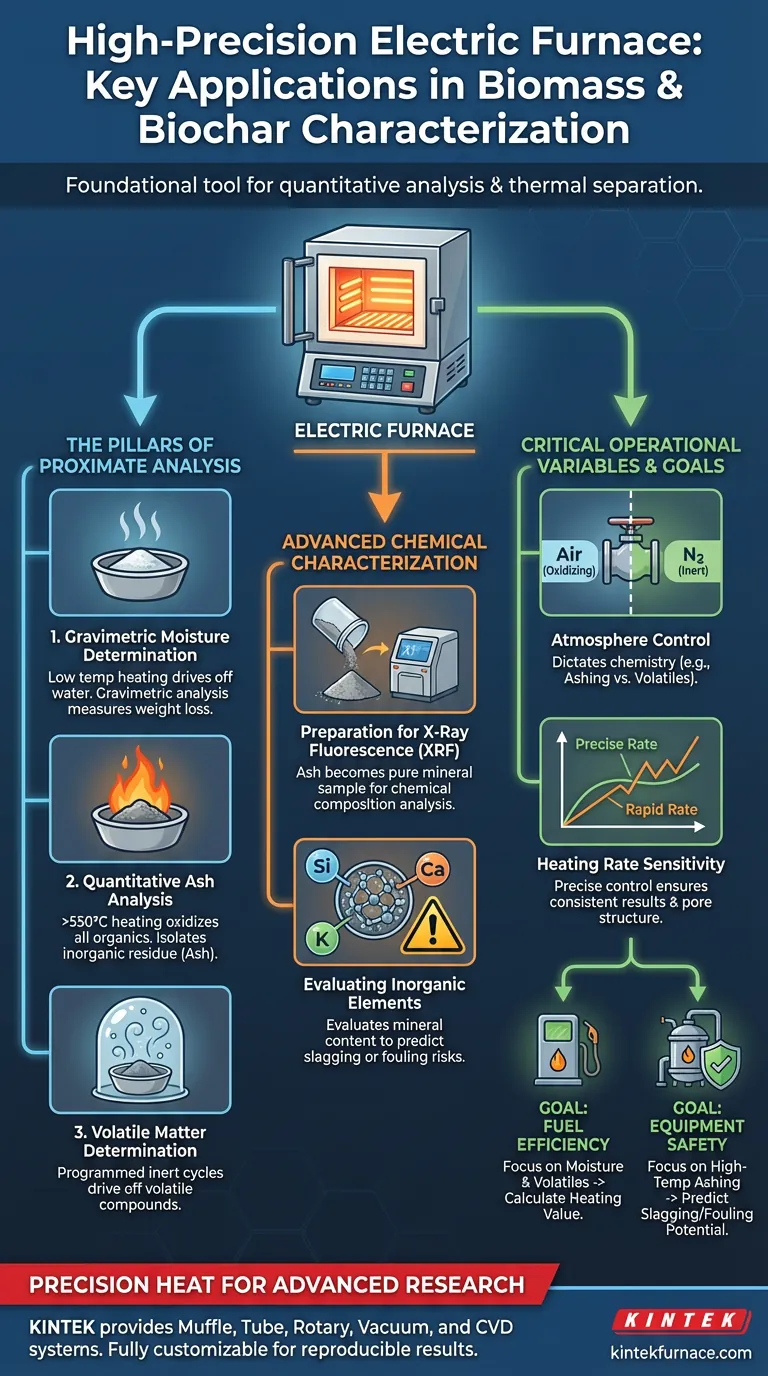
A high-precision electric furnace serves as the foundational tool for quantitative analysis in biomass and biochar research. Its primary applications are the determination of moisture content through controlled gravimetric methods and the execution of ashing processes at temperatures exceeding 550°C to isolate inorganic material for chemical composition analysis.
By providing exact temperature control and programmable heating profiles, these furnaces allow researchers to isolate specific material components—water, volatiles, and ash. This thermal separation is the prerequisite for deeper investigation into the material's inorganic elemental composition.

The Pillars of Proximate Analysis
Proximate analysis is the standard method for characterizing fuel sources. The high-precision electric furnace is the engine behind this process, isolating components based on their thermal stability.
Gravimetric Moisture Determination
The furnace is used to heat samples to specific, relatively low temperatures to drive off water content.
By measuring the weight loss before and after this thermal treatment, researchers calculate the moisture content via gravimetric analysis. This is the first critical step in standardizing biomass samples for further testing.
Quantitative Ash Analysis
To determine the amount of non-combustible material in a sample, the furnace performs ashing processes.
This involves heating the biomass or biochar to temperatures of 550°C or higher. At these temperatures, all organic matter is oxidized, leaving behind only the inorganic residue (ash) for quantification.
Volatile Matter Determination
Beyond moisture and ash, high-temperature programmable furnaces are used to measure volatile matter.
By executing specific programmed heating cycles, often in the absence of oxygen, researchers can drive off volatile compounds. This data is essential for understanding how the material will behave during combustion or gasification.
Advanced Chemical Characterization
The furnace does not just measure weight loss; it prepares the sample for sophisticated chemical profiling.
Preparation for X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF)
The ash produced during the high-temperature combustion process is not merely waste; it is a sample prepared for X-ray Fluorescence (XRF).
The electric furnace ensures that all organic carbon is removed, leaving a pure mineral sample. This allows XRF instruments to accurately analyze the chemical composition of the inorganic elements.
Evaluating Inorganic Elements
Understanding the inorganic composition is vital for predicting equipment performance.
Data derived from furnace-prepared ash helps evaluate mineral content, which directly influences slagging or fouling risks in industrial gasification reactors.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While high-precision furnaces are powerful tools, accurate characterization requires careful management of operational variables.
The Role of Atmosphere Control
The internal environment of the furnace dictates the chemistry of the process.
While ashing requires an oxidizing atmosphere (air), determining volatile matter or synthesizing biochar requires inert atmospheres (like nitrogen). Using the wrong atmosphere will yield invalid characterization data.
Heating Rate Sensitivity
The speed at which the furnace ramps up temperature impacts the material's structure.
Precise control over heating rates (e.g., 20°C per minute) is necessary to ensure consistent results. Rapid heating may entrap volatiles or alter the pore structure, skewing the final compositional analysis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When utilizing a high-precision electric furnace, your specific research objectives should dictate your operational parameters.
- If your primary focus is Fuel Efficiency: Prioritize the precise determination of moisture and volatile matter to calculate the heating value of the biomass.
- If your primary focus is Equipment Safety: Focus on high-temperature ashing (550°C+) to prepare samples for XRF analysis, allowing you to predict slagging and fouling potential.
Mastering the thermal profile of your furnace is the key to unlocking accurate, reproducible data regarding the chemical and physical properties of your biochar.
Summary Table:
| Application | Process Temperature | Primary Objective | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture Determination | Low Temperature | Drive off water content | Gravimetric Analysis |
| Ashing Process | > 550°C | Isolate inorganic material | Quantitative Oxidation |
| Volatile Matter | Programmed Cycles | Identify combustible compounds | Controlled Heating |
| XRF Sample Prep | High Temperature | Mineral composition analysis | Organic Carbon Removal |
Precision Heat for Advanced Biomass Research
Unlock the full potential of your biochar and biomass research with equipment designed for uncompromising accuracy. KINTEK provides industry-leading Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all precision-engineered to meet the rigorous demands of proximate analysis and sample preparation.
Backed by expert R&D and high-end manufacturing, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to your specific heating profiles and atmospheric requirements. Ensure reproducible results and protect your industrial reactors from slagging and fouling risks today.
Contact KINTEK for a Custom Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Jiří Ryšavý, Thangavel Sangeetha. Co-Gasification of Pistachio Shells with Wood Pellets in a Semi-Industrial Hybrid Cross/Updraft Reactor for Producer Gas and Biochar Production. DOI: 10.3390/fire7030087
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a forced air drying oven for biochar? Optimize Moringa Oleifera Shell Pre-treatment
- Why is multiple remelting necessary for Bi-Sb alloys? Achieve Perfect Compositional Uniformity Today
- Why must the filling of the working medium into a sodium heat pipe be performed inside a protective glovebox?
- How does CFD simulation software optimize fuel combustion? Transform Furnace Efficiency with Digital Twins
- How is the pore structure of EN-LCNF characterized? Advanced BET and DFT Analysis of Carbon Nanosheets
- What is the role of high-temperature calcination equipment in Waste Tire Charcoal preparation? Master WTC Pyrolysis
- What is the role of industrial electric drying ovens in FDSSC titanium photoanode treatment? Enhance Solar Efficiency
- Why Roast SiC Particles for 2024Al/Gr/SiC Composites? Optimize Surface Modification and Bonding



















