmable furnaces provide the thermal precision required to transform raw biochar into actionable data regarding its chemical stability and mineral load. This characterization is vital for mitigating operational risks, such as equipment fouling, and for ensuring the efficiency of waste-to-energy conversion systems.
Characterizing Chemical Composition through Proximate Analysis
Determining Moisture and Volatiles
Industries use programmable furnaces to execute staged heating protocols that first drive off moisture and then release volatile organic compounds. This data is critical for determining the energy density of the biochar and its suitability as a fuel or soil amendment.
Quantifying Ash Content and Stability
By heating samples to high temperatures in the presence of air, the furnace removes all combustible carbon, leaving only the inorganic ash residue. This measurement allows producers to understand the purity of the biochar and the total mineral load present in the original feedstock.
Controlled Atmospheric Testing
These furnaces allow for the introduction of inert gases or reactive air to simulate different industrial environments. This versatility is essential for understanding how biochar reacts under varying thermal conditions without the interference of unintended oxidation.
Predictive Modeling for Gasification Performance
Evaluating Slagging and Fouling Risks
In industrial gasification, the minerals in biochar can melt and deposit on reactor walls, a process known as slagging or fouling. Programmable furnaces help researchers analyze mineral behavior at high temperatures to predict and prevent these costly mechanical failures.
Characterizing Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) Biochar
Biochar derived from MSW often contains a complex mix of minerals that vary significantly by batch. Industrial operators rely on furnace analysis to evaluate these specific mineral profiles, ensuring the feedstock meets safety and performance standards for energy production.
Optimizing Downstream Reactions
Precise temperature control allows for the identification of the exact point at which mineral components reach their fusion temperature. This information enables engineers to tune gasifiers to operate just below these critical thresholds, maximizing uptime and efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Thermal Gradients and Sample Size
While programmable furnaces offer high precision, the internal temperature may vary slightly depending on the sample's placement and volume. Small-scale furnace results must be carefully scaled to reflect the realities of large-scale industrial reactors.
Throughput vs. Accuracy
Detailed programmed heating cycles can be time-consuming, creating a bottleneck in high-volume industrial testing environments. Operators must often balance the need for granular data with the practical requirements of rapid feedstock processing.
Atmospheric Limitations
Although most furnaces support inert gases, the integrity of the seal and the flow rate can impact the consistency of the results. Inconsistent atmospheric control can lead to partial oxidation, which skews the data regarding volatile matter and carbon stability.
Applying This Data to Your Industrial Goals
To effectively integrate programmable furnace analysis into your workflow, you must align your testing protocols with your specific operational objectives.
- If your primary focus is quality control for fuel production: Prioritize the standardized determination of volatile matter and ash content to ensure consistent energy output and regulatory compliance.
- If your primary focus is protecting gasification equipment: Concentrate on high-temperature mineral analysis to identify the fusion points that lead to slagging and fouling.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse feedstocks like MSW: Use automated heating programs to characterize the high variability in mineral content across different waste batches.
By mastering the thermal profile of your biochar, you can transform a variable byproduct into a predictable and high-value industrial asset.
Summary Table:
| Analysis Type | Key Parameters Measured | Industrial Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Proximate Analysis | Moisture, Volatile Matter, Ash Content | Determines energy density and fuel suitability. |
| Mineral Characterization | Ash Residue & Mineral Load | Predicts and prevents slagging and fouling in reactors. |
| Atmospheric Testing | Oxidation & Thermal Stability | Simulates industrial environments using inert or reactive gases. |
| Gasification Modeling | Fusion Temperatures | Optimizes reactor uptime and maximizes processing efficiency. |
Optimize Your Biochar Characterization with KINTEK
Maximize your industrial efficiency and protect your equipment from costly fouling and slagging. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the rigorous demands of biochar analysis and thermochemical research.
Our lab high-temperature furnaces provide the thermal precision and atmospheric control you need to transform raw feedstock into actionable data. Whether you are processing MSW or optimizing fuel production, we offer fully customizable solutions tailored to your unique laboratory needs.
Ready to elevate your thermal processing? Contact KINTEK today for a customized solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Despina Vamvuka, Petros Tsilivakos. Energy Recovery from Municipal Solid Waste through Co-Gasification Using Steam or Carbon Dioxide with Olive By-Products. DOI: 10.3390/en17020304
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How is a laboratory box resistance furnace utilized in the heat treatment and testing of high-speed steel samples?
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace in PI microfibers? Enhance Polyimide Thermal Imidization
- What precautions should be taken for the first use or after long-term shutdown of a muffle furnace? Ensure Safe, Reliable Operation from Day One
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in g-C3N4 synthesis? Optimize Your Photocatalyst Production
- What are the general characteristics and advantages of box type resistance furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Your Lab
- What role does a muffle furnace play in NHoHMM fabrication? Mastering Precision Solid-State Dewetting
- What is the working principle of a muffle furnace? Master Precise, Contamination-Free Heating
- How does a muffle furnace control the atmosphere around the sample? Achieve Precise Material Processing



















