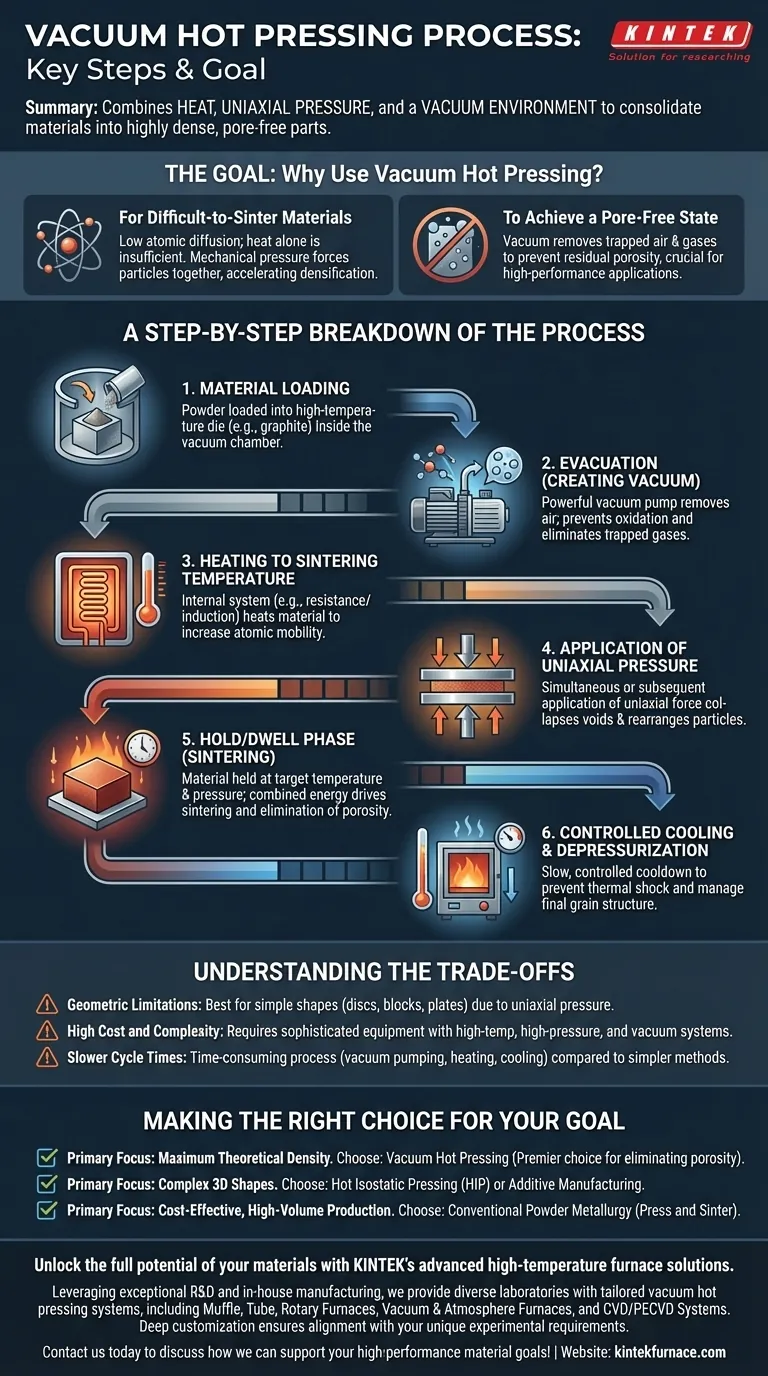
In short, the vacuum hot pressing process consists of loading a material into a sealed chamber, creating a vacuum, simultaneously heating the material to a high temperature, and applying mechanical pressure to it. The process concludes with a controlled cooling cycle before the finished, densified part is removed.
Vacuum hot pressing is a material consolidation technique that combines heat, uniaxial pressure, and a vacuum environment in a single, controlled process. Its primary purpose is to produce highly dense, pore-free materials that are difficult or impossible to create using heat or pressure alone.
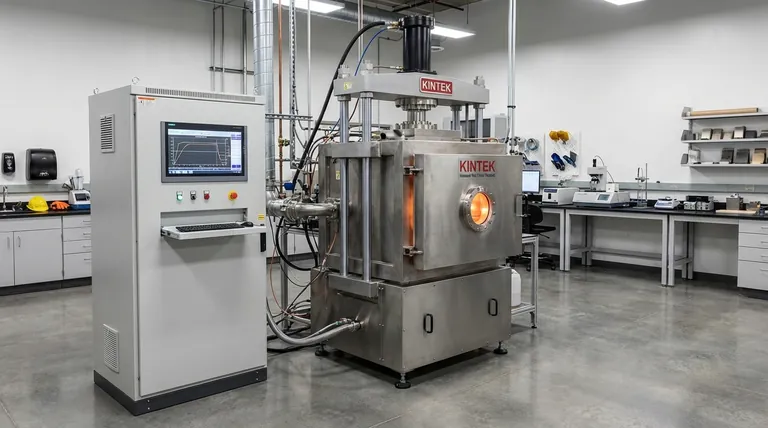

The Goal: Why Use Vacuum Hot Pressing?
Vacuum hot pressing is not a universal solution; it is a specialized process used when standard sintering methods are insufficient. It is chosen to achieve specific, high-performance material properties.
### For Difficult-to-Sinter Materials
Some advanced ceramics or metal alloys have very low atomic diffusion coefficients. This means their atoms are reluctant to move and bond together, even at high temperatures, making them difficult to densify.
The mechanical pressure in hot pressing physically forces the material's particles together, overcoming this sluggishness and accelerating the densification process.
### To Achieve a Pore-Free State
For many high-performance applications, internal pores are critical defects. The vacuum environment is essential for removing air and other gases trapped between the initial powder particles.
Without a vacuum, these gases would be trapped during densification, creating residual porosity that compromises the final material's mechanical, optical, or thermal properties.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process
Each stage of the vacuum hot pressing cycle is precisely controlled to manipulate the material's microstructure and achieve the desired final properties.
### 1. Material Loading
The process begins by placing the raw material, typically in powder form, into a die made of a high-temperature-resistant material like graphite. This entire assembly is then loaded into the vacuum chamber.
### 2. Evacuation (Creating the Vacuum)
Once the chamber is sealed, a powerful vacuum pump system removes the air. This step is critical for preventing oxidation of the material at high temperatures and for extracting gases that would otherwise become trapped as pores.
### 3. Heating to Sintering Temperature
An internal heating system, often using electrical resistance or induction, raises the temperature of the material and die. The heat provides the thermal energy needed to increase atomic mobility, which is a prerequisite for particles to bond together.
### 4. Application of Uniaxial Pressure
Simultaneously with or shortly after reaching the target temperature, a hydraulic or mechanical press mechanism applies a compressive, one-directional (uniaxial) force to the material via plungers or rams. This mechanical energy physically collapses voids and rearranges particles.
### 5. Hold/Dwell Phase (Sintering)
The material is held at the target temperature and pressure for a specific duration. During this "dwell time," the combined thermal and mechanical energy drives the sintering process—the bonding of particles and the elimination of remaining porosity to form a solid, dense part.
### 6. Controlled Cooling and Depressurization
After the hold time is complete, the pressure is released and the furnace begins a controlled cooling cycle. A slow, controlled cooldown is vital to prevent thermal shock, which could crack the newly formed part, and to manage the final grain structure of the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum hot pressing has practical limitations that must be considered when selecting a manufacturing process.
### Geometric Limitations
Because pressure is applied in a single direction (uniaxially), the process is best suited for producing relatively simple shapes like discs, blocks, and plates. Creating complex, three-dimensional geometries is extremely difficult.
### High Cost and Complexity
A vacuum hot press is a sophisticated piece of equipment that integrates high-temperature furnaces, high-pressure hydraulics, and high-vacuum systems. This complexity results in significant capital investment and higher operational costs.
### Slower Cycle Times
The entire process—including pumping down to vacuum, slow heating ramps, dwell time, and especially the controlled cooling phase—is time-consuming. It is not well-suited for high-volume, rapid production compared to simpler pressing and sintering methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if vacuum hot pressing is the correct approach, evaluate your project's most critical requirement.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum theoretical density: Vacuum hot pressing is a premier choice for eliminating porosity in materials where performance cannot be compromised.
- If your primary focus is fabricating complex 3D shapes: Consider alternative methods like Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) or additive manufacturing, which are not constrained by uniaxial pressure.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production: Conventional powder metallurgy (press and sinter) may be more suitable for materials and applications with less stringent density requirements.
Ultimately, understanding the interplay of heat, pressure, and vacuum empowers you to select the right tool for your specific material challenge.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Material Loading | Place powder into a high-temperature die | Prepare material for processing in a sealed chamber |
| 2. Evacuation | Remove air to create a vacuum | Prevent oxidation and eliminate trapped gases |
| 3. Heating | Raise temperature to sintering level | Increase atomic mobility for particle bonding |
| 4. Pressure Application | Apply uniaxial force | Collapse voids and rearrange particles |
| 5. Hold/Dwell Phase | Maintain temperature and pressure | Drive sintering to eliminate porosity |
| 6. Controlled Cooling | Slowly reduce temperature | Prevent thermal shock and manage grain structure |
Unlock the full potential of your materials with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored vacuum hot pressing systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements, helping you achieve superior density and performance in ceramics and alloys. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-performance material goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What considerations guide the selection of heating elements and pressurization methods for a vacuum hot press furnace?
- What are the primary components of a vacuum hot press furnace? Master the Core Systems for Precise Material Processing
- What role does a high-performance laboratory hot press machine play in curing? Unlock Superior Composite Strength
- Which process parameters must be optimized for specific materials in a vacuum hot press furnace? Achieve Optimal Density and Microstructure
- What is a vacuum hot press furnace? Unlock Superior Material Performance



















