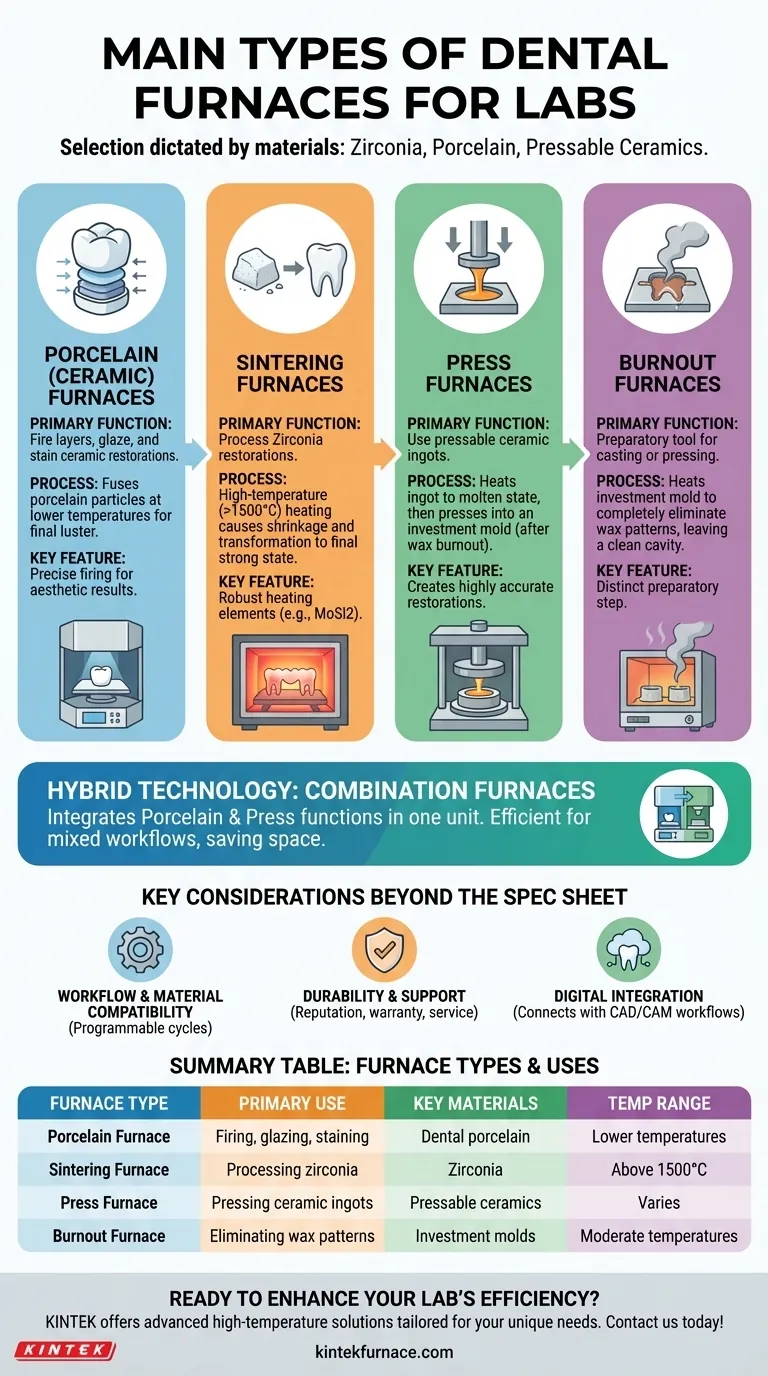
In a modern dental laboratory, there are four primary types of furnaces, each engineered for a specific material and process: porcelain furnaces, sintering furnaces, press furnaces, and burnout furnaces. While they all use heat to process dental restorations, their functions are distinct and not interchangeable. Some modern units, known as combination furnaces, merge the capabilities of porcelain and press furnaces to add versatility to a lab's workflow.
The core principle is that the type of furnace a lab requires is dictated entirely by the materials it uses. Zirconia, layered porcelain, and pressable ceramics each demand a unique thermal process, making furnace selection a critical decision that defines a lab's production capabilities.

The Core Furnace Categories in a Modern Lab
Understanding the function of each furnace type is the first step in equipping a lab for success. Each is a specialized tool designed for a specific stage of dental restoration fabrication.
Porcelain (Ceramic) Furnaces
Porcelain furnaces are used for the final stage of creating ceramic restorations like crowns, bridges, and veneers. Their primary job is to fire layers of dental porcelain, fusing the particles together to create a strong, dense structure.
These furnaces are also used for glazing and staining, which gives the restoration its final, life-like luster and customized shading. They operate at lower temperatures compared to sintering furnaces.
Sintering Furnaces
Sintering furnaces are high-temperature powerhouses built for one primary purpose: processing zirconia. After a zirconia restoration is milled from a pre-sintered block, it is in a soft, chalk-like state.
The sintering furnace heats the restoration to extreme temperatures (often above 1500°C), causing the material to shrink significantly and transform into its final, incredibly strong state. These units require robust heating elements, such as molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2), to reliably reach and maintain these temperatures.
Press Furnaces
Press furnaces are designed for use with pressable ceramic ingots. In this technique, a wax model of the restoration is created and encased in an investment material.
After the wax is burned out, the mold is placed in the press furnace with a ceramic ingot. The furnace heats the ingot until it becomes molten, and then a plunger "presses" the fluid ceramic into the mold. This method is popular for creating highly accurate and durable restorations like inlays, onlays, and veneers.
Burnout Furnaces
Burnout furnaces are a preparatory tool used in workflows involving casting or pressing. Their sole function is to heat an investment mold to completely eliminate the wax pattern inside, leaving a clean, empty cavity.
This process is a critical prerequisite before either casting molten metal or pressing ceramic into the mold. It is a distinct step that requires a separate, dedicated piece of equipment.
The Rise of Hybrid Technology
To optimize space and investment, manufacturers have developed units that combine the functions of two different furnace types.
Combination Furnaces
The most common hybrid is the ceramic combination furnace, which integrates the functions of a porcelain furnace and a press furnace. This allows a lab to both fire layered ceramics and press ceramic ingots within a single machine.
These units offer excellent versatility for labs that handle a mixed workflow but may not have the volume to justify two separate, dedicated machines.
The Limits of a "Jack of All Trades"
While combination units are efficient, labs with a very high volume of either pressed or layered restorations may still prefer dedicated machines. A specialized furnace is often built to optimize one process, potentially offering slightly faster cycle times or greater capacity for that specific task.
Key Considerations Beyond the Spec Sheet
Choosing a furnace involves more than just its primary function. The following factors are critical for making a sound long-term investment.
Workflow and Material Compatibility
The furnace must align with your lab's chosen materials. Different brands of zirconia or porcelain have unique, manufacturer-specified firing and sintering schedules. A modern, programmable furnace is essential to store these cycles and ensure consistent, predictable results for every case.
Durability and Support
A furnace is a cornerstone of lab production; downtime is incredibly costly. Evaluating the manufacturer's reputation, warranty coverage, and customer support is just as important as evaluating the technical specifications. A reliable machine from a company with responsive service is a non-negotiable asset.
Integration with Digital Dentistry
Modern advancements are increasingly integrating furnaces with digital workflows. For example, designs created with CAD software can be sent to a 3D printer or milling machine, with the final product moving directly to the appropriate furnace for sintering, streamlining the entire production process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your lab's primary output dictates your equipment needs. Use this guide to determine your starting point.
- If your primary focus is high-strength zirconia restorations: You require a dedicated, high-temperature sintering furnace capable of handling specific zirconia sintering cycles.
- If your primary focus is aesthetic layered porcelain (PFMs, veneers): A programmable porcelain furnace for precise firing, glazing, and staining is your essential tool.
- If your lab has a mixed workflow with pressable ceramics and layered porcelain: A combination press-and-fire furnace offers the best balance of versatility and space efficiency.
- If you perform casting for metal frameworks or work with pressables: A separate burnout furnace is necessary for the initial wax elimination stage.
By matching the furnace technology to your lab's specific services, you make a strategic investment that directly enables high-quality, efficient production.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Use | Key Materials | Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porcelain Furnace | Firing, glazing, staining | Dental porcelain | Lower temperatures |
| Sintering Furnace | Processing zirconia | Zirconia | Above 1500°C |
| Press Furnace | Pressing ceramic ingots | Pressable ceramics | Varies |
| Burnout Furnace | Eliminating wax patterns | Investment molds | Moderate temperatures |
Ready to enhance your dental lab's efficiency with the perfect furnace? KINTEK offers advanced high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, tailored for labs working with zirconia, ceramics, and more. Our deep customization ensures precise fit for your unique needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your production goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when choosing a dental sintering furnace? Ensure Quality and Efficiency for Your Lab
- Why is calibration important for dental sintering furnaces? Ensure Perfect Restorations and Avoid Costly Failures
- What are some common mistakes when operating dental sintering furnaces? Avoid Costly Errors for Perfect Zirconia Restorations
- How has the sintering process innovated dental zirconia applications? Boost Strength, Precision, and Efficiency
- What factors determine the quality of sintered zirconia restorations? Master Material, Equipment, and Technique



















