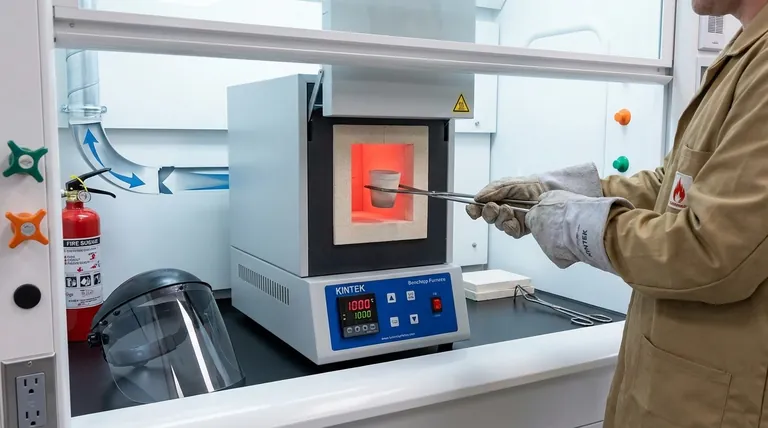
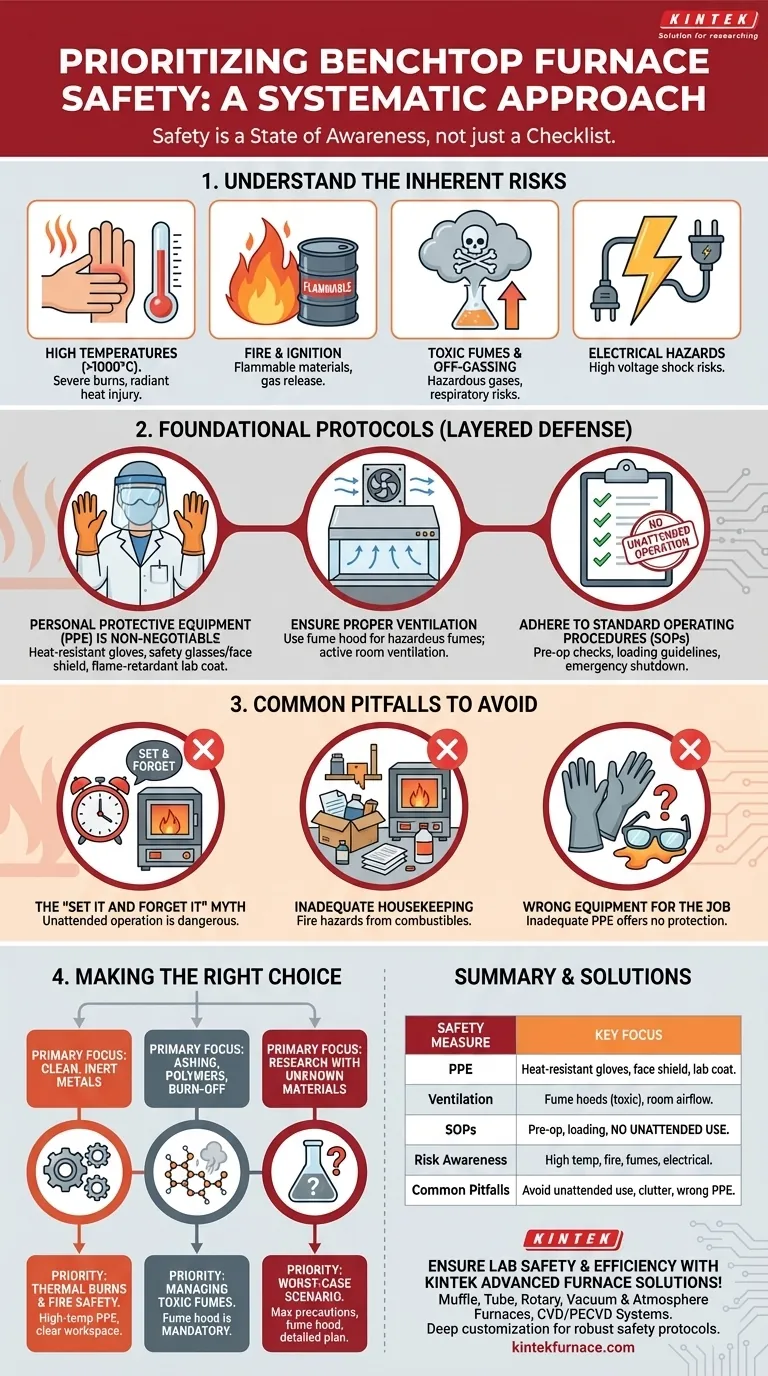
Prioritizing safety with a benchtop furnace is not a matter of following a single rule, but of implementing a system. The key measures involve a comprehensive understanding of the specific hazards of your process, the mandatory use of appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), ensuring adequate ventilation to handle fumes, and strictly adhering to established operating and fire safety protocols.
True furnace safety transcends a simple checklist. It is a state of awareness, where the operator understands that the combination of extreme heat, electricity, and variable materials creates a dynamic risk environment that must be proactively managed, not just reacted to.

First, Understand the Inherent Risks
Before you can implement effective safety measures, you must have a clear understanding of the specific dangers a benchtop furnace presents. These risks are not theoretical; they are present during every single operation.
High Temperatures and Thermal Burns
The most obvious risk is the extreme heat, which can exceed 1000°C. Direct contact causes severe burns instantly, but radiant heat can also cause injury from a distance or damage nearby equipment.
Fire and Ignition Hazards
Placing flammable materials in or near the furnace can lead to fire. Additionally, some materials, when heated, can release flammable gases, creating an ignition risk inside the furnace chamber or in the surrounding area.
Toxic Fumes and Off-Gassing
Many materials release toxic or harmful gases when heated. This process, known as off-gassing, can occur with polymers, binders, treated samples, or unknown contaminants. Without proper ventilation, these fumes can pose a serious respiratory hazard.
Electrical Hazards
Benchtop furnaces are high-power devices. They present significant electrical shock risks, particularly during maintenance or in the event of a malfunction. The internal wiring and heating elements carry dangerous voltages.
Implementing Foundational Safety Protocols
With a clear understanding of the risks, you can implement a layered defense system. Each layer is critical; a failure in one can be caught by another.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is Non-Negotiable
Proper PPE is your last line of defense against an accident. Its purpose is to shield you from thermal, chemical, and splash hazards.
Your minimum required PPE should include:
- Heat-resistant gloves specifically rated for the temperatures you are handling.
- Safety glasses with side shields or a full face shield to protect from splashes and radiant heat.
- A flame-retardant lab coat or apron to protect your body and prevent your clothing from igniting.
Ensure Proper Ventilation and Airflow
Proper ventilation is essential for mitigating the risk of toxic fumes and off-gassing. Never operate a furnace in a small, sealed room.
For processes known to produce hazardous fumes, operation within a fume hood is mandatory. For all other work, ensure the room has active ventilation to prevent the buildup of heat, gases, or the displacement of oxygen.
Adhere to Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Formal procedures remove guesswork and ensure consistency. Your SOPs should include pre-operation checks, clear guidelines on loading and unloading materials, and emergency shutdown instructions. Never leave a furnace running unattended, especially during critical heating or cooling phases.
Understanding the Common Pitfalls
Even with established protocols, certain oversights can undermine your safety efforts. Recognizing these common failure points is crucial for building a robust safety culture.
The Misconception of "Set It and Forget It"
A furnace is not a simple oven. Materials can react unexpectedly at high temperatures. Leaving a furnace unattended removes your ability to respond to a sudden change, such as unexpected smoke, fire, or equipment malfunction.
The Danger of Inadequate Housekeeping
A cluttered workspace around a furnace is a significant fire hazard. Combustible materials like paper, solvents, or cardboard boxes must be kept far away from the unit. A clean, clear area ensures you have safe access and reduces the risk of secondary ignition.
Using the Wrong Equipment for the Job
Not all PPE is created equal. Standard laboratory gloves will melt and offer no protection from the high heat of a furnace. Similarly, standard safety glasses do not protect against the intense radiant heat that can damage your eyes over time. Always match your equipment to the specific hazard.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific process dictates which safety measures require the most stringent focus. Use this framework to prioritize your efforts.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating clean, inert metals: Your main concerns are thermal burns and fire safety. Prioritize high-temperature PPE and maintaining a clear, non-combustible workspace.
- If your primary focus is ashing, burn-off, or processing polymers: Your absolute priority is managing toxic fumes. Operation within a properly functioning fume hood is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is research with unknown or novel materials: You must assume a worst-case scenario. This requires maximum precautions, including a fume hood, comprehensive PPE, and a detailed plan for unexpected reactions.
A systematic approach to safety transforms this powerful tool from a potential hazard into a predictable and secure asset for your work.
Summary Table:
| Safety Measure | Key Focus |
|---|---|
| Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) | Heat-resistant gloves, safety glasses, flame-retardant lab coat |
| Ventilation | Use fume hoods for toxic fumes; ensure room airflow for heat and gas control |
| Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) | Pre-operation checks, loading/unloading guidelines, no unattended operation |
| Risk Awareness | Understand high temperatures, fire hazards, toxic off-gassing, and electrical dangers |
| Common Pitfalls | Avoid unattended use, poor housekeeping, and incorrect PPE selection |
Ensure your lab's safety and efficiency with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability precisely meets your unique experimental needs, helping you implement robust safety protocols. Don't compromise on protection—contact us today to discuss how our products can enhance your workflow and safeguard your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in LSCF modification? Achieve Precise Thermal Foundation for Advanced Ceramics
- What is the critical role of a high-temperature muffle furnace in converting biomass into Fe-N-BC?
- What is the core function of a muffle furnace in biomass activation? Optimize Carbonization & Pore Development
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in ZnO-SP preparation? Master Nanoscale Synthesis Control
- How is the thermal stability of KBaBi compounds evaluated? Discover Precise XRD & Heat Treatment Limits



















