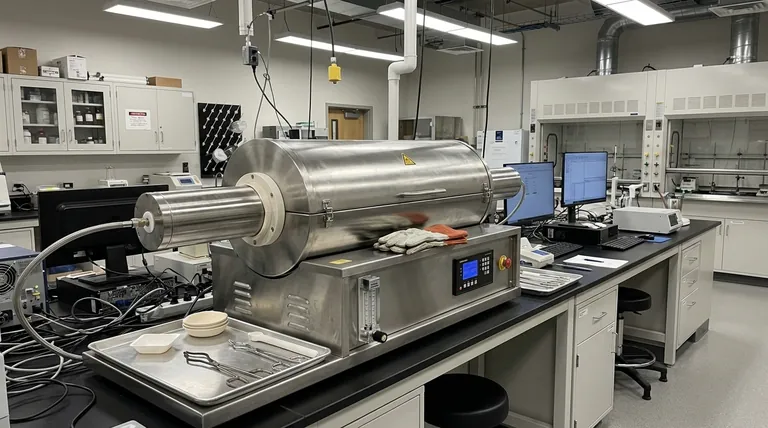
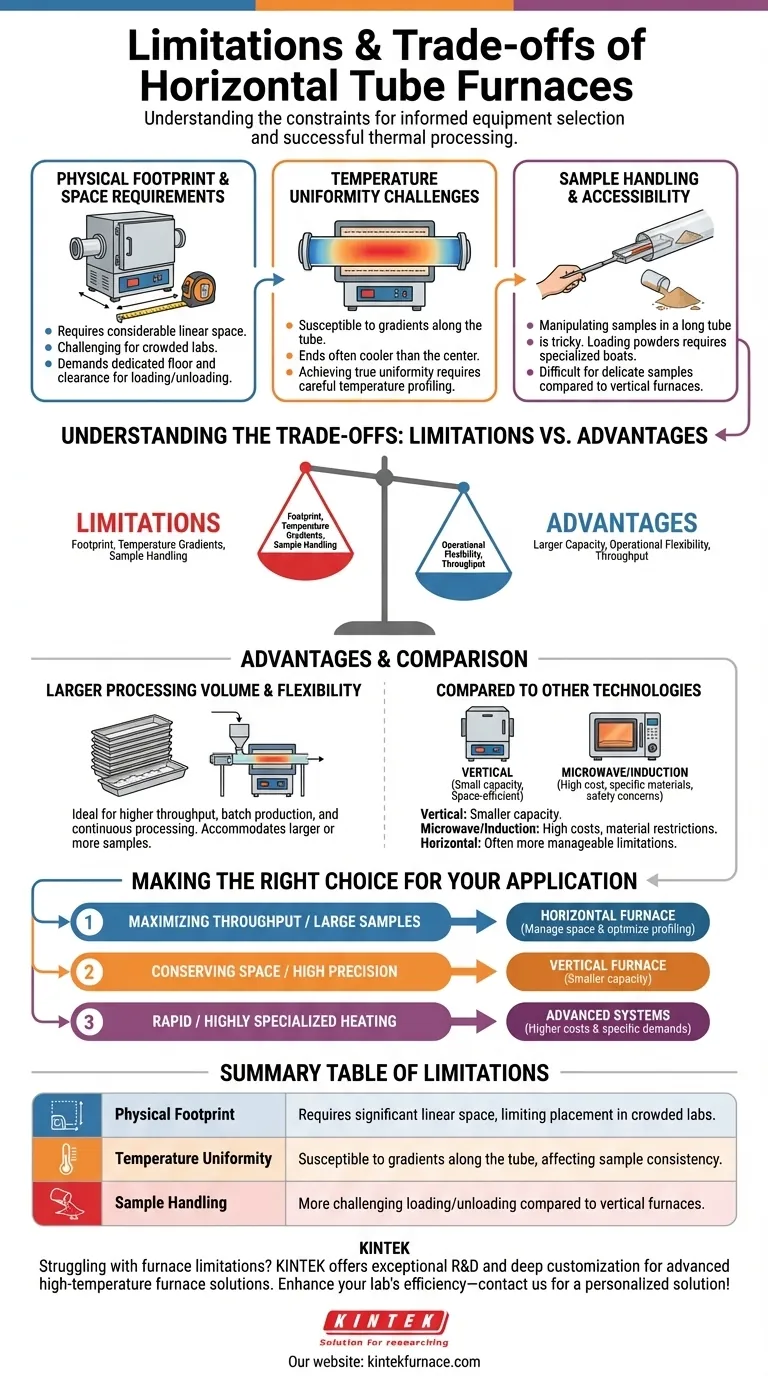
In short, the primary limitations of a horizontal tube furnace are its significant physical footprint, the potential for temperature gradients along the sample's length, and challenges related to sample handling. These factors require careful consideration of lab space and process optimization to ensure consistent results.
While horizontal tube furnaces are celebrated for their large capacity and operational flexibility, their limitations force a critical trade-off between throughput and precision. Understanding these constraints is the key to selecting the right equipment and designing a successful thermal process.

The Core Limitations in Detail
To properly evaluate a horizontal tube furnace, you must understand its inherent operational and physical constraints. These are not necessarily deal-breakers, but factors that must be managed.
Physical Footprint and Space Requirements
A horizontal tube furnace, by its nature, requires considerable linear space. Unlike its vertical counterpart, it cannot be easily situated on a crowded benchtop or tucked into a corner.
This larger footprint often demands dedicated floor space, which can be a significant constraint in labs or facilities where space is at a premium. The layout must account not only for the furnace itself but also for clearance at both ends for loading, unloading, and maintenance.
The Challenge of Temperature Uniformity
While designed to provide excellent heat distribution, horizontal furnaces can be susceptible to temperature gradients. The ends of the process tube are often cooler than the center due to heat loss to the surrounding environment.
This means that for longer samples or multiple samples spread along the tube, there can be slight but meaningful temperature variations. Achieving true uniformity often requires careful temperature profiling, using multi-zone heating elements, or restricting the sample to the validated central hot zone.
Sample Handling and Accessibility
Manipulating samples within a long, horizontal tube can be more challenging compared to a vertical furnace. Loading powders or granular materials evenly requires specialized sample boats to prevent spillage.
Inserting and retrieving delicate samples without contact with the tube walls demands steady hands and appropriate tools. In contrast, vertical furnaces often benefit from gravity, simplifying the loading and unloading of certain sample types.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Limitations vs. Advantages
The limitations of a horizontal furnace do not exist in a vacuum. They are direct trade-offs for its most significant benefits, especially when compared to alternative furnace technologies.
The Advantage: Larger Processing Volume
The primary reason to choose a horizontal furnace is its capacity. Its design naturally accommodates larger individual samples or a greater number of smaller samples in a single batch.
This makes it highly suitable for applications requiring higher throughput, whether for batch production or for continuous processing setups where materials are fed through the tube.
The Advantage: Operational Flexibility
Horizontal furnaces offer straightforward flexibility in sample loading and observation. The horizontal orientation is often more intuitive for manual processes and can be more easily integrated into automated, continuous-flow systems.
How Other Furnaces Compare
It is crucial to contextualize these limitations. Vertical furnaces, while space-efficient, typically offer a smaller working capacity.
More advanced technologies like microwave or induction furnaces have their own severe drawbacks, including extremely high equipment and maintenance costs, material restrictions (e.g., induction requires metal tubes), and significant safety considerations. Compared to these, the limitations of a standard horizontal furnace are often far more manageable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by the specific goals of your thermal processing work. A limitation in one context is an acceptable trade-off in another.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput or processing large samples: A horizontal furnace is likely the correct choice, provided you dedicate the resources to managing its space and optimizing its temperature profile.
- If your primary focus is conserving lab space or running smaller, high-precision experiments: A vertical furnace may be a more efficient solution, assuming its smaller capacity is not a constraint.
- If your primary focus is rapid or highly specialized heating: You may need to evaluate advanced systems like induction or microwave furnaces, but be prepared for their higher costs and specific operational demands.
Ultimately, recognizing the practical constraints of a horizontal tube furnace empowers you to properly select, install, and operate it for successful and repeatable outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Footprint | Requires significant linear space, limiting placement in crowded labs. |
| Temperature Uniformity | Susceptible to gradients along the tube, affecting sample consistency. |
| Sample Handling | More challenging loading/unloading compared to vertical furnaces. |
Struggling with furnace limitations? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Enhance your lab's efficiency and overcome space and temperature challenges—contact us today for a personalized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis



















