In the production of high-performance materials, the choice of melting technology is a foundational decision that dictates the quality, consistency, and ultimate performance of the final product. The primary advantages of vacuum melting furnaces are their ability to create an exceptionally pure environment, provide precise control over the entire melting and solidification process, and consequently produce metals and alloys with superior, highly repeatable mechanical properties.
The core challenge in advanced metallurgy isn't just melting metal; it's controlling the chaotic environment in which it happens. Vacuum furnaces solve this by removing the atmosphere—and all its contaminants—from the equation, transforming melting from a basic process into a precise act of material engineering.

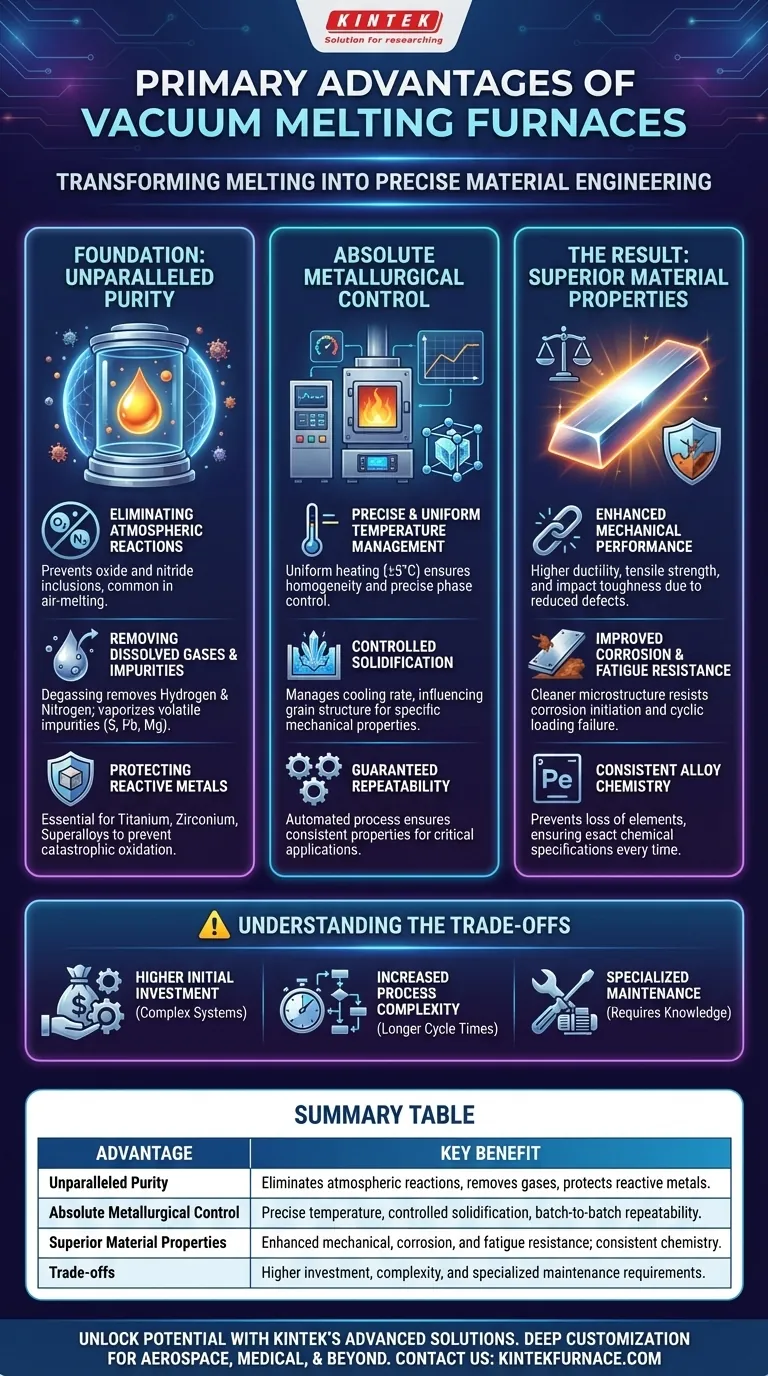
The Foundation: Unparalleled Purity
The defining advantage of vacuum melting is the creation of a pristine, controlled environment. This directly addresses the most common sources of defects and inconsistencies in metal alloys.
Eliminating Atmospheric Reactions
By removing the air, a vacuum furnace fundamentally prevents unwanted reactions. Gases like oxygen and nitrogen, which are unavoidable in traditional air-melting, cannot react with the molten metal.
This is critical for preventing the formation of oxide and nitride inclusions, which act as points of weakness and can initiate cracks or failures in the final component.
Removing Dissolved Gases and Impurities
The vacuum environment actively pulls dissolved gases, such as hydrogen and nitrogen, out of the liquid metal. This process, known as degassing, significantly reduces porosity.
Furthermore, the low pressure encourages the vaporization of elements with high vapor pressures, effectively removing volatile impurities like sulfur, lead, and magnesium, which can compromise an alloy's integrity.
Protecting Reactive Metals
For reactive metals like titanium, zirconium, and certain superalloys, a vacuum is not just beneficial—it is essential.
Melting these materials in the presence of oxygen would cause immediate, catastrophic oxidation, rendering the alloy useless. The vacuum serves as a perfectly inert shield.
Achieving Absolute Metallurgical Control
Beyond purity, vacuum technology provides an unprecedented level of control over the physical and chemical processes of alloy creation.
Precise and Uniform Temperature Management
Vacuum furnaces allow for highly uniform heating, often within a narrow range of ±5°C. This consistency is vital for ensuring all alloying elements are fully dissolved and the melt is homogenous.
Computerized controls enable precise temperature profiles, including rapid heating and controlled cooling (quenching), allowing for specific metallurgical phases and microstructures to be achieved.
Controlled Solidification
How a metal solidifies is just as important as how it melts. Vacuum furnaces provide a controlled environment to manage the solidification rate.
This allows engineers to influence the grain structure of the final casting, which directly impacts mechanical properties like strength, ductility, and fatigue life.
Guaranteed Repeatability
The combination of a controlled atmosphere and automated process management leads to exceptional batch-to-batch consistency.
For critical industries like aerospace, medical, and defense, this repeatability is non-negotiable. It ensures that a part manufactured today will have the exact same properties as one manufactured a year from now.
The Result: Superior Material Properties
The ultimate goal of this purity and control is to produce a fundamentally better material.
Enhanced Mechanical Performance
Alloys produced in a vacuum consistently exhibit improved mechanical properties. The reduction of inclusions and porosity leads to significantly higher ductility, tensile strength, and impact toughness.
Improved Corrosion and Fatigue Resistance
A cleaner, more homogenous microstructure means fewer sites for corrosion to initiate. The absence of internal defects also drastically improves the material's resistance to fatigue failure under cyclic loading.
Consistent Alloy Chemistry
The vacuum prevents the loss of easily oxidized alloying elements and allows for precise management of the final composition. This ensures the material meets its exact chemical specification, every time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum melting is a specialized process with important considerations.
Higher Initial Investment
Vacuum furnace systems are more complex and carry a higher capital cost than their atmospheric counterparts, involving vacuum pumps, chamber seals, and sophisticated control systems.
Increased Process Complexity and Cycle Time
Achieving and maintaining a high vacuum adds steps to the melting process, such as pump-down time. This generally results in longer cycle times compared to simpler air-melting methods.
Specialized Maintenance
The vacuum pumps, seals, and instrumentation require specialized knowledge for operation and maintenance to ensure the system performs reliably and holds a proper vacuum.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum furnace hinges on the performance requirements of your end product.
- If your primary focus is maximum material purity and performance for critical applications (e.g., aerospace, medical implants, nuclear components): Vacuum melting is the industry standard and often the only viable choice.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive metals like titanium or nickel-based superalloys: The inert environment provided by a vacuum is absolutely essential to prevent ruinous oxidation.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of standard-grade alloys where minor impurities are acceptable: The cost and complexity of vacuum melting may not be justified, and traditional air-melting is likely more economical.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum melting is a strategic decision to eliminate environmental variables and gain absolute control over your material's final properties.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Unparalleled Purity | Eliminates atmospheric reactions, removes dissolved gases, and protects reactive metals from oxidation. |
| Absolute Metallurgical Control | Provides precise temperature management, controlled solidification, and guaranteed batch-to-batch repeatability. |
| Superior Material Properties | Enhances mechanical performance, improves corrosion and fatigue resistance, and ensures consistent alloy chemistry. |
| Trade-offs | Higher initial investment, increased process complexity, and specialized maintenance requirements. |
Unlock the full potential of your materials with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with vacuum melting furnaces, including our Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems, tailored to your unique experimental needs. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise performance for critical applications in aerospace, medical, and beyond. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your material production with superior purity and control!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















